Abstract
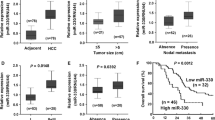
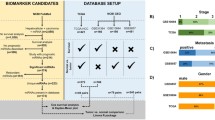
The aim of our study is to identify microRNAs (miRNAs) that have significance in the prognosis and pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The miRNAs differentially expressed in HCC were examined by using a human miRNA microarray dataset, and then the acquired candidates were screened by another microarray dataset. As a result, we got 25 miRNAs which were aberrantly expressed in cancer and meanwhile predicated distinct prognosis. Among them, miR-139-5p was down-regulated in HCC and its low expression in cancer tissue meant poor prognosis. Additionally, we demonstrated that its low expression was also related to several clinicopathologic characteristics such as vein invasion, BCLC stage, p-AKT expression, and pIGFR1 expression. In vitro, it has been discovered that treatment of HCC cells with a miR-139-5p mimic lead to inhibition of cell growth and migration. Moreover, luciferase assay showed that KPNA4 was not the direct target of miR-139-5p. Ectopic expression of miR-139-5p has not repressed the expression of KPNA4, but inhibited the nuclear import of NF-κB and phosphorylation of Akt. In conclusion, for the first time, we identify 25 deregulated miRNAs that are associated with prognosis and prove that miR-139-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in HCC and its low expression predicts poor prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(11):845–56.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are MicroRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20.
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, et al. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(1):167–75.
Ji J, Shi J, Budhu A, Yu Z, Forgues M, Roessler S, et al. MicroRNA expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(15):1437–47.
Bader AG. miR-34-a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 2012;3:120.
Wei R, Huang GL, Zhang MY, Li BK, Zhang HZ, Shi M, et al. Clinical significance and prognostic value of microRNA expression signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(17):4780–91.
Li W, Xie L, He X, Li J, Tu K, Wei L, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(7):1616–22.
Sato F, Hatano E, Kitamura K, Myomoto A, Fujiwara T, Takizawa S, et al. MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e16435.
Shih TC, Tien YJ, Wen CJ, Yeh TS, Yu MC, Huang CH, et al. MicroRNA-214 downregulation contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J Hepatol. 2012;57(3):584–91.
Toffanin S, Hoshida Y, Lachenmayer A, Villanueva A, Cabellos L, Minguez B, et al. MicroRNA-based classification of hepatocellular carcinoma and oncogenic role of miR-517a. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(5):1618–28.e16.
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS, et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010;70(24):10202–12.
Agrawal T, Gupta GK, Agrawal DK. Calcitriol decreases expression of importin alpha3 and attenuates RelA translocation in human bronchial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(5):1093–103.
Sun X, Icli B, Wara AK, Belkin N, He S, Kobzik L, et al. MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-kappaB-mediated vascular inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(6):1973–90.
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA, Ray SD. Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: new perspectives on therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:62–74. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.029 %/Copyright (c) 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Qiu G, Lin Y, Zhang H, Wu D. miR-139-5p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;463(3):315–21.
Wu L, Cai C, Wang X, Liu M, Li X, Tang H. MicroRNA-142-3p, a new regulator of RAC1, suppresses the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(9):1322–30.
Bae HJ, Noh JH, Kim JK, Eun JW, Jung KH, Kim MG, et al. MicroRNA-29c functions as a tumor suppressor by direct targeting oncogenic SIRT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2014;33(20):2557–67.
Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Park SJ, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):8089–102.
Liu Z, Tu K, Liu Q. Effects of microRNA-30a on migration, invasion and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(17):3089–97.
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, Yuan S, Wang R, Pan Z, et al. Double-negative feedback loop between microRNA-422a and forkhead box (FOX)G1/Q1/E1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth and metastasis. Hepatology. 2015;61(2):561–73.
Tryndyak VP, Ross SA, Beland FA, Pogribny IP. Down-regulation of the microRNAs miR-34a, miR-127, and miR-200b in rat liver during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by a methyl-deficient diet. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48(6):479–87.
Hernandez JM, Elahi A, Clark CW, Wang J, Humphries LA, Centeno B, et al. miR-675 mediates downregulation of Twist1 and Rb in AFP-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S625–35.
Zhang S, Zhang H, Zhu J, Zhang X, Liu Y. MiR-522 contributes to cell proliferation of human glioblastoma cells by suppressing PHLPP1 expression. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie. 2015;70:164–9.
Zhang ZL, Bai ZH, Wang XB, Bai L, Miao F, Pei HH. miR-186 and 326 predict the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and affect the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0118814.
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z, Quan C, et al. MiR-139-5p inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 2014;5(11):851–61.
Sun C, Sang M, Li S, Sun X, Yang C, Xi Y, et al. Hsa-miR-139-5p inhibits proliferation and causes apoptosis associated with down-regulation of c-met. Oncotarget. 2015;6(37):39756–92.
Zhang HD, Sun DW, Mao L, Zhang J, Jiang LH, Li J, et al. MiR-139-5p inhibits the biological function of breast cancer cells by targeting Notch1 and mediates chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;465(4):702–13.
Xu W, Hang M, Yuan CY, Wu FL, Chen SB, Xue K. MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in human non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(4):3864–70.
Duz MB, Karatas OF, Guzel E, Turgut NF, Yilmaz M, Creighton CJ et al. Identification of miR-139-5p as a saliva biomarker for tongue squamous cell carcinoma: a pilot study. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016;39(2):187–93.
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M, Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN, et al. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(9):1156–62.
Mi L, Chen Y, Zheng X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Mo D, et al. MicroRNA-139-5p suppresses 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte differentiation through notch and IRS1/PI3K/Akt insulin signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(7):1195–204.
Maoa R, Zou F, Yang L, Lin S, Li Y, Ma M, et al. The loss of MiR-139-5p promotes colitis-associated tumorigenesis by mediating PI3K/AKT/Wnt signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;69:153–61.
Papangeli I, Kim J, Maier I, Park S, Lee A, Kang Y, et al. MicroRNA 139-5p coordinates APLNR-CXCR4 crosstalk during vascular maturation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11268.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the colleagues in our laboratory for their suggestion and encouragement. The first author is particularly grateful to Yang Hu, a graduate of Kent State University, for her language assistance. The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81172350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ding, Q., Li, Y. et al. Reanalysis of microRNA expression profiles identifies novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Tumor Biol. 37, 14779–14787 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5369-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5369-3