Abstract
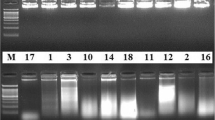
Rice is an important agricultural crop providing nutrition for humans worldwide. Rice white tip nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi, is a nematode causing economic yield losses globally in rice-growing areas. Because A. besseyi is a seed-transmitted nematode, its rapid and accurate identification is important for seed certification and quarantine purposes. Here, we developed species-specific primers for the small subunit ribosomal DNA region of the Aphelenchoides genus to identify A. besseyi. DNA was extracted from juveniles and directly infected tissues, such as hulls, brown rice and paddy rice. A. besseyi was easily and rapidly detected from plant tissues without nematode extraction. Because the extraction of A. besseyi from plant tissues is time-consuming and labour-intensive, the developed method may be applied to seed certification and quarantine approaches. To our knowledge, this is the first report directly identifying A. besseyi from infected plant tissues.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam MAM, Phillips MS, Blok VC (2007) Molecular diagnostic key for identification of single juveniles of seven common and economically important species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp). Plant Pathol 56:190–197
De Jesus DS, Olıveıra CMG, Roberts D, Blok VC, Neilson R, Prior T et al (2016) Morphological and molecular characterisation of Aphelenchoides besseyi and A. fujianensis (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from rice and forage grass seeds in Brazil. Nematology 18:337–356
Devran Z, Söğüt MA (2009) Distribution and ıdentification of root-knot nematodes from Turkey. J Nematol 41:128–133
EPPO (2009) PQR database. Paris, France: European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization. www.eppo.org. Accessed
Evlice E, Kepenekçi İ, Tülek A (2013) Prevalence of rice white tip nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942) in rice production areas in Çankırı and Çorum provinces. Bitki Koruma Bülteni 53:51–56
Fortuner R, Williams KJO (1975) Review of literature on Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942, the nematode causing ‘white tip’ disease in rice. Helminthol Abstr B44:1–40
Hooper DJ (1986) Extraction of free living stages from soil. In: Southey JF (ed) Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London, pp 5–30
Karataş SE, Aktas M, Kepenekçi İ (2007) A study of taxonomic characteristics, intensities and prevalence of plant parasitic nematode species in rice plants in Çankırı and Çorum districts. Proceedings of the Third Plant Protection Congress of Turkey 253
Lehman, PS (2004) Cost-benefits of nematode management through regulatory programs. In: Chen ZX, Chen SY, Dickson DW (eds) Nematology advances and perspectives, vol 2. CAB International, pp 1133–1177
Mısırlıoğlu B, Pehlivan E (2000) Distribution of white tip nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942) in the rice field of Balıkesir and Çanakkale provinces. Entomology Congress of Turkey, pp 561–568
Öztürk G, Enneli S (1997) Determination of Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie (Aphelenchida: Aphelenchoididae) (the white tip nematode) harmful on rice for the first time in Turkey. Turk J Entomol 21:129–132
Rybarczyk-Mydłowska K, Mooyman P, Van Megen H, Van Den Elsen S, Vervoort M, Veenhuizen P et al (2012) Small subunit ribosomal DNA-based phylogenetic analysis of foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) and their quantitative detection in complex DNA back grounds. Phytopathology 102:1153–1160
Sambrook, J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Tamura I, Kegasawa K (1956) Studies on the ecology of the rice nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, V. On the abnormal growth of rice plant and decrease in yield caused by rice nematode. Jpn J Ecol 9:120–124
Tülek A, Çobanoglu S (2010) Distribution of the rice white tip nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi, in rice growing areas in thrace region of Turkey. Nematol Mediterr 38:215–217
Tülek A, Çobanoglu S (2011) Nematode density and occurrence in paddy seeds ınfected by rice white-tip nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi chtistie) in some rice Cultivars. Proceedings of the Fourth Plant Protection Congress of Turkey, pp 179
Zijlstra C, Donkers-Venne DTH, Fargette M (2000) Identification of Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria using sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) based PCR assays. Nematology 2:847–853
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Akdeniz University (Project No: FBA-2014-124). Elvan Sert Çelik from Akdeniz University for her DNA isolation assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devran, Z., Tülek, A., Mıstanoğlu, İ. et al. A rapid molecular detection method for Aphelenchoides besseyi from rice tissues. Australasian Plant Pathol. 46, 43–48 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-016-0452-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-016-0452-1