Abstract
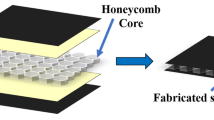
A simple and cost-effective manufacturing process was employed to prepare composite honeycomb sandwich panels for aerospace applications. Carbon fiber–epoxy matrix composite facesheets were first prepared by vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding, and later these facesheets were bonded with the Nomex\(^{\textregistered }\) honeycomb core by compression technique wherein the whole sandwich assembly containing facesheets, epoxy- based adhesive film and honeycomb core was clamped between two parallel metallic plates followed by curing in oven. Different curing temperatures, i.e., 100, 110, 120 and 130\({^{\circ }}\)C, and curing times, i.e., 2 and 3 h, were employed to optimize the curing parameters of the adhesive film to join CF–epoxy facesheets with the honeycomb core. The optimization of the curing parameters was related to the maximum load-bearing capability of composite honeycomb sandwich panels under three-point bend test and associated mechanical properties. It was shown that the composite honeycomb sandwich panels cured at 130\({^{\circ }}\)C for 3 h demonstrated maximum mechanical performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rion, J.; et al.: Ultra-light asymmetric photovoltaic sandwich structures. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 40(8), 1167–1173 (2009)
Composite, H.: HexWeb tm honeycomb sandwich design technology. http (2004)
Fagerberg, L.; Zenkert, D.: Imperfection-induced wrinkling material failure in sandwich panels. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 7(3), 195–219 (2005)
Harris, B.; Crisman, W.: Face-wrinkling mode of buckling of sandwich panels. ASCE J Eng Mech Div 91, 93–111 (1965)
Ley, R.P., Lin, W., Mbanefo, U.: Facesheet wrinkling in sandwich structures. In: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Langley Research Center (1999)
Avery, J.L.; Sankar, B.V.: Compressive failure of sandwich beams with debonded face-sheets. J. Compos. Mater. 34(14), 1176–1199 (2000)
Cantwell, W.; Davies, P.: A test technique for assessing core-skin adhesion in composite sandwich structures. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 13(3), 203–205 (1994)
Cantwell, W.; Davies, P.: A study of skin-core adhesion in glass fibre reinforced sandwich materials. Appl. Compos. Mater. 3(6), 407–420 (1996)
Ratcliffe, J.; Cantwell, W.: A new test geometry for characterizing skin-core adhesion in thin-skinned sandwich structures. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19(15), 1365–1367 (2000)
Cantwell, W.; et al.: Interfacial fracture in sandwich laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 59(14), 2079–2085 (1999)
Velecela, O.; Found, M.; Soutis, C.: Crushing energy absorption of GFRP sandwich panels and corresponding monolithic laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 38(4), 1149–1158 (2007)
Yu, S.; Cleghorn, W.: Free flexural vibration analysis of symmetric honeycomb panels. J. Sound Vib. 284(1), 189–204 (2005)
Wang, B.; Yang, M.: Damping of honeycomb sandwich beams. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 105(1), 67–72 (2000)
Kim, H.-Y.; Hwang, W.: Effect of debonding on natural frequencies and frequency response functions of honeycomb sandwich beams. Compos. Struct. 55(1), 51–62 (2002)
Fan, H.; et al.: An experiment study on the failure mechanisms of woven textile sandwich panels under quasi-static loading. Compos. Part B Eng. 41(8), 686–692 (2010)
Langdon, G.; et al.: The response of sandwich structures with composite face sheets and polymer foam cores to air-blast loading: preliminary experiments. Eng. Struct. 36, 104–112 (2012)
Okada, R.; Kortschot, M.: The role of the resin fillet in the delamination of honeycomb sandwich structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 62(14), 1811–1819 (2002)
Rion, J.; Leterrier, Y.; Månson, J.-A.E.: Prediction of the adhesive fillet size for skin to honeycomb core bonding in ultra-light sandwich structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 39(9), 1547–1555 (2008)
Grimes, G.C.: The adhesive–honeycomb relationship. In: Applied Polymer Symposium (1966)
Frostig, Y.; Baruch, M.: Bending of sandwich beams with transversely flexible core. AIAA J. 28(3), 523–531 (1990)
Soares, B.; Reis, L.; Silva, A.: Testing of sandwich structures with cork agglomerate cores. In: Eighth International Conference on Sandwich Structures (ICSS 8), Porto (2008)
Carlsson, L.; Sendlein, L.; Merry, S.: Literature survey. J. Compos. Mater. 25(1), 101–116 (1991)
Giglio, M.; Gilioli, A.; Manes, A.: Numerical investigation of a three point bending test on sandwich panels with aluminum skins and NomexTM honeycomb core. Comput. Mater. Sci. 56, 69–78 (2012)
Bénard, Q.; Fois, M.; Grisel, M.: Peel ply surface treatment for composite assemblies: chemistry and morphology effects. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 36(11), 1562–1568 (2005)
Benard, Q.; et al.: Influence of the polymer surface layer on the adhesion of polymer matrix composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 22(1), 51–61 (2009)
Bénard, Q.; Fois, M.; Grisel, M.: Roughness and fibre reinforcement effect onto wettability of composite surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(10), 4753–4758 (2007)
Johnson, A.; Sims, G.: Mechanical properties and design of sandwich materials. Composites 17(4), 321–328 (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooq, U., Ahmad, M.S., Rakha, S.A. et al. Interfacial Mechanical Performance of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels for Aerospace Applications. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 1775–1782 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2307-z