Abstract
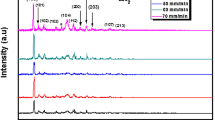
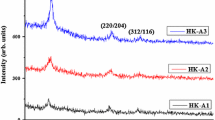
The growth of quality Cu(In,Ga)Se2 photovoltaic absorber without secondary phases is very important for improving the solar cell efficiency. Although X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy can identify the secondary phases, they provide insufficient information because of their insufficient resolution and complexity in analysis. In general, normal Raman spectroscopy is better for the analysis of secondary phases. On the other hand, the Raman signal provides information for film depths of less than 300 nm, and the Raman information cannot represent the properties of the entire film. In this regard, the authors introduce a new way of identifying secondary phases in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 films using depth Raman analysis. The as-prepared film was polished using a dimple grinder, which expanded a 2 μm thick film to approximately 1 mm, which is more than sufficient to resolve the depth distribution. Raman analysis indicated that the Cu(In,Ga)Se2 film showed different secondary phases, such as CuIn3Se5, InSe and CuSe, present in different depths of the film, whereas XPS provided complex information about the phases. Overall, the present study emphasizes that the Raman depth profile is more efficient for the identification of secondary phases in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films than XPS and XRD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, W. Warta, and E. D. Dunlop, Progress in Photovoltatics: Research and Applications 23, 1 (2015).
D. Schmid, M. Ruckh, F. Grunwald, and H. W. Schock, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 2902 (1993).
W. K. Kim, S. Kim, E. A. Payzant, S. A. Speakman, S. Yoon, R. M. Kaczynski, R. D. Acher, T. J. Anderson, O. D. Crisalle, S.-S. Lic, and V. Craciund, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 1915 (2005).
J. H. Park, I. S. Yang, and H. Y. Cho, Appl. Phys. A 58, 125 (1994).
M. Ganchev, J. Iljina, L. Kaupmees, T. Raadik, O. Volobujeva, A. Mere, M. Altosaar, J. Raudoja, and E. Mellikov, Thin Solid Films 519, 7394 (2011).
F. Zheng, J. Y. Shen, Y. Q. Liu, W. K. Kim, M. Y. Chu, M. Ider, X.-H. Bao, and T. J. Anderson, Calphad 32, 432 (2008).
S. Merdes, R. Mainz, J. Klaer, A. Meeder, H. Rodriguez- Alvarez, H. W. Schock, M. C. Lux-Steiner, and R. Klenk, Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 95, 864 (2011).
E. Rudigier, J. Djordjevic, C. von Klopmann, B. Barcones, A. Pérez-Rodríguez, and R. Scheer, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 1954 (2005).
C.-H. Chung, S.-H. Li, B. Lei, W. Yang, W. W. Hou, B. Bob, and Y. Yang, Chem. Mater. 23, 964 (2011).
J. Weszka, P. Daniel, A. Burian, A. M. Burian, and A. T. Nguyen, J. Non-Crystal. Solids 265, 98 (2000).
X. Fontané, V. Izquierdo-Roca, L. Calvo-Barrio, and J. Álvarez-Garcia, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 121907 (2009).
C. M. Ruiz, X. Fontané, A. Fairbrother, V. Izquierdo-Roca, C. Broussillou, S. Bodnar, A. Pérez-Rodríguez, and V. Bermúdez, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 091106 (2013).
D. G. Moon, S. Ahn, J. H. Yun, A. Cho, H. Gwak, S. K. Ahn, K. Shin, K. Yoon, H.-D. Lee, H. Pak, and S. Kwon, Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 95, 2786 (2011).
J. H. Ely, T. R. Ohno, T. E. Furtak, and A. K. Nelson, Thin Solid Films 371, 36 (2000).
J. Alvarez-Garcı́a, E. Rudigier, N. Rega, B. Barcones, R Scheer, A. Pérez-Rodrı́guez, A. Romano-Rodrı́guez, and J. R. Morante, Thin Solid Films 431, 122 (2003).
A.V. Naumkin, A. Kraut-Vass, Stephen W. Gaarenstroom, and C. J. Powell, NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database, U.S. Secretary of Commerce on Behalf of the United States of America, <http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/>
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beak, G.Y., Jeon, CW. XPS and Raman study of slope-polished Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films. Electron. Mater. Lett. 12, 399–403 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-016-6044-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-016-6044-y