Abstract
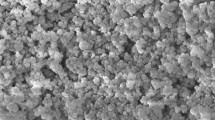
This study presents tribological enhancement properties of 40–80 nm copper (II) oxide (CuO, nanopowder, ~ 50 nm, 99.9% trace metal basis), copper iron oxide (CuFe2O4, nanopowder < 100 nm, 98.5% trace metal basis), and copper zinc iron oxide (CuZnFe2O4, nanopowder < 100 nm, 99.5% trace metal basis) nanoparticles incorporated (0.1 wt%) in SAE 5W-40 engine lubricant (base oil). Friction and wear evaluations were performed on the sample discs (62–65 HRC, 100 Cr6 steel) using pin-on-disc tribotester. The samples were immersed in the base oil and the nano-oil (oil with each nanoparticle) ambients one after another. Stribeck parameter was analyzed to determine the effects of oil bath temperature and pin-sliding speed on friction and wear within different lubrication regimes. Due to excess increment in an average coefficient of friction (ACOF) above the nanoparticle concentration of 0.1 wt%, the aforementioned amount was used for all experiments. The physical structure of the nanoparticles was examined via scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy analyses were conducted to observe the topography of the worn surfaces. Thermogravimetry (TG)–differential scanning calorimetry measurements were also carried out in order to determine the nanoparticle accumulation on the worn surfaces (thermal stability) and to have an idea about probable surface chemical decomposition. A maximum reduction of 50.8% in ACOF was observed for 5W-40 + CuZnFe2O4 suspension under the temperature of 40 °C and sliding speed of 1 m/s. Furthermore, minimum surface roughness was also determined for the sample processed in 5W-40 + CuZnFe2O4 under the temperature of 70 °C and sliding speed of 0.5 m/s.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, K.; Hwang, Y.; Cheong, S.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.: Understanding the role of nanoparticles in nano-oil lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 35(2), 127–131 (2009)
Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, B.; Xing, D.; Guo, Y.; Fan, R.: Investigation of the mending effect and mechanism of copper nano-particles on a tribologically stressed surface. Tribol. Lett. 17(4), 961–966 (2004)
Tao, X.; Jiazheng, Z.; Kang, X.: The ball-bearing effect of diamond nanoparticles as an oil additive. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 29(11), 2932–2937 (1996)
Padgurskas, J.; Rukuiza, R.; Prosyčevas, I.; Kreivaitis, R.: Tribological properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and Co nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 60, 224–232 (2013)
Tarasov, S.; Kolubaev, A.; Belyaev, S.; Lerner, M.; Tepper, F.: Study of friction reduction by nanocopper additives to motor oil. Wear 252(1–2), 63–69 (2002)
Yu, H.L.; Xu, Y.; Shi, P.J.; Xu, B.S.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.M.: Characterization and nano-mechanical properties of tribofilms using Cu nanoparticles as additives. Sur. Coat. Technol. 203(1–2), 28–34 (2008)
Choi, Y.; Lee, C.; Hwang, Y.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Choi, C.; Jung, M.: Tribological behavior of copper nanoparticles as additives in oil. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(2), 124–127 (2009)
Borda, F.L.G.; Oliveira, S.J.R.; Lazaro, L.M.S.M.; Leiroz, A.J.K.: Experimental investigation of the tribological behavior of lubricants withadditive containing copper nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 117, 52–58 (2018)
Akl, S.Y.; Abdel-Rehim, A.A.; Elsoudy, S.: An experimental investigation of tribological performance of a lubricant using different nano additives. SAE Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.4271/2018-01-0833
Gupta, R.N.; Harsha, A.P.: Tribological study of castor oil with surface-modified CuO nanoparticles in boundary lubrication. Ind. Lub. Tribol. 70(4), 700–710 (2018)
Pena-Paras, L.; Gutiérrez, J.; Irigoyen, M.; Lozano, M.; Velarde, M.; Maldonado-Cortes, D.; Taha-Tijerina, J.: Study on the anti-wear properties of metal-forming lubricants with TiO2 and CuO nanoparticle additives. Mat. Sci. Eng. 400, 1–7 (2018)
Ali, M.K.A.; Fuming, P.; Younus, H.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A.A.; Essa, F.A.; Elagouz, A.; Xianjun, H.: Fuel economy in gasoline engines using Al2O3/TiO2 nanomaterials as nanolubricant additives. Appl. Energy 211, 461–478 (2018)
Kotia, A.; Borkakoti, S.; Ghosh, S.K.: Wear and performance analysis of a 4-stroke diesel engine employing nanolubricants. Particuology 37, 54–63 (2018)
Rajendhran, N.; Palanisamy, S.; Shyma, A.P.; Venkatachalam, R.: Enhancing the thermophysical and tribological performance of gear oil using Ni-promoted ultrathin MoS2 nanocomposites. Tribol. Int. 124, 156–168 (2018)
Suryawanshi, S.R.; Pattiwar, J.T.: Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles blended with lubricating oil on the tribological performance of the journal bearing. Tribol. Ind. 40(3), 370–391 (2018)
Pandey, A. K., Nandgaonkar, M., Pandey, U., Suresh, S.: Experimental investigation of the effect of karanja oil biodiesel with cerium oxide nano particle fuel additive on lubricating oil tribology and engine wear in a heavy duty 38.8 L,780 HP Military CIDI diesel engine. SAE Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.4271/2018-01-1753
Wu, Y.Y.; Tsui, W.C.; Liu, T.C.: Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262(7–8), 819–825 (2007)
Hernández Battez, A.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández, J.E.; Díaz Fernández, J.M.; Machado, A.; Riba, J.: CuO, ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles as antiwear additive in oil lubricants. Wear 265(3–4), 422–428 (2008)
Hernández Battez, A.; Viesca, J.L.; González, R.; Blanco, D.; Asedegbega, E.; Osorio, A.: Friction reduction properties of a CuO nanolubricant used as lubricant for a NiCrBSi coating. Wear 268(1), 325–328 (2010)
Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Mai, L.; Bicheng, C.; Turkson, R.F.; Qingping, C.: Reducing frictional power losses and improving the scuffing resistance in automotive engines using hybrid nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Wear 364–365, 270–281 (2016)
Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Mai, L.; Qingping, C.; Turkson, R.F.; Bicheng, C.: Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 103, 540–554 (2016)
Zin, V.; Agresti, F.; Barison, S.; Colla, L.; Gondolini, A.; Fabrizio, M.: The synthesis and effect of copper nanoparticles on the tribological properties of lubricant oils. Nanotechnology 12, 751–759 (2013)
Asadauskas, S.J.; Kreivaitis, R.; Bikulčius, G.; Grigucevičienė, A.; Padgurskas, J.: Tribological effects of Cu, Fe and Zn nano-particles, suspended in mineral and bio-based oils. Lub. Sci. 28, 157–176 (2016)
Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Feng, D.; Wang, H.: Anti-wear and friction–reduction mechanism of Sn and Fe nanoparticles as additives of multialkylated cyclopentanes under vacuum condition. Vacuum 87, 75–80 (2013)
Mangam, V.; Bhattacharya, S.; Das, K.; Das, S.: Friction and wear behavior of Cu–CeO2 nanocomposite coatings synthesized by pulsed electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205(3), 801–805 (2010)
Peng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.: Tribological behaviors of surfactant-functionalized carbon nanotubes as lubricant additive in water. Tribol. Lett. 25(3), 247–253 (2007)
Zin, V.; Agresti, F.; Barison, S.; Colla, L.; Mercadelli, E.; Fabrizio, M.; Pagura, C.: Tribological properties of engine oil with carbon nano-horns as nano-additives. Tribol. Lett. 55(1), 45–53 (2014)
Li, S.; Bhushan, B.: Lubrication performance and mechanisms of Mg/Al-, Zn/Al-, and Zn/Mg/Al-layered double hydroxide nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Appl. Sur. Sci. 378, 308–319 (2016)
Arumugam, S.; Sriram, G.: Preliminary study of nano- and microscale TiO2 additives on tribological behavior of chemically modified rapeseed oil. Tribol. Trans. 56(5), 797–805 (2013)
Krishna Sabareesh, R.; Gobinath, N.; Sajith, V.; Das, S.; Sobhan, C.B.: Application of TiO2 nanoparticles as a lubricant-additive for vapor compression refrigeration systems: an experimental investigation. Int. J. Refrig 35(7), 1989–1996 (2012)
Wan, Q.; Jin, Y.; Sun, P.; Ding, Y.: Tribological behavior of a lubricant oil containing boron nitride nanoparticles. Proc. Eng. 102, 1038–1045 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Cukurova University, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Department of Physics and Hitit University, Scientific Technical Application and Research Center, for their technical assistance.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Cukurova University, Scientific Research Projects, under Grant number FBA-2017-8351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmaz, A.C. Tribological Enhancement Features of Various Nanoparticles as Engine Lubricant Additives: An Experimental Study. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1125–1134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04243-5