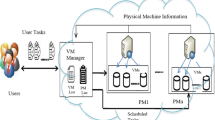
Abstract
Efficient Scheduling of tasks is essential in cloud computing to provision the virtual resources to the tasks, effectively by minimizing makespan and maximizing resource utilization in cloud computing. Existing scheduling algorithms talks about makespan and resource utilization, but very few authors addressed the issues named as migration time, energy consumption, total power cost in datacenters. These three mentioned metrics are essential in the view of cloud provider, as by minimizing migration time, energy consumption and total power cost in datacenters cloud provider will be directly benefited. This paper introduces task scheduling by using Cat Swarm Optimization algorithm, which addresses the parameters makespan, migration time, Energy Consumption and Total Power Cost at Datacenters. Scheduling of tasks were done by calculating priorities of tasks at task level, and calculating priorities of VMs at VM level to schedule appropriate mapping of tasks onto VMs. It is implemented by using cloudsim simulator and input to the algorithm is generated randomly from the cloudsim for total power cost, we have used HPC2N and NASA workloads, which are parallel workload archives, which were given as an input to the algorithm. Proposed algorithm is compared against existing algorithms like PSO and CS. From the simulation results, we have observed that we got a significant improvement in different parameters when we used HPC2N and NASA workloads. Makespan is improved by 16%, 10%, 27%, 20% by using HPC2N and NASA workload over PSO and CS algorithms, respectively. Energy Consumption is minimized by 22%, 12%, 31%, 21% by using HPC2N and NASA workload over PSO and CS algorithms, respectively. Total Power cost is minimized by 31% and 39% over PSO and CS algorithms, respectively. Migration time is minimized by 34%, 29%, 20%, 14% by using HPC2N and NASA workloads over PSO and CS algorithms, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebadifard, F.; Babamir, S.M.: A PSO-based task scheduling algorithm improved using a load-balancing technique for the cloud computing environment. Concur. Comput. Practice Exp 30(12), e4368 (2018)
Moon, Y.J.; HeonChang, Y.; Gil, J.-M.; Lim, J.B.: A slave ants based ant colony optimization algorithm for task scheduling in cloud computing environments. HCIS 7(1), 1–10 (2017)
Rekha, P.M.; Dakshayini, M.: Efficient task allocation approach using genetic algorithm for cloud environment. Clust. Comput. 22(4), 1241–1251 (2019)
Prem Jacob, T.; Pradeep, K.: A multi-objective optimal task scheduling in cloud environment using cuckoo particle swarm optimization. Wireless Personal Commun. 109(1), 315–331 (2019)
Prasanna Kumar, K.R.; Kousalya, K.: Amelioration of task scheduling in cloud computing using crow search algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(10), 5901–5907 (2020)
Calheiros, R.N.; Ranjan, R.; Beloglazov, A.; De Rose, C.A.; Buyya, R.: CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Software Practice Exp. 41, 23–50 (2011)
HPC2N: The HPC2N Seth log; 2016. http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/labs/parallel/workload/l_hpc2n/.0
NASA:https://www.cse.huji.ac.il/labs/parallel/workload/l_nasa_ ipsc/
Pradeep, K.; Prem Jacob, T.: A hybrid approach for task scheduling using the cuckoo and harmony search in cloud computing environment. Wireless Personal Commun. 101(4), 2287–2311 (2018)
Loheswaran, K.; Daniya, T.; Karthick, K.: Hybrid cuckoo search algorithm with iterative local search for optimized task scheduling on cloud computing environment. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 16(5–6), 2065–2071 (2019)
Madni, S.H.; Hussain, M.S.; Latiff, A.; Ali, J.: Multi-objective-oriented cuckoo search optimization-based resource scheduling algorithm for clouds. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(4), 3585–3602 (2019)
Gabi, D., Ismail A.S., and Dankolo N.M: Minimized makespan based improved cat swarm optimization for efficient task scheduling in cloud datacenter. Proceedings of the 2019 3rd High Performance Computing and Cluster Technologies Conference. 2019
Gabi, D., et al.: Orthogonal Taguchi-based cat algorithm for solving task scheduling problem in cloud computing. Neural Comput. Appl. 30(6), 1845–1863 (2018)
Sudheer, M.S.; Vamsi Krishna, M.: Dynamic PSO for task scheduling optimization in cloud computing. Int J Recent Technol Eng 8(2), 332–338 (2019)
Aslam, S. et al: Towards energy efficiency and power trading exploiting renewable energy in Cloud data centers. International Conference on Advances in the Emerging Computing Technologies (AECT). IEEE, 2019.
Chu, S-C; Tsai, P-W; Pan J-S: Cat swarm optimization. Pacific Rim international conference on artificial intelligence. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2006
Sharafi, Y.; Khanesar, M.A.; Teshnehlab, M.: Discrete binary cat swarm optimization algorithm. In: 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer, Control and Communication (IC4), pp. 1–6 (2013)
Chu, S.C.; Tsai, P.W.: Computational intelligence based on the behavior of cats. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 3, 163–173 (2007)
Abed-alguni, B.H.; Alawad, N.A.: Distributed Grey Wolf Optimizer for scheduling of workflow applications in cloud environments. Appl. Soft Comput. 102, 107113 (2021)
Mansouri, N.; Zade, B.M.H.; Javidi, M.M.: Hybrid task scheduling strategy for cloud computing by modified particle swarm optimization and fuzzy theory. Comput. Ind. Eng. 130, 597–633 (2019)
Domanal, S.G.; Reddy, G.R.M.: An efficient cost optimized scheduling for spot instances in heterogeneous cloud environment. Future Generation Comput. Syst. 84, 11–21 (2018)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my Research Supervisors and University members and I also would like to thank the reviewers who gave the necessary comments for my manuscript.
Funding
There is no disclosures and no financial interests and we have not taken any fund from any agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
New Authors were contributed in Revision of Abstract and adding a new metric mentioned in the revised manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangalampalli, S., Swain, S.K. & Mangalampalli, V.K. Multi Objective Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing Using Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 1821–1830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06076-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06076-7