Abstract
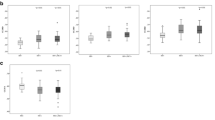
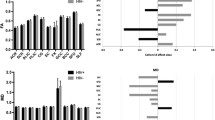
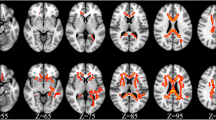
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder remains prevalent in HIV-infected individuals despite effective antiretroviral therapy. As these individuals age, comorbid cerebrovascular disease will likely impact cognitive function. Effective tools to study this impact are needed. This study used diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to characterize brain microstructural changes in HIV-infected individuals with and without cerebrovascular risk factors. Diffusion-weighted MRIs were obtained in 22 HIV-infected subjects aged 50 years or older (mean age = 58 years, standard deviation = 6 years; 19 males, three females). Tensors were calculated to obtain fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) maps. Statistical comparisons accounting for multiple comparisons were made between groups with and without cerebrovascular risk factors. Abnormal glucose metabolism (i.e., impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, or diabetes mellitus) was associated with significantly higher MD (false discovery rate (FDR) critical p value = 0.008) and lower FA (FDR critical p value = 0.002) in the caudate and lower FA in the hippocampus (FDR critical p value = 0.004). Pearson correlations were performed between DTI measures in the caudate and hippocampus and age- and education-adjusted composite scores of global cognitive function, memory, and psychomotor speed. There were no detectable correlations between the neuroimaging measures and measures of cognition. In summary, we demonstrate that brain microstructural abnormalities are associated with abnormal glucose metabolism in the caudate and hippocampus of HIV-infected individuals. Deep gray matter structures and the hippocampus may be vulnerable in subjects with comorbid abnormal glucose metabolism, but our results should be confirmed in further studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-beta
- APOE ε4:
-
Apolipoprotein epsilon 4
- ATP-III:
-
Adult Treatment Panel III
- BDI-II:
-
Beck Depression Inventory II
- cART:
-
Combination antiretroviral therapy
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- IDE:
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- NPZ-3-mem:
-
Age- and education-adjusted composite score of memory
- NPZ-3-pm:
-
Age- and education-adjusted composite score of psychomotor speed
- NPZ-8:
-
Age- and education-adjusted composite score of global cognitive function
- OGTT:
-
2-h oral glucose tolerance test
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- ROIs:
-
Regions of interest
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
American Diabetes Association (2009) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2009. Diabetes Care 32(Suppl 1):S13–S61
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Assaf Y, Pasternak O (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: a review. J Mol Neurosci 34:51–61
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994a) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66:259–267
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994b) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson 103:247–254
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Becker JT, Kingsley L, Mullen J et al (2009) Vascular risk factors, HIV serostatus, and cognitive dysfunction in gay and bisexual men. Neurology 73:1292–1299
Becker JT, Maruca V, Kingsley LA et al (2011a) Factors affecting brain structure in men with HIV disease in the post-HAART era. Neuroradiology 54:113–121
Becker JT, Sanders J, Madsen SK et al (2011b) Subcortical brain atrophy persists even in HAART-regulated HIV disease. Brain Imag Behav 5:77–85
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Biostatis Soc 57:289–300
Brown TT, Cole SR, Li X et al (2005) Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. Arch Intern Med 165:1179–1184
Brown TT, Xu X, John M et al (2009) Fat distribution and longitudinal anthropometric changes in HIV-infected men with and without clinical evidence of lipodystrophy and HIV-uninfected controls: a substudy of the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. AIDS Res Ther 6:8
Chang L, Wong V, Nakama H et al (2008) Greater than age-related changes in brain diffusion of HIV patients after 1 year. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 3:265–274
Chen Y, An H, Zhu H et al (2009) White matter abnormalities revealed by diffusion tensor imaging in non-demented and demented HIV+ patients. NeuroImage 47:1154–1162
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (2001) Executive summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 285:2486–2497
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (2002) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 106:3143–3421
Filippi CG, Ulug AM, Ryan E, Ferrando SJ, van Gorp W (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging of patients with HIV and normal-appearing white matter on MR images of the brain. Ajnr 22:277–283
Gongvatana A, Schweinsburg BC, Taylor MJ et al (2009) White matter tract injury and cognitive impairment in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. J Neurovirol 15:187–195
Gongvatana A, Cohen RA, Correia S et al (2011) Clinical contributors to cerebral white matter integrity in HIV-infected individuals. J Neurovirol 17:477–486
Gorelick PB, Bowler JV (2010) Advances in vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke; J Cereb Circ 41:e93–e98
Hoare J, Fouche JP, Spottiswoode B et al (2011) White-matter damage in clade C HIV-positive subjects: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 23:308–315
Jellinger KA (2008) Morphologic diagnosis of “vascular dementia”—a critical update. J Neurol Sci 270:1–12
Justman JE, Benning L, Danoff A et al (2003) Protease inhibitor use and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in a large cohort of HIV-infected women. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 32:298–302
Kallianpur KJ, Kirk GR, Sailasuta N et al (2011) Regional cortical thinning associated with detectable levels of HIV DNA. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr285
Kuper M, Rabe K, Esser S et al (2011) Structural gray and white matter changes in patients with HIV. J Neurol 258:1066–1075
Lamport DJ, Lawton CL, Mansfield MW, Dye L (2009) Impairments in glucose tolerance can have a negative impact on cognitive function: a systematic research review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:394–413
Leow A, Huang SC, Geng A et al (2005) Inverse consistent mapping in 3D deformable image registration: its construction and statistical properties. Inf Process Med Imaging 19:493–503
McMurtray A, Kwee S, Grace T, Shikuma C (2008) Changes in cerebral glucose metabolism associated with the presence of the apolipoprotein E4 allele in older HIV seropositive individuals. In: 11th RCMI International Symposium on Health Disparities, 2008, Honolulu, Hawaii
Nakamoto BK, Jahanshad N, Kallianpur K, Shikuma C, Valcour VG, Thompson PM (2010) Impact of ApoE and cerebrovascular risk factors on brain structure and cognition in HIV in the HAART era. In: CROI, 2010 February 16–19, San Francisco, CA
Nakamoto BK, Valcour VG, Kallianpur K et al (2011) Impact of cerebrovascular disease on cognitive function in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 57:e66–e68
Navia BA, Cho ES, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19:525–535
Ovbiagele B, Nath A (2011) Increasing incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with HIV infection. Neurology 76:444–450
Pfefferbaum A, Rosenbloom MJ, Adalsteinsson E, Sullivan EV (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging with quantitative fibre tracking in HIV infection and alcoholism comorbidity: synergistic white matter damage. Brain 130:48–64
Pfefferbaum A, Rosenbloom MJ, Rohlfing T, Kemper CA, Deresinski S, Sullivan EV (2009) Frontostriatal fiber bundle compromise in HIV infection without dementia. AIDS (London, England) 23:1977–1985
Ragin AB, Wu Y, Storey P, Cohen BA, Edelman RR, Epstein LG (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging of subcortical brain injury in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Neurovirol 11:292–298
S Roriz-Filho J, Sa-Roriz TM, Rosset I et al (2009) (Pre)diabetes, brain aging, and cognition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:432–443
Schmitt FA, Bigley JW, McKinnis R, Logue PE, Evans RW, Drucker JL (1988) Neuropsychological outcome of zidovudine (AZT) treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med 319:1573–1578
Shiramizu B, Paul R, Williams A et al (2007) HIV proviral DNA associated with decreased neuropsychological function. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 19:157–163
Strauss E, Sherman EMS, Spreen O (2006) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms, and commentary, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Thames AD, Foley JM, Panos SE et al (2011) Past stimulant abuse is associated with reduced basal ganglia and hippocampal integrity in older HIV+ adults. A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study 2:129–134
Tien PC, Schneider MF, Cole SR et al (2008) Antiretroviral therapy exposure and insulin resistance in the Women's Interagency HIV study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 49:369–376
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2007) Screening for high blood pressure: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force reaffirmation recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med 147:783–786
Valcour VG, Shikuma CM, Shiramizu BT et al (2005) Diabetes, insulin resistance, and dementia among HIV-1-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 38:31–36
Valcour VG, Sacktor NC, Paul RH et al (2006) Insulin resistance is associated with cognition among HIV-1-infected patients: the Hawaii Aging With HIV cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 43:405–410
Valcour V, Maki P, Bacchetti P et al (2012) Insulin resistance and cognition among HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected adult women: The Women’s Interagency HIV Study. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 28(5):447–53
Wright EJ, Grund B, Robertson K et al (2010) Cardiovascular risk factors associated with lower baseline cognitive performance in HIV-positive persons. Neurology 75:864–873
Acknowledgments
BKN, KJK, DCC, and CMS are funded in part by research grants P20RR011091, U54NS43049, and U54RR026136. NJ and PT are funded in part by R01 EB008432 and EB 007813, and R01 AG040060 and a UCLA Medical Informatics Fellowship (NJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Beau K. Nakamoto and Neda Jahanshad contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamoto, B.K., Jahanshad, N., McMurtray, A. et al. Cerebrovascular risk factors and brain microstructural abnormalities on diffusion tensor images in HIV-infected individuals. J. Neurovirol. 18, 303–312 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-012-0106-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-012-0106-1