Abstract
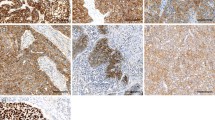
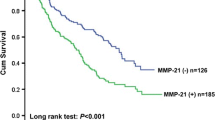
The migration and invasion inhibitory protein (MIIP) was shown to function as a tumor suppressor gene in gliomas by inhibiting tumor cell growth, migration, and invasion. However, its role and clinical significance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) have not been elucidated. We investigated the correlation of MIIP expression and clinical outcome in a group of surgically resected ESCCs. Tissue microarrays constructed of 253 surgically resected ESCC primary tumors and paired paracancerous normal esophageal epithelia were used for MIIP evaluation by immunohistochemistry. The clinical and prognostic significance of MIIP expression was analyzed statistically. The expression of MIIP expression in cancer tissues was increased significantly in comparison with the paired paracancerous normal epithelia (P < 0.001). And, MIIP expression was associated with ESCC cells’ differentiation (P < 0.001). By Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients with low MIIP expression exhibited significantly improved overall survival (OS, P = 0.039) and a tendency of improved disease-free survival (DFS, P = 0.086) than those with high MIIP expression. In addition, MIIP expression could distinguish OS or DFS of patients with tumors in stage T3–4 (P = 0.020, 0.028), N0 (P = 0.008, 0.032), and stage II (P = 0.004, 0.019), as well as at lower thoracic esophagus (P = 0.024, 0.090). Multivariate analysis showed that MIIP expression was an independent prognostic factor in ESCC OS and DFS. In conclusion, MIIP expressed higher in ESCCs than in paracancerous normal esophageal epithelia and was a positive, independent prognostic factor in resected ESCCs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Herskovic A, Russell W, Liptay M, Fidler MJ, Al-Sarraf M. Esophageal carcinoma advances in treatment results for locally advanced disease: review. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(5):1095–103.
Yang HX, Feng W, Wei JC, Zeng TS, Li ZD, Zhang LJ, et al. Support vector machine-based nomogram predicts postoperative distant metastasis for patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(5):1109–16.
Song SW, Fuller GN, Khan A, Kong S, Shen W, Taylor E, et al. IIp45, an insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) binding protein, antagonizes IGFBP-2 stimulation of glioma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(24):13970–5.
Wu Y, Song SW, Sun J, Bruner JM, Fuller GN, Zhang W. IIp45 inhibits cell migration through inhibition of HDAC6. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(6):3554–60.
Ji P, Smith SM, Wang Y, Jiang R, Song SW, Li B, et al. Inhibition of gliomagenesis and attenuation of mitotic transition by MIIP. Oncogene. 2010;29(24):3501–8.
Wang X, Liu H, Wang X, An Y. Clinical significance of migration and invasion inhibitor protein expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(6):2417–22.
Song F, Zhang L, Ji P, Zheng H, Zhao Y, Zhang W, et al. Altered expression and loss of heterozygosity of the migration and invasion inhibitory protein (MIIP) gene in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(6):2771–8.
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, et al. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 1998;4(7):844–7.
Wen J, Luo KJ, Hu Y, Yang H, Fu JH. Metastatic lymph node CHIP expression is a potential prognostic marker for resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(5):1668–75.
Wang Y, Wen J, Zhang W. MIIP, a cytoskeleton regulator that blocks cell migration and invasion, delays mitosis, and suppresses tumorogenesis. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011;12(1):68–73.
Hu N, Wang C, Ng D, Clifford R, Yang HH, Tang ZZ, et al. Genomic characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from a high-risk population in China. Cancer Res. 2009;69(14):5908–17.
Shi ZZ, Shang L, Jiang YY, Hao JJ, Zhang Y, Zhang TT, et al. Consistent and differential genetic aberrations between esophageal dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma detected by array comparative genomic hybridization. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(21):5867–78.
Mariette C, Dahan L, Mornex F, Maillard E, Thomas PA, Meunier B, et al. Surgery alone versus chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for stage I and II esophageal cancer: final analysis of randomized controlled phase III trial FFCD 9901. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(23):2416–22.
Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, Zalcberg JR, Simes RJ, Barbour A, et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(7):681–92.
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(22):2074–84.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81201843), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. S2012040007150), and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (Grant No. 20120171120109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81201843), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (grant number S2012040007150), and Chinese Ministry of Education (grant number 20120171120109).
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Jing Wen and Qian-Wen Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, J., Liu, QW., Luo, KJ. et al. MIIP expression predicts outcomes of surgically resected esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Tumor Biol. 37, 10141–10148 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4633-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4633-2