Abstract
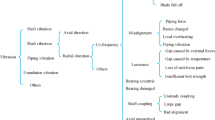
Reciprocating compressor is extensively used in petrochemical industry and other fields. However, due to the nonlinearity of the system, it is usually difficult for traditional methods to extract reliable fault features from its vibration signal and achieve satisfactory diagnostic accuracy under the condition of high intensity noise. In this paper, a novel fault recognition method for reciprocating compressor is proposed on the basis of signal rearrangement and attention mechanism assisted convolutional neural network. Firstly, to enhance the features of the raw signal without information loss and avoid artificial feature extraction, a novel signal rearrangement method, that can convert the raw data into 2-D format, is developed. The proposed signal rearrangement method can bring the data points into a straight line (45 degrees counterclockwise from the horizontal), which can reinforce the characteristics of the raw data and make it more intuitive. Besides, to enable the network to make adequate use of the characteristics of different channels and take global feature into consideration, the attention mechanism is introduced into the convolutional neural network classifier through the SE module of the SENet. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by experiments, and the experimental results show that, the diagnostic accuracy of the proposed method reaches 99.4%. In addition, even under strong noise, the method of this work can still maintain an accuracy of 90.2%. Compared with other typical methods, the method suggested in this work not only holds a higher recognition accuracy, but also a stronger ability of anti-noise.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Lee, J.: A compound interpolation envelope local mean decomposition and its application for fault diagnosis of reciprocating compressors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 110, 273–295 (2018)
Potocnik, P.: Semi-supervised vibration-based classification and condition monitoring of compressors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 93, 51–65 (2017)
Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.C.; Ma, B.: Fault diagnosis of reciprocating compressor using a novel ensemble empirical mode decomposition-convolutional deep belief network. Measurement 156, 107619 (2020)
Duan, L.X.; Wang, X.D.; Xie, M.Y.; Yuan, Z.: Auxiliary-model-based domain adaptation for reciprocating compressor diagnosis under variable conditions. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 34(6), 3595–3604 (2018)
Sim, H.Y.; Ramli, R.; Saifizul, A.; Song, M.F.: Detection and estimation of valve leakage losses in reciprocating compressor using acoustic emission technique. Measurement 152, 107315 (2020)
Xiao, S.G.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, H.Z.; Lin, Y.; Song, M.M.; Zhang, H.L.: Nonlinear dynamics of coupling rub-impact of double translational joints with subsidence considering the flexibility of piston rod. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(2), 1203–1229 (2020)
Mayadevi, N.; Mini, V.P.; Kumar, R.H.; Prins, S.: Fuzzy-based intelligent algorithm for diagnosis of drive faults in induction motor drive system. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 45(3), 1385–1395 (2020)
Yao, Y.; Xie, B.; Lei, L.; Li, Y.S.; Yin, Q.: Signal enhancement method for mechanical fault diagnosis in flexible drive-train. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(3), 2554–2563 (2021)
Zhang, H.L.; Ren, Z.Y.; Xin, S.J.; Liu, S.L.; Lan, C.; Sun, X.: A scale-adaptive positive selection algorithm based on B-cell immune mechanisms for anomaly detection. Eng. Appl. AI. 94, 103805 (2020)
Feng, K.; Smith, W.A.; Borghesani, P.; Randall, R.B.; Peng, Z.X.: Use of cyclostationary properties of vibration signals to identify gear wear mechanisms and track wear evolution. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 150, 107258 (2021)
Xiao, S.G.; Liu, S.L.; Jiang, F.; Song, M.M.; Cheng, S.G.: Nonlinear dynamic response of reciprocating compressor system with rub-impact fault caused by subsidence. J. Vib. Control. 25(11), 1737–1751 (2019)
Meng, Z.; Shi, G.X.; Wang, F.L.: Vibration response and fault characteristics analysis of gear based on time-varying mesh stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 148, 103786 (2020)
Xiao, S.G.; Liu, S.L.; Song, M.M., et al.: Coupling rub-impact dynamics of double translational joints with subsidence for time-varying load in a planar mechanical system. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 48, 451–486 (2020)
Wei, Y.; Liu, S.L.: Numerical analysis of the dynamic behavior of a rotor-bearing-brush seal system with bristle interference. J. Mech. Sci. Tech. 33(8), 3895–3903 (2019)
Pan, B.; Shi, Z.; Xu, X.: R-VCANet: a new deep-learning-based hyperspectral image classification method. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 10(5): 1975–1986 (2017)
Brunetti, A.; Buongiorno, D.; Trotta, G.F.; Bevilacqua, V.: Computer vision and deep learning techniques for pedestrian detection and tracking: a survey. Neurocomputing 300, 17–33 (2018)
Nguyen, V.N.; Jenssen, R.; Roverso, D.: Automatic autonomous vision-based power line inspection: a review of current status and the potential role of deep learning. Int. J. Elect. Power Energy Syst. 99, 107–120 (2018)
Zhao, D.F.; Liu, S.L.; Cheng, S.G.: Parallel multi-scale entropy and it’s application in rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Measurement 168, 108333 (2021)
Raj, E.F.I.; Balaji, M.: Analysis and classification of faults in switched reluctance motors using deep learning neural networks. Arab J. Sci. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05051-y
Pan, Z.Z.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.J., et al.: A two-stage method based on extreme learning machine for predicting the remaining useful life of rolling-element bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 144, 106899 (2020)
Wen, L.; Li, X.Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.: A new convolutional neural network based data-driven fault diagnosis method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(7), 5990–5998 (2017)
Ma, Y.F.; Jia, X.S.; Bai, H.J.; Liu, G.Z.: A new fault diagnosis method based on convolutional neural network and compressive sensing. J. Mech. Sci. Tech. 33(11), 5177–5188 (2019)
Pan, T.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Qu, C.; Zhou, Z.T.: A method for mechanical fault recognition with unseen classes via unsupervised convolutional adversarial auto-encoder. Meas. Sci. Technol. 32(3), 035113 (2021)
Wu, Z.C.; Jiang, P.C.; Ding, C.; Feng, F.Z.; Chen, T.: Intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Comput. Ind. 108, 53–61 (2019)
Zhao, D.F.; Liu, S.L.; Gu, D.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.: Enhanced data-driven fault diagnosis for machines with small and unbalanced data based on variational auto-encoder. Meas. Sci. Technol. 31, 035004 (2020)
Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Lee, C.K.; Shin, Y.J.: Detection and assessment of I&C cable faults using time-frequency R-CNN-based reflectometry. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(2), 1581–1590 (2021)
Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. arXiv: 1**7***09.01507 (2017)
Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Q.: Understanding and improving deep learning-based rolling bearing fault diagnosis with attention mechanism. Signal Process. 161, 136–154 (2019)
Xu, K.; Ba, J.L.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Zemel, R.S.; Bengio, Y.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, vol 37, pp. 2048–2057 (2015)
Zhou, Y.R.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Chen, L.: A spatiotemporal attention mechanism-based model for multi-step citywide passenger demand prediction. Inform. Sci. 513, 372–385 (2020)
Li, Y.; Zeng, J.B.; Shan, S.G.: Occlusion aware facial expression recognition using CNN with attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(5), 2439–2450 (2019)
Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM. 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.; Hovy, E.: Hierarchical attention networks for document classification. Proceedings of NAACL-HLT 2016, 1480–1489 (2016)
Chan, W.; Jaitly, N.; Le, Q.V.; Vinyals, O.: Listen, attend and spell. arXiv: 1**5**0**8.0121 (2015)
Kingma, D.; Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv: 1***412**.6980 (2014)
Maaten, L.; Hinton, G.E.: Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (52075310), Grant (11802168), and Grant (61603238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflict of interests with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Liu, S., Zhang, H. et al. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Reciprocating Compressor Based on Attention Mechanism Assisted Convolutional Neural Network Via Vibration Signal Rearrangement. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 7827–7840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05515-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05515-9