Abstract
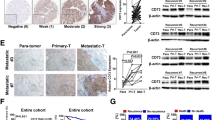
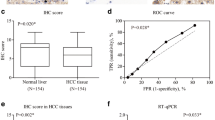
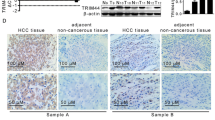
Although growing body of evidences have identified a critical role for receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) in mediating cell death signaling, its possible contribution to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression remains unclear. Here, we displayed that expression of RIP1 was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues than in adjacent liver tissues from 81.9 % HCC patients (P < 0.001) by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining. Overexpression of RIP1 was found positively associated with HBV infection, advanced TNM staging, portal vein invasion, and intrahepatic metastases. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis indicated that patients with higher RIP1 expression in HCC tissues suffered from unfavorable postsurgical survival. Higher RIP1 expression in HCC tissues was also confirmed to be an independent poor prognostic predictor. Knockdown of RIP1 resulted in suppression of cell viability and proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in MHCC97h cells. Nevertheless, enforced expression of RIP1 promoted cell viability and proliferation of Huh7 cells and inhibited cell apoptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that RIP1 exerted its function on HCC progression via activating AKT/Bcl-2/BAX signaling. In conclusion, our results provided the evidence of RIP1 overexpression in HCC, and RIP1 could be a novel predictive factor of unfavorable prognosis in HCC patients. Activation of AKT/Bcl-2/BAX signaling contributed to RIP1 promoting HCC progression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Bruix J, Gores GJ, Mazzaferro V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut. 2014;63:844–55.
Zhong JH, Ke Y, Wang YY, Li LQ. Liver resection for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and macrovascular invasion, multiple tumours, or portal hypertension. Gut. 2015;64:520–1.
Shimoda M, Tago K, Shiraki T, Mori S, Kato M, Aoki T, Kubota K. Risk factors for early recurrence of single lesion hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. World J Surg 2016.
Harada N, Shirabe K, Maeda T, Kayashima H, Takaki S, Maehara Y. Comparison of the outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal hypertension after liver resection versus radiofrequency ablation. World J Surg 2016.
Zhang D, Lin J, Han J. Receptor-interacting protein (rip) kinase family. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7:243–9.
Ofengeim D, Yuan J. Regulation of rip1 kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:727–36.
Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, Cornelis S, Vandenabeele P. Rip1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell’s decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:400–10.
LaRocca TJ, Sosunov SA, Shakerley NL. Ten VS, Ratner AJ. Hyperglycemic conditions prime cells for rip1-dependent necroptosis. J Biol Chem 2016.
Kelliher MA, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F, Stanger BZ, Leder P. The death domain kinase rip mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappab signal. Immunity. 1998;8:297–303.
Varfolomeev E, Vucic D. Un)expected roles of c-iaps in apoptotic and nfkappab signaling pathways. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:1511–21.
Darding M, Meier P. Iaps: guardians of ripk1. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:58–66.
Obitsu S, Sakata K, Teshima R, Kondo K. Eleostearic acid induces rip1-mediated atypical apoptosis in a kinase-independent manner via ERK phosphorylation, ros generation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e674.
Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of tnf receptor i-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–90.
Ranjan K, Pathak C. Fadd regulates NF-kappab activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflipl to induce apoptosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22787.
Zheng X, Song T, Dou C, Jia Y, Liu Q. Ctbp2 is an independent prognostic marker that promotes gli1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:3752–69.
Song T, Dou C, Jia Y, Tu K, Zheng X. Timp-1 activated carcinoma-associated fibroblasts inhibit tumor apoptosis by activating sdf1/cxcr4 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12061–79.
Gai X, Lu Z, Tu K, Liang Z, Zheng X. Caveolin-1 is up-regulated by gli1 and contributes to gli1-driven EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e84551.
Han W, Xie J, Fang Y, Wang Z, Pan H. Nec-1 enhances shikonin-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells by inhibition of rip-1 and erk1/2. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:7212–25.
Gai X, Tu K, Lu Z, Zheng X. Mrc2 expression correlates with tgfbeta1 and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:15011–25.
Zheng X, Gai X, Ding F, Lu Z, Tu K, Yao Y, Liu Q. Histone acetyltransferase pcaf up-regulated cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via acetylating histone h4 and inactivating AKT signaling. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:96.
Wang L, Du F, Wang X. Tnf-alpha induces two distinct caspase-8 activation pathways. Cell. 2008;133:693–703.
Zheng L, Bidere N, Staudt D, Cubre A, Orenstein J, Chan FK, Lenardo M. Competitive control of independent programs of tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced cell death by tradd and rip1. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:3505–13.
Chen D, Yu J, Zhang L. Necroptosis: an alternative cell death program defending against cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1865:228–36.
Qiu X, Klausen C, Cheng JC, Leung PC. Cd40 ligand induces rip1-dependent, necroptosis-like cell death in low-grade serous but not serous borderline ovarian tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1864.
Zhang YF, He W, Zhang C, Liu XJ, Lu Y, Wang H, Zhang ZH, Chen X, DX X. Role of receptor interacting protein (rip) 1 on apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated necroptosis during acetaminophen-evoked acute liver failure in mice. Toxicol Lett. 2014;225:445–53.
Huang C, Luo Y, Zhao J, Yang F, Zhao H, Fan W, Ge P. Shikonin kills glioma cells through necroptosis mediated by rip-1. PLoS One. 2013;8:e66326.
Zhu G, Ye J, Huang Y, Zheng W, Hua J, Yang S, Zhuang J, Wang J. Receptor-interacting protein-1 promotes the growth and invasion in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2016;48:2387–98.
Zhu G, Chen X, Wang X, Li X, Du Q, Hong H, Tang N, She F, Chen Y. Expression of the rip-1 gene and its role in growth and invasion of human gallbladder carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1152–65.
Liu XY, Lai F, Yan XG, Jiang CC, Guo ST, Wang CY, Croft A, Tseng HY, Wilmott JS, Scolyer RA, Jin L, Zhang XD. Rip1 kinase is an oncogenic driver in melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1736–48.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81301743 and 81572733 to Xin Zheng), Research Fund for the doctoral Program of High Education of China from Ministry of Education (no. 20120201120090 to Xin Zheng), Key Science and Technology Program of Shaanxi Province (no. 2014K11-01-01-21 to Xin Zheng), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Basic Research Operating expenses Program of Central College sponsored by Xi’an Jiaotong University to Xin Zheng.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The study was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University according to the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (no. 20080301, 6 May 2008).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Cong Wang and Bowen Yao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Yao, B., Xu, M. et al. RIP1 upregulation promoted tumor progression by activating AKT/Bcl-2/BAX signaling and predicted poor postsurgical prognosis in HCC. Tumor Biol. 37, 15305–15313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5342-1