Abstract
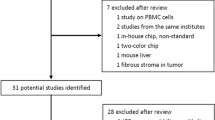
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) are the members of hepatobiliary diseases. Both types of cancer often exert high levels of similarity in terms of phenotypic characteristics, thus leading to difficulties in HCC and CCA differential diagnoses. In this study, a transcriptome meta-analysis was performed on HCC and CCA microarray data to identify differential transcriptome networks and potential biomarkers for HCC and CCA. Raw data from nine gene expression profiling datasets, consisting of 1,185 samples in total, were methodologically compiled and analyzed. To evaluate differentially expressed (DE) genes in HCC and CCA, the levels of gene expression were compared between cancer and its normal counterparts (i.e., HCC versus normal liver and CCA versus normal bile duct) using t test (P < 0.05) and k-fold validation. A total of 226 DE genes were specific to HCC, 249 DE genes specific to CCA, and 41 DE genes in both HCC and CCA. Gene ontology and pathway enrichment analyses revealed different patterns between functional transcriptome networks of HCC and CCA. Cell cycle and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathways were exclusively dysregulated in HCC whereas complement and coagulation cascades as well as glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism were prodominantly differentially expressed in CCA. Our meta-analysis revealed distinct dysregulation in transcriptome networks between HCC and CCA. Certain genes in these networks were discussed in the context of HCC and CCA transition, unique characteristics of HCC and CCA, and their potentials as HCC and CCA differential biomarkers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 20-HETE :
-
20-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- -OH-E1 :
-
4-Hydroxyestrone
- CCA :
-
Cholangiocarcinoma
- DE :
-
Differentially expressed
- EMT :
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition process
- GO :
-
Gene ontology
- HCC :
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HPA :
-
Human protein atlas project
- KEGG :
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- NL :
-
Normal liver
- NB :
-
Normal bile duct
References
McGlynn KA, Tarone RE, El-Serag HB. A comparison of trends in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2006;15:1198–203.
Gomaa A-I, Khan S-A, Toledano M-B, Waked I, Taylor-Robinson S-D. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:4300–8.
Bragazzi MC, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Venere R, Semeraro R, Gentile R, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: epidemiology and risk factors. Transl Gastrointest Cancer. 2011;1:21–32.
Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–25.
Gatto M, Bragazzi MC, Semeraro R, Napoli C, Gentile R, Torrice A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: update and future perspectives. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:253–60.
Woo HG, Lee J-H, Yoon J-H, Kim CY, Lee H-S, Jang JJ, et al. Identification of a cholangiocarcinoma-like gene expression trait in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3034–41.
Seok JY, Na DC, Woo HG, Roncalli M, Kwon SM, Yoo JE, et al. A fibrous stromal component in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a cholangiocarcinoma-like gene expression trait and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatology. 2012;55:1776–86.
Zhu K, Dai Z, Zhou J. Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: progression in early diagnosis, prognosis, and personalized therapy. Biomark Res. 2013;1:10.
Radwan NA, Ahmed NS. The diagnostic value of arginase-1 immunostaining in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma from metastatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma as compared to HepPar-1. Diagn Pathol. 2012;7:149.
Seeree P, Pearngam P, Kumkate S, Janvilisri T. An omics perspective on molecular biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics of cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Gen. 2015;2015:179528.
Tulalamba W, Larbcharoensub N, Sirachainan E, Tantiwetrueangdet A, Janvilisri T. Transcriptome meta-analysis reveals dysregulated pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:5931–42.
Xue T-C, Zhang B-H, Ye S-L, Ren Z-G. Differentially expressed gene profiles of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma by integrated microarray analysis. Tumor Biol. 2015;36:5891–9.
Coulouarn C, Cavard C, Rubbia-Brandt L, Audebourg A, Dumont F, Jacques S, et al. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinomas exhibit progenitor features and activation of Wnt and TGFβ signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:1791–6.
Roessler S, Jia H-L, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye Q-H, Lee J-S, et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10202–12.
Kim SM, Leem S-H, Chu I-S, Park Y-Y, Kim SC, Kim S-B, et al. Sixty-five gene-based risk score classifier predicts overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55:1443–52.
Sia D, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Roayaie S, Ferrer J, Tabak B, et al. Integrative molecular analysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals 2 classes that have different outcomes. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:829–40.
Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reyniès A, Balabaud C, Rebouissou S, Jeannot E, et al. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology. 2007;45:42–52.
Andersen JB, Spee B, Blechacz BR, Avital I, Komuta M, Barbour A, et al. Genomic and genetic characterization of cholangiocarcinoma identifies therapeutic targets for tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1021–31.e15.
Woo HG, Park ES, Cheon JH, Kim JH, Lee J-S, Park BJ, et al. Gene expression-based recurrence prediction of hepatitis B virus-related human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2056–64.
Oishi N, Kumar MR, Roessler S, Ji J, Forgues M, Budhu A, et al. Transcriptomic profiling reveals hepatic stem-like gene signatures and interplay of miR-200c and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56:1792–803.
Chiang DY, Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Peix J, Newell P, Minguez B, et al. Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6779–88.
de Jonge HJM, Fehrmann RSN, de Bont ESJM, Hofstra RMW, Gerbens F, Kamps WA, et al. Evidence based selection of housekeeping genes. PLoS One. 2007;2:e898.
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang W, Bhagabati N, et al. TM4: a free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques. 2003;34:374–8.
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z, Zhang B. WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit (WebGestalt): update 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W77–83.
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D808–15.
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13:2498–504.
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419.
Edenberg HJ. The genetics of alcohol metabolism: role of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase variants. Alcohol Res Health. 2007;30:5–13.
Mezey E, Holt PR. The inhibitory effect of ethanol on retinol oxidation by human liver and cattle retina. Exp Mol Pathol. 1971;15:148–56.
Morgan TR, Mandayam S, Jamal MM. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S87–96.
Min L, Ji Y, Bakiri L, Qiu Z, Cen J, Chen X, et al. Liver cancer initiation is controlled by AP-1 through SIRT6-dependent inhibition of survivin. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:1203–11.
Cotoi CG, Khorsandi SE, Pleşea IE, Quaglia A. Whole-genome DASL gene expression profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma sub-populations isolated by laser microdissection on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded liver tissue samples. Romanian J Morphol Embryol. 2012;53:893–902.
Chaerkady R, Harsha HC, Nalli A, Gucek M, Vivekanandan P, Akhtar J, et al. A quantitative proteomic approach for identification of potential biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:4289–98.
Kraiklang R, Pairojkul C, Khuntikeo N, Imtawil K, Wongkham S, Wongkham C. A novel predictive equation for potential diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89337.
Ben-Menachem T. Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;19:615–7.
Nakajima M. Smoking behavior and related cancers: the role of CYP2A6 polymorphisms. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2007;9:538–44.
Yamazaki H, Inui Y, Yun CH, Guengerich FP, Shimada T. Cytochrome P450 2E1 and 2 A6 enzymes as major catalysts for metabolic activation of N-nitrosodialkylamines and tobacco-related nitrosamines in human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis. 1992;13:1789–94.
Raunio H, Juvonen R, Pasanen M, Pelkonen O, Pääkkö P, Soini Y. Cytochrome P4502A6 (CYP2A6) expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1998;27:427–32.
Satarug S, Lang MA, Yongvanit P, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang E, Mairiang P, et al. Induction of cytochrome P450 2 A6 expression in humans by the carcinogenic parasite infection, Opisthorchiasis viverrini. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 1996;5:795–800.
Powell PK, Wolf I, Jin R, Lasker JM. Metabolism of arachidonic acid to 20-hydroxy-5,8,11, 14-eicosatetraenoic acid by P450 enzymes in human liver: involvement of CYP4F2 and CYP4A11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;285:1327–36.
Ishizuka T, Cheng J, Singh H, Vitto MD, Manthati VL, Falck JR, et al. 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid stimulates nuclear factor-kappaB activation and the production of inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324:103–10.
Iizuka N, Oka M, Hamamoto Y, Mori N, Tamesa T, Tangoku A, et al. Altered levels of cytochrome P450 genes in hepatitis B or C virus-infected liver identified by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2004;1:53–8.
Tanaka S, Mogushi K, Yasen M, Ban D, Noguchi N, Irie T, et al. Oxidative stress pathways in noncancerous human liver tissue to predict hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence: a prospective, multicenter study. Hepatology. 2011;54:1273–81.
Turgeon D, Carrier JS, Lévesque E, Hum DW, Bélanger A. Relative enzymatic activity, protein stability, and tissue distribution of human steroid-metabolizing UGT2B subfamily members. Endocrinology. 2001;142:778–87.
Ritter JK, Chen F, Sheen YY, Lubet RA, Owens IS. Two human liver cDNAs encode UDP-glucuronosyltransferases with 2 log differences in activity toward parallel substrates including hyodeoxycholic acid and certain estrogen derivatives. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1992;31:3409–14.
Getoff N, Gerschpacher M, Hartmann J, Huber JC, Schittl H, Quint RM. The 4-hydroxyestrone: electron emission, formation of secondary metabolites and mechanisms of carcinogenesis. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2010;98:20–4.
Nakamura A, Nakajima M, Yamanaka H, Fujiwara R, Yokoi T. Expression of UGT1A and UGT2B mRNA in human normal tissues and various cell lines. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008;36:1461–4.
Gestl SA, Green MD, Shearer DA, Frauenhoffer E, Tephly TR, Weisz J. Expression of UGT2B7, a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase implicated in the metabolism of 4-hydroxyestrone and all-trans retinoic acid, in normal human breast parenchyma and in invasive and in situ breast cancers. Am J Pathol. 2002;160:1467–79.
Janss AJ, Maity A, Tang CB, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG, Sutton L, et al. Decreased cyclin B1 expression contributes to G2 delay in human brain tumor cells after treatment with camptothecin. Neuro-Oncol. 2001;3:11–21.
Weng L, Du J, Zhou Q, Cheng B, Li J, Zhang D, et al. Identification of cyclin B1 and Sec62 as biomarkers for recurrence in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:39.
Duong FHT, Christen V, Lin S, Heim MH. Hepatitis C virus-induced up-regulation of protein phosphatase 2 A inhibits histone modification and DNA damage repair. Hepatology. 2010;51:741–51.
Maiorano D, Lutzmann M, Méchali M. MCM proteins and DNA replication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:130–6.
Kearsey SE, Maiorano D, Holmes EC, Todorov IT. The role of MCM proteins in the cell cycle control of genome duplication. BioEssays. 1996;18:183–90.
Qin L-X, Tang Z-Y. The prognostic molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:385–92.
Marshall AE, Rushbrook SM, Vowler SL, Palmer CR, Davies RJ, Gibbs P, et al. Tumor recurrence following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: role of tumor proliferation status. Liver Transpl. 2010;16:279–88.
Chen M, Zhang J, Li N, Qian Z, Zhu M, Li Q, et al. Promoter hypermethylation mediated downregulation of FBP1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma and colon cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25564.
Li L, Lian B, Li C, Li W, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Integrative analysis of transcriptional regulatory network and copy number variation in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e98653.
Henkel C, Schwamborn K, Zimmermann HW, Tacke F, Kühnen E, Odenthal M, et al. From proteomic multimarker profiling to interesting proteins: thymosin-β4 and kininogen-1 as new potential biomarkers for inflammatory hepatic lesions. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:2176–88.
Bior AD, Pixley RA, Colman RW. Domain 5 of kininogen inhibits proliferation of human colon cancer cell line (HCT-116) by interfering with G1/S in the cell cycle. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:403–11.
Zhang X, Xiao Z, Liu X, Du L, Wang L, Wang S, et al. The potential role of ORM2 in the development of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e31868.
Bambace NM, Holmes CE. The platelet contribution to cancer progression. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:237–49.
Akarasereenont P, Al E. Cholangiocarcinoma cell induced platelet aggregation via activation of thrombin and cyclooxygenase. Siriraj Med J. 2009;61:8–12.
Yang Y, Hu D, Wang L, Liang C, Hu X, Xu J, et al. Comparison of two serpins of Clonorchis sinensis by bioinformatics, expression, and localization in metacercaria. Pathog Glob Health. 2014;108:179–85.
Sriwanitchrak P, Viyanant V, Chaijaroenkul W, Srivatanakul P, Gram HR, Eursiddhichai V, et al. Proteomics analysis and evaluation of biomarkers for detection of cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:1503–10.
Sandanayake NS, Sinclair J, Andreola F, Chapman MH, Camuzeaux S, Webster GJ, et al. PWE-055 characterisation of serum proteins in biliary tract cancer, primary sclerosing cholangitis and immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis using 2-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Gut. 2010;59:A106.
Subrungruanga I, Thawornkunob C, Chawalitchewinkoon-Petmitrc P, Pairojkul C, Wongkham S, Petmitrb S. Gene expression profiling of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:557–63.
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Díaz-Prado S, Reboredo M, Medina V, Lorenzo-Patiño MJ, Iglesias-Díaz P, et al. Evaluation of Plakophilin-3 mRNA as a biomarker for detection of circulating tumor cells in gastrointestinal cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2010;19:1432–40.
Jackstadt R, Röh S, Neumann J, Jung P, Hoffmann R, Horst D, et al. AP4 is a mediator of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Exp Med. 2013;210:1331–50.
Wang W, Zhang J, Zhan X, Lin T, Yang M, Hu J, et al. SOX4 is associated with poor prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;452:614–21.
Hass HG, Nehls O, Jobst J, Frilling A, Vogel U, Kaiser S. Identification of osteopontin as the most consistently over-expressed gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: detection by oligonucleotide microarray and real-time PCR analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2501–10.
Matsui T, Matsukawa Y, Sakai T, Nakamura K, Aoike A, Kawai K. Effect of ammonia on cell-cycle progression of human gastric cancer cells. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995;7(Suppl 1):S79–81.
Snell K, Natsumeda Y, Eble JN, Glover JL, Weber G. Enzymic imbalance in serine metabolism in human colon carcinoma and rat sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1988;57:87–90.
Limoli CL, Giedzinski E. Induction of chromosomal instability by chronic oxidative stress. Neoplasia. 2003;5:339–46.
Kumar M, Zhao X, Wang XW. Molecular carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: one step closer to personalized medicine? Cell Biosci. 2011;1:5.
Yin P, Zhao C, Li Z, Mei C, Yao W, Liu Y, et al. Sp1 is involved in regulation of cystathionine γ-lyase gene expression and biological function by PI3K/Akt pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell Signal. 2012;24:1229–40.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Medical Research Council (MRC) through UK-Thailand Research Collaborations (Newton Fund), the Thailand Research Fund (grant no. DBG5980006), and Mahidol University to TJ. SL is a recipient of the Development and Promotion of Science and Technology Talented Project (DPST) scholarship. JT is a recipient of the Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Somsak Likhitrattanapisal and Jaitip Tipanee equal contributors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Likhitrattanapisal, S., Tipanee, J. & Janvilisri, T. Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles identifies differential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 12755–12766 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5186-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5186-8