Abstract
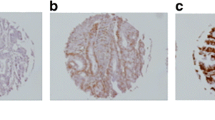
The CXCL12-CXCR4 axis is proposed to mediate metastasis formation. In this study, we examined CXCL12, CXCR4 and the relative CXCL12-CXCR4 expression as prognostic factors in two cohorts of colon cancer patients. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridization (ISH) were used to study CXCR4, CXCL12 and relative CXCL12-CXCR4 expression in tissue microarrays. Our study included totally 596 patients, 290 in cohort 1 and 306 in cohort 2. For tumour, node, metastasis (TNM) stage III, low nuclear expression of CXCR4 was a positive prognostic factor for 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) in cohort 1 (P = 0.007) and cohort 2 (P = 0.023). In multivariate analysis for stage III, nuclear expression of CXCR4 in cohort 1 was confirmed as a prognostic factor for DFS (hazard ratio (HR), 0.27; 95 % CI, 0.09 to 0.77). For TNM stage III, high cytoplasmic expression of CXCL12 was associated with better 5-year DFS in both cohorts (P = 0.006 and P = 0.006, respectively). We further validated the positive prognostic value of CXCL12 expression for 5-year DFS in stage III with ISH (P = 0.022). For TNM stage III, the relative CXCL12-CXCR4 expression (CXCL12 > CXCR4 vs CXCL12 = CXCR4 vs CXCL12 < CXCR4) was a prognostic factor for 5-year DFS in cohort 1 (92 % vs 46 % vs 31 %, respectively; P < 0.001) and cohort 2 (92 % vs 66 % vs 30 %, respectively; P = 0.006). In conclusion, CXCL12 and relative CXCL12-CXCR4 expression are independent prognostic factors for 5-year DFS in TNM stage III colon cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J. GLOBOCAN 2012 cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC cancerbase No. 11. 2013.
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM. Chemokines as mediators of tumor angiogenesis and neovascularization. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:685–90.
Teicher BA, Fricker SP. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2927–31.
Don-Salu-Hewage AS, Chan SY, McAndrews KM, Chetram MA, Dawson MR, Bethea DA, et al. Cysteine (C)-x-C receptor 4 undergoes transportin 1-dependent nuclear localization and remains functional at the nucleus of metastatic prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57194.
Kim J, Takeuchi H, Lam ST, Turner RR, Wang HJ, Kuo C, et al. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer patients increases the risk for recurrence and for poor survival. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2744–53.
Speetjens FM, Liefers GJ, Korbee CJ, Mesker WE, van de Velde CJ, van Vlierberghe RL, et al. Nuclear localization of CXCR4 determines prognosis for colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Microenviron. 2009;2:1–7.
Akishima-Fukasawa Y, Nakanishi Y, Ino Y, Moriya Y, Kanai Y, Hirohashi S. Prognostic significance of CXCL12 expression in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:202–10.
Yoshitake N, Fukui H, Yamagishi H, Sekikawa A, Fujii S, Tomita S, et al. Expression of SDF-1 alpha and nuclear CXCR4 predicts lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1682–9.
Wendt MK, Johanesen PA, Kang-Decker N, Binion DG, Shah V, Dwinell MB. Silencing of epithelial CXCL12 expression by DNA hypermethylation promotes colonic carcinoma metastasis. Oncogene. 2006;25:4986–97.
Drury LJ, Wendt MK, Dwinell MB. CXCL12 chemokine expression and secretion regulates colorectal carcinoma cell anoikis through Bim-mediated intrinsic apoptosis. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12895.
Drury LJ, Ziarek JJ, Gravel S, Veldkamp CT, Takekoshi T, Hwang ST, et al. Monomeric and dimeric CXCL12 inhibit metastasis through distinct CXCR4 interactions and signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:17655–60.
Dahl O, Fluge O, Carlsen E, Wiig JN, Myrvold HE, Vonen B, et al. Final results of a randomised phase III study on adjuvant chemotherapy with 5 FU and levamisol in colon and rectum cancer stage II and III by the Norwegian Gastrointestinal Cancer Group. Acta Oncol (Stockholm, Sweden). 2009;48:368–76.
Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, Haller DG, Laurie JA, Goodman PJ, et al. Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. New Engl J Med. 1990;322:352–8.
Storli KE, Sondenaa K, Furnes B, Eide GE. Outcome after introduction of complete mesocolic excision for colon cancer is similar for open and laparoscopic surgical treatments. Dig Surg. 2013;30:317–27.
Stanisavljevic L, Sondenaa K, Storli KE, Leh S, Nesvik I, Gudlaugsson E, et al. The total number of lymph nodes in resected colon cancer specimens is affected by several factors but the lymph node ratio is independent of these. APMIS. 2014;122:490–8.
Sorbye H, Dahl O. Nordic 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin bolus schedule combined with oxaliplatin (Nordic FLOX) as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Acta Oncol. 2003;42:827–31.
Glimelius B, Jakobsen A, Graf W, Berglund A, Gadeberg C, Hansen P, et al. Bolus injection (2–4 min) versus short-term (10–20 min) infusion of 5-fluorouracil in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a prospective randomised trial. Nordic Gastrointestinal Tumour Adjuvant Therapy Group. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990). 1998;34:674–8.
Fischer T, Nagel F, Jacobs S, Stumm R, Schulz S. Reassessment of CXCR4 chemokine receptor expression in human normal and neoplastic tissues using the novel rabbit monoclonal antibody UMB-2. PLoS One. 2008;3:e4069.
Sakai N, Yoshidome H, Shida T, Kimura F, Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M, et al. CXCR4/CXCL12 expression profile is associated with tumor microenvironment and clinical outcome of liver metastases of colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2012;29:101–10.
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM. Statistics Subcommittee of the NCIEWGoCD. REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Nat Clin Prac Oncol. 2005;2:416–22.
Barratt PL, Seymour MT, Stenning SP, Georgiades I, Walker C, Birbeck K, et al. DNA markers predicting benefit from adjuvant fluorouracil in patients with colon cancer: a molecular study. Lancet. 2002;360:1381–91.
Wang SC, Lin JK, Wang HS, Yang SH, Li AF, Chang SC. Nuclear expression of CXCR4 is associated with advanced colorectal cancer. Int J Color Dis. 2010;25:1185–91.
Rosenberg R, Engel J, Bruns C, Heitland W, Hermes N, Jauch KW, et al. The prognostic value of lymph node ratio in a population-based collective of colorectal cancer patients. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1070–8.
Zhuo W, Jia L, Song N, Lu XA, Ding Y, Wang X, et al. The CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine pathway: a novel axis regulates lymphangiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:5387–98.
Heckmann D, Maier P, Laufs S, Wenz F, Zeller WJ, Fruehauf S, et al. CXCR4 expression and treatment with SDF-1alpha or Plerixafor modulate proliferation and chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells. Transl Oncol. 2013;6:124–32.
Ierano C, Giuliano P, D’Alterio C, Cioffi M, Mettivier V, Portella L, et al. A point mutation (G574A) in the chemokine receptor CXCR4 detected in human cancer cells enhances migration. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1228–37.
Rubie C, Frick VO, Ghadjar P, Wagner M, Justinger C, Faust SK, et al. CXC receptor-4 mRNA silencing abrogates CXCL12-induced migration of colorectal cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2011;9:22.
Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, Wanzeck J, Wojakowski W, Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005;23:879–94.
D’Alterio C, Avallone A, Tatangelo F, Delrio P, Pecori B, Cella L, et al. A prognostic model comprising pT stage, N status, and the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 powerfully predicts outcome in neoadjuvant resistant rectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:379–90.
Kekelidze M, D’Errico L, Pansini M, Tyndall A, Hohmann J. Colorectal cancer: current imaging methods and future perspectives for the diagnosis, staging and therapeutic response evaluation. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:8502–14.
Bertelsen CA, Neuenschwander AU, Jansen JE, Wilhelmsen M, Kirkegaard-Klitbo A, Tenma JR, et al. Disease-free survival after complete mesocolic excision compared with conventional colon cancer surgery: a retrospective, population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:161–8.
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. New Engl J Med. 2004;350:2343–51.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Norwegian Cancer Society grant (grant no. 422146). The study was also supported by Haraldsplass Deaconess Hospital and Health Region West. We thank Christine Drengenes, Benedikte Rosenlund and Yvonne Muller for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
(PDF 24050 kb)
Online Resource 2
(PDF 21998 kb)
Online Resource 3
(XLSX 12 kb)
Online Resource 4
(XLSX 12 kb)
Online Resource 5
(XLSX 12 kb)
Online Resource 6
(XLSX 13 kb)
Online Resource 7
(XLSX 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanisavljević, L., Aßmus, J., Storli, K.E. et al. CXCR4, CXCL12 and the relative CXCL12-CXCR4 expression as prognostic factors in colon cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 7441–7452 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4591-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4591-8