Abstract
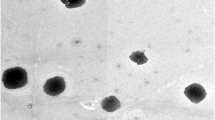
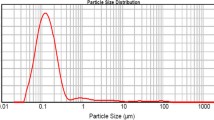
The purpose of this study was to develop a nanosuspension of a poorly soluble drug felodipine by nanoprecipitation to achieve superior in vitro dissolution and high oral absorption in vivo in rats. Felodipine nanosuspensions were prepared by precipitation with ultrasonication method using polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) as stabilizers. The particle size of nanosuspension with PVA was 60–200 nm, while with HPMC is 300–410 nm. The in vitro dissolution and pharmacokinetics of optimized nanosuspensions were studied after oral administration in male wistar rats. The results showed significant improvement during in vitro dissolution and in vivo plasma level. Dissolution studies of lyophillised nanoparticles showed that up to 93.0 % dissolved in 2 h. In the in vivo evaluation, nanosuspension exhibited significant increase in AUC0–24, C max and decrease in t max. The findings revealed that particle size reduction can influence felodipine absorption in gastrointestinal tract and nanosuspension can enhance oral bioavailability of felodipine in rats.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboul-Einien MA (2009) Formulation and evaluation of felodipine in soft gels with a solubilized core. Asian J Pharm Sci 4(3):144–160
Abrahamsson B, Johansson D, Torstensson A, Wingstrand K (1994) Evaluation of solubilizers in the drug release of hydrophilic matrix extended-release tablets of felodipine. Pharm Res 11:1093–1097
Bernhard BH, Muller RH (1999) Lab-scale production unit design for nanosuspensions of sparingly soluble cytotoxic drugs. Pharm Sci Tech Today 2:336–339
Diez I, Colom H, Moreno J, Obach R, Peraire C, Domenech JA (1991) Comparative in vitro study of transdermal absorption of a series of calcium channel antagonists. J Pharm Sci 80(931):934
Dong-Han W, Min-Soo K, Sibeum L, Jeong-Sook P, Sung-Joo H (2005) Improved physicochemical characteristics of felodipine solid dispersion particles by supercritical anti solvent precipitation process. Int J Pharm 301:199–208
Douroumis D, Fahr A (2006) Nano- and micro-particulate formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs by using a novel optimized technique. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 63:173–175
Durol AB, Greenblatt DJ (1997) Analysis of zolpidem in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection: application to single-dose pharmacokinetic studies. J Anal Toxicol 21:388–392
Gao L, Zhang D, Chen M, Duan C, Dai W, Jia L, Zhao W (2008) Studies on pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of oridonin nanosuspensions, Int J Pharm 355:321–327
George M, Ghosh I (2013) Identifying the correlation between drug/stabilizer properties and critical quality attributes (CQAs) of nanosuspension formulation prepared by wet media milling technology. Eur J Pharm Sci 48:142–152
Hai-Xia Z, Jie-X W, Zhi-Bing Z, Yuan L, Zhi-Gang S, Jian-Feng C (2009) Micronization of atorvastatin calcium by antisolvent precipitation process. Int J Pharm 374:106–113
Hany SMA, Peter Y, Nicholas B (2009) Preparation of hydrocortisone nanosuspension through a bottom-up nanoprecipitation technique using microfluidic reactors. Int J Pharm 375:107–113
Hintz RJ, Johnson KC (1989) The effect of particle size distribution on dissolution rate and oral absorption. Int J Pharm 51:9–17
Horn D, Rieger J (2001) Organic nanoparticles in the aqueous phase-theory, experiment and use. Angew Chem Int Ed 40:4330–4361
Karavas E, Ktistis G, Xenakis A, Georgarakis E (2005) Miscibility behaviour and formation mechanism of stabilized felodipine polivinylpyrrolidone amorphous nanodispersions. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 31:473–489
Keck CM, Muller RH (2006) Drug nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs produced by high pressure homogenization. Eur J Pharm Sci 62:3–16
Kerc J, Srcic S, Mohar M, Smid-Korbar J (1991) Some physicochemical properties of glassy felodipine. Int J Pharm 68:25–33
Kesisoglou F, Panmai S, Wu Y (2007) Nanosizing—oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:631–644
Kim BK, Hwang SJ, Park JB, Park HJ (2005) Characteristics of felodipine-located poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microparticles. J. Microenc 22:193–203
Lee DW, Hwang SJ, Park JB, Park HJ (2003) Preparation and release characteristics of polymer-coated and blended alginate microspheres. J Microenc 20:179–192
Li XS, Wang JX, Shen ZG, Zhang PY, Chen JF, Yun J (2007) Preparation of uniform prednisolone microcrystals by a controlled microprecipitation method. Int J Pharm 342:26–32
Louhi-Kultanen M, Karjalainen M, Rantanen J, Huhtanen M, Kallas J (2006) Crystallization of glycine with ultrasound. Int J Pharm 320:23–29
Luque de Castro MD, Priego-Capote F (2007) Ultrasound-assisted crystallization (sonocrystallization). Ultrason Sonochem 14:717–724
Martine LV, Laurence F, Young-Il K, Maurice H, Philippe M (1998) Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles containing an antihypertensive agent. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 46:137–143
Matteucci ME, Brettmann BK, Rogers TL, Elder EJ, Williams RO, Johnston KP (2007) Design of potent amorphous drug nanoparticles for rapid generation of highly supersaturated media. Mol Pharm 4:4782–4793
Möschwitzer J, Achleitner G, Pomper H, Muller RH (2004) Development of an intravenously injectable chemically stable aqueous omeprazole formulation using nanosuspension technology. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58:615–619
Müller RH, Peters K (1998) Nanosuspensions for the formulation of poorly soluble drugs I. Preparation by a size-reduction technique. Int J Pharm 160:229–237
Pathak P, Meziani MJ, Desai T, Sun Y-P (2006) Formation and stabilization of ibuprofen nanoparticles in supercritical fluid processing. J Supercrit Fluids 37:279–286
Patravale VB, Date AA, Kulkarni RM (2004) Nanosuspensions: a promising drug delivery strategy. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:827–840
Rabinow BE (2004) Nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Drug Discov 3:785–796
Reverchon E (1999) Supercritical antisolvent precipitation of micro- and nanoparticles. J Supercrit Fluids 15:1–21
Rogers T, Gillespie IB, Hitt JE, Fransen KL, Crowl CA, Tucker CJ, Kupperblatt GB, Becker JN, Wilson DL, Todd C, Elder EJ (2004) Development and characterization of a scalable controlled precipitation process to enhance the dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharm Res 21:2048–2057
Sahu BP, Das MK (2013) Nanosuspension for enhancement of oral bioavailability of felodipine. Appl Nanosci. doi:10.1007/s13204-012-0188-3
Saltiel E, Ellrodt AG, Monk JP, Langley MS (1988) Felodipine. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs 36:387–428
Van Eerdenbrugh B, Froyen L, Martens JA, Blaton N, Augustijns P, Brewster M, Van den Mooter G (2007) Characterization of physico-chemical properties and pharmaceutical performance of sucrose co-freeze-dried solid nanoparticulate powders of the anti-HIV agent loviride prepared by media milling. Int J Pharm 338:198–206
Van Eerdenbrugh B, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P (2008) Top-down production of drug nanocrystals: nanosuspension stabilization, miniaturization and transformation into solid products. Int J Pharm 364:64–75
Veerareddy PR, Poluri K, Sistla R, Chaganty S, Vennishetty VK (2012) Formulation development and comparative pharmacokinetic evaluation of felodipine nanoemulsion in SD rats. Am J Pharm Tech Res 2:931–945
Weis M, Mortensen SA, Rassing MR (1994) Bioavailability of four oral coenzyme Q10 formulations in healthy volunteers. Mol Aspects Med 15:273–280
Wingstrand K, Abrahamson B, Edgar B (1990) Bioavailability from felodipine extended-release tablets with different dissolution properties Int. J Pharm 60:151–156
Xia D, Quan P, Piao H, Sun S, Yin Y, Cui F (2010) Preparation of stable nitrendipine nanosuspensions using the precipitation–ultrasonication method for enhancement of dissolution and oral bioavailability. Eur J Pharm Sci 40:325–334
Xiong R, Lu W, Li J, Wang P, Xu R, Chen T (2008) Preparation and characterization of intravenously injectable nimodipine nanosuspension. Int J Pharm 350:338–343
Yuancai D, Wai KN, Jun H, Shoucang S, Reginald BHT (2010) A continuous and highly effective static mixing process for antisolvent precipitation of nanoparticles of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int J Pharm 386:256–261
Zaghloul AA, Gurley B, Khan M (2002) Bioavailability assessment of oral coenzyme Q10 formulations in dogs. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 28:1195–1200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, B.P., Das, M.K. Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of felodipine nanosuspension. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 39, 183–193 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-013-0158-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-013-0158-5