Abstract
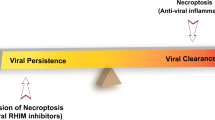
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a fundamental and widespread cell biological process that is distinct from cell necrosis and can be induced by a wide variety of stimuli including viral infections. Apoptosis may occur via either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathways and confers several advantages to the virally infected host including the prevention of further viral propagation and the potential inhibition and resolution of inflammatory processes. Several viruses have been shown to have the capacity to induce apoptosis in susceptible cells including herpes simplex virus, Varicella-zoster virus, rabies virus, human immunodeficiency virus, and reovirus. Apoptosis has also been observed in human African trypanosomiasis which is an infection caused by a protozoan parasite. The mechanisms leading to apoptosis may differ depending on the type of infection. Apoptosis has been reported in several neurodegenerative diseases and also psychiatric disorders but the true clinical significance of such observations is not certain, and, though interesting, it is very difficult to ascribe causation in these conditions. The presence of inflammation in the central nervous system in any neurological condition, including those associated with a viral infection, is not necessarily an absolute marker of serious disease and the notion of ‘good’ versus ‘bad’ inflammation is considered to be valid in some circumstances. The precise relationship between viruses, apoptosis, and inflammation is viewed as a complex one requiring further investigation to unravel and understand its nature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed M, Lock M, Miller CG, Fraser NW (2002) Regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript that protect cells from apoptosis in vitro and protect neuronal cells in vivo. J Virol 76:717–729
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Aubert M, Pomeranz LE, Blaho JA (2007) Herpes simplex virus blocks apoptosis by precluding mitochondrial cytochrome c release independent of caspase activation in infected human epithelial cells. Apoptosis 12:19–35
Avison MJ, Nath A, Berger JR (2002) Understanding pathogenesis and treatment of HIV dementia: a role for magnetic resonance? Trends Neurosci 25:468–473
Baloul L, Camelo S, Lafon M (2004) Up-regulation of Fas ligand (FasL) in the central nervous system: a mechanism of immune evasion by rabies virus. J Neurovirol 10:372–382
Chen L, Liu J, Xu C, Keblesh J, Zang W, Xiong H (2011) HIV-1gp120 induces neuronal apoptosis through enhancement of 4-aminopyridine-senstive outward K+ currents. PLoS One 6(10):e25994. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025994
Chi X, Amet T, Byrd D, Chang KH, Shah K, Hu N, Grantham A, Hu S, Duan J, Tao F, Nicol G, Yu Q (2011) Direct effects of HIV-1 Tat on excitability and survival of primary dorsal root ganglion neurons: possible contribution to HIV-1-associated pain. PLoS One 6(9):e24412. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024412
Clarke P, Beckham JD, Leser JS, Hoyt CC, Tyler KL (2009) Fas-mediated apoptotic signaling in the mouse brain following reovirus infection. J Virol 83:6161–6170
Dehghani L, Meamar R, Askari G, Khorvash F, Shaygannejad V, Pour AF, Javanmard SH (2013) The effect of pioglitazone on the Alzheimer’s disease-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Prev Med 4(Suppl 2):S205–S210
Djordjević VV, Ristić T, Lazarević D, Cosić V, Vlahović P, Djordjević VB (2012) Schizophrenia is associated with increased levels of serum Fas and FasL. Clin Chem Lab Med 50:1049–1054
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Konowal A, Freed PW, Westcott JY, Henson PM (1998) Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J Clin Invest 101:890–898
Gibney SM, Drexhage HA (2013) Evidence for a dysregulated immune system in the etiology of psychiatric disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharm 8:900–920
Girard M, Bisser S, Courtioux B, Vermot-Desroches C, Bouteille B, Wijdenes J, Preud’homme JL, Jauberteau MO (2003) In vitro induction of microglial and endothelial cell apoptosis by cerebrospinal fluids from patients with human African trypanosomiasis. Int J Parasitol 33:713–720
Goodkin ML, Ting AT, Blaho JA (2003) NF-kappaB is required for apoptosis prevention during herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J Virol 77:7261–7280
Guo L, Xing Y, Pan R, Jiang M, Gong Z, Lin L, Wang J, Xiong G, Dong J (2013) Curcumin protects microglia and primary rat cortical neurons against HIV-1 gp120-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. PLoS One 8(8):e70565. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070565
Hagman S, Raunio M, Rossi M, Dastidar P, Elovaara I (2011) Disease-associated inflammatory biomarker profiles in blood in different subtypes of multiple sclerosis: prospective clinical and MRI follow-up study. J Neuroimmunol 234:141–147
Henson PM, Bratton DL (2013) Antiinflammatory effects of apoptotic cells. J Clin Invest 123:2773–2774
Hood C, Cunningham AL, Slobedman B, Boadle RA, Abendroth A (2003) Varicella-zoster virus-infected human sensory neurons are resistant to apoptosis, yet human foreskin fibroblasts are susceptible: evidence for a cell-type-specific apoptotic response. J Virol 77:12852–12864
Hood C, Cunningham AL, Slobedman B, Arvin AM, Sommer MH, Kinchington PR, Abendroth A (2006) Varicella-zoster virus ORF63 inhibits apoptosis of primary human neurons. J Virol 80:1025–1031
James SF, Mahalingam R, Gilden D (2012) Does apoptosis play a role in varicella zoster virus latency and reactivation? Viruses 4:1509–1514
Jin L, Perng GC, Carpenter D, Mott KR, Osorio N, Naito J, Brick DJ, Jones C, Wechsler SL (2007) Reactivation phenotype in rabbits of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing an unrelated antiapoptosis gene in place of latency-associated transcript. J Neurovirol 13:78–84
Kennedy PGE (2004) Human African trypanosomiasis of the CNS: current issues and challenges. J Clin Invest 113(4):496–504
Kennedy PGE (2013) Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). Lancet Neurol 12:186–194
Kennedy PGE, Chaudhuri A (2002) Herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:237–238
Kennedy PGE, Cohrs RJ (2010) Varicella-zoster virus human ganglionic latency: a current summary. J Neurovirol 16:411–418
Kennedy PG, Grinfeld E, Bell JE (2000) Varicella-zoster virus gene expression in latently infected and explanted human ganglia. J Virol 74:11893–11898
Kennedy PG, Rodgers J, Bradley B, Hunt SP, Gettinby G, Leeman SE, de Felipe C, Murray M (2003) Clinical and neuroinflammatory responses to meningoencephalitis in substance P receptor knockout mice. Brain 126:1683–1690
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Kominsky DJ, Bickel RJ, Tyler KL (2002) Reovirus-induced apoptosis requires both death receptor- and mitochondrial-mediated caspase-dependent pathways of cell death. Cell Death Differ 9:926–933
Kraft RM, Nguyen ML, Yang XH, Thor AD, Blaho JA (2006) Caspase 3 activation during herpes simplex virus 1 infection. Virus Res 120:163–175
Li S, Carpenter D, Hsiang C, Wechsler SL, Jones C (2010) Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript inhibits apoptosis and promotes neurite sprouting in neuroblastoma cells following serum starvation by maintaining protein kinase B (AKT) levels. J Gen Virol 91:858–866
Liu X, Li Q, Dowdell K, Fischer ER, Cohen JI (2012) Varicella-Zoster virus ORF12 protein triggers phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and inhibits apoptosis. J Virol 86:3143–3151
Meraz-Ríos MA, Toral-Rios D, Franco-Bocanegra D, Villeda-Hernández J, Campos-Peña V (2013) Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Integr Neurosci 7(59):1–15
Mitchell BM, Bloom DC, Cohrs RJ, Gilden DH, Kennedy PG (2003) Herpes simplex virus-1 and varicella-zoster virus latency in ganglia. J Neurovirol 9:194–204
Mogi M, Harada M, Kondo T, Mizuno Y, Narabayashi H, Riederer P, Nagatsu T (1996) The soluble form of Fas molecule is elevated in parkinsonian brain tissues. Neurosci Lett 220:195–198
Mueller NH, Gilden DH, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R, Nagel MA (2008) Varicella zoster virus infection: clinical features, molecular pathogenesis of disease, and latency. Neurol Clin 26:675–697
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A (2000) Cytokines in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 58:143–151
Nagel MA, Choe A, Traktinskiy I, Cordery-Cotter R, Gilden D, Cohrs RJ (2011) Varicella-zoster virus transcriptome in latently infected human ganglia. J Virol 85:2276–2287
Nath A (2002) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins in neuropathogenesis of HIV dementia. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S193–S198
Perng GC, Jones C, Ciacci-Zanella J, Stone M, Henderson G, Yukht A, Slanina SM, Hofman FM, Ghiasi H, Nesburn AB, Wechsler SL (2000) Virus-induced neuronal apoptosis blocked by the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript. Science 287:1500–1503
Rodgers J, McCabe C, Gettinby G, Bradley B, Condon B, Kennedy PGE (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging to assess blood-brain barrier damage in murine trypanosomiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84:344–350
Rohn TT, Head E, Nesse WH, Cotman CW, Cribbs DH (2001) Activation of caspase-8 in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol Dis 8:1006–1016
Steiner I, Kennedy PGE (1993) Molecular biology of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 7:137–159
Sun XM, MacFarlane M, Zhuang J, Wolf BB, Green DR, Cohen GM (1999) Distinct caspase cascades are initiated in receptor-mediated and chemical-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:5053–5060
Tewari M, Monika VRK, Menon M, Seth P (2014) Astrocytes mediate HIV-1 Tat-induced neuronal damage via ligand-gated ion channel P2X7R. J Neurochem. doi:10.1111/jnc.12953
Thornberry NA (1997) The caspase family of cysteine proteases. Br Med Bull 53:478–490
Towfighi A, Skolasky RL, St Hillaire C, Conant K, McArthur JC (2004) CSF soluble Fas correlates with the severity of HIV-associated dementia. Neurology 62:654–656
Uzan M, Erman H, Tanriverdi T, Sanus GZ, Kafadar A, Uzun H (2006) Evaluation of apoptosis in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with severe head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:1157–1164
Wyllie AH (1997) Apoptosis: an overview. Br Med Bull 53:451–465
Young LS, Dawson CW, Eliopoulos AG (1997) Viruses and apoptosis. Br Med Bull 53:509–521
Acknowledgments
Most of this article was written while I was on a sabbatical period at the Center for Infection and Immunity at Columbia University, New York, USA. I wish to thank Drs. Mady Hornig and W. Ian Lipkin for helpful and stimulating discussions.
Conflict of interest
I declare that I have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennedy, P.G.E. Viruses, apoptosis, and neuroinflammation—a double-edged sword. J. Neurovirol. 21, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-014-0306-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-014-0306-y