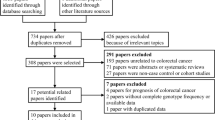
Abstract
Interleukin (IL)-6 and the downstream Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway have previously been reported to be important in the development of colorectal cancer (CRC), and several studies have shown the relationship between the polymorphisms of related genes in this pathway with the risk of CRC. However, the findings of these related studies are inconsistent. Moreover, there has no systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the relationship between genetic variants in IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and CRC susceptibility. Hence, we conducted a meta-analysis to explore the relationship between polymorphisms in IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway genes and CRC risk. Eighteen eligible studies with a total of 13,795 CRC cases and 18,043 controls were identified by searching PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library databases for the period up to September 15, 2015. Odds ratios (ORs) and their 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were used to calculate the strength of the association. Our results indicated that IL-6 genetic variants in allele additive model (OR = 1.05, 95 % CI = 1.00, 1.09) and JAK2 genetic variants (OR = 1.40, 95 % CI = 1.15, 1.65) in genotype recessive model were significantly associated with CRC risk. Moreover, the pooled data revealed that IL-6 rs1800795 polymorphism significantly increased the risk of CRC in allele additive model in Europe (OR = 1.07, 95 % CI = 1.01, 1.14). In conclusion, the present findings indicate that IL-6 and JAK2 genetic variants are associated with the increased risk of CRC while STAT3 genetic variants not. We need more well-designed clinical studies covering more countries and population to definitively establish the association between genetic variants in IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and CRC susceptibility.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29. doi:10.3322/caac.20138.
Jawad N, Direkze N, Leedham SJ. Inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. Recent results in cancer research Fortschritte der Krebsforschung Progres dans les recherches sur le cancer. 2011;185:99–115. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-03503-6_6.
Wang SW, Hu J, Guo QH, Zhao Y, Cheng JJ, Zhang DS, et al. AZD1480, a JAK inhibitor, inhibits cell growth and survival of colorectal cancer via modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(5):1991–8. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3477.
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang QC, Zhang YJ, et al. Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2008;10(3):287–97.
Gordziel C, Bratsch J, Moriggl R, Knosel T, Friedrich K. Both STAT1 and STAT3 are favourable prognostic determinants in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(1):138–46. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.274.
Candido J, Hagemann T. Cancer-related inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33 Suppl 1:S79–84. doi:10.1007/s10875-012-9847-0.
Yu Y, Wang W, Zhai S, Dang S, Sun M. IL6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(8):8457–63. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1699-4.
Wang SW, Sun YM. The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway: potential therapeutic strategies in treating colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2014;44(4):1032–40. doi:10.3892/ijo.2014.2259 (Review).
Landi S, Moreno V, Gioia-Patricola L, Guino E, Navarro M, de Oca J, et al. Association of common polymorphisms in inflammatory genes interleukin (IL)6, IL8, tumor necrosis factor alpha, NFKB1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63(13):3560–6.
Theodoropoulos G, Papaconstantinou I, Felekouras E, Nikiteas N, Karakitsos P, Panoussopoulos D, et al. Relation between common polymorphisms in genes related to inflammatory response and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2006;12(31):5037–43.
Gaustadnes M, Orntoft TF, Jensen JL, Torring N. Validation of the use of DNA pools and primer extension in association studies of sporadic colorectal cancer for selection of candidate SNPs. Hum Mutat. 2006;27(2):187–94. doi:10.1002/humu.20248.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Lewis CM, Knight J. Introduction to genetic association studies. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2012;2012(3):297–306. doi:10.1101/pdb.top068163.
Gunter MJ, Canzian F, Landi S, Chanock SJ, Sinha R, Rothman N. Inflammation-related gene polymorphisms and colorectal adenoma. Canc Epidemiol Biomark Prevent Pub Am Assoc Canc Res, cosponsored by Am Soc Prev Oncol. 2006;15(6):1126–31. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0042.
Vogel U, Christensen J, Dybdahl M, Friis S, Hansen RD, Wallin H, et al. Prospective study of interaction between alcohol, NSAID use and polymorphisms in genes involved in the inflammatory response in relation to risk of colorectal cancer. Mutat Res. 2007;624(1-2):88–100. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.04.006.
Slattery ML, Wolff RK, Herrick JS, Caan BJ, Potter JD. IL6 genotypes and colon and rectal cancer. Canc Cause Contr CCC. 2007;18(10):1095–105. doi:10.1007/s10552-007-9049-x.
Wilkening S, Tavelin B, Canzian F, Enquist K, Palmqvist R, Altieri A, et al. Interleukin promoter polymorphisms and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(6):1202–6. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn101.
Kury S, Buecher B, Robiou-du-Pont S, Scoul C, Colman H, Le Neel T, et al. Low-penetrance alleles predisposing to sporadic colorectal cancers: a French case-controlled genetic association study. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:326. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-8-326.
Vasku A, Vokurka J, Bienertova-Vasku J. Obesity-related genes variability in Czech patients with sporadic colorectal cancer: preliminary results. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24(3):289–94. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0553-6.
Tsilidis KK, Helzlsouer KJ, Smith MW, Grinberg V, Hoffman-Bolton J, Clipp SL, et al. Association of common polymorphisms in IL10, and in other genes related to inflammatory response and obesity with colorectal cancer. Canc Cause Contr CCC. 2009;20(9):1739–51. doi:10.1007/s10552-009-9427-7.
Cacev T, Jokic M, Loncar B, Krizanac S, Kapitanovic S. Interleukin-6-174 G/C polymorphism is not associated with IL-6 expression and susceptibility to sporadic colon cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2010;29(4):177–82. doi:10.1089/dna.2009.0950.
Hawken SJ, Greenwood CM, Hudson TJ, Kustra R, McLaughlin J, Yang Q, et al. The utility and predictive value of combinations of low penetrance genes for screening and risk prediction of colorectal cancer. Hum Genet. 2010;128(1):89–101. doi:10.1007/s00439-010-0828-1.
Ognjanovic S, Yamamoto J, Saltzman B, Franke A, Ognjanovic M, Yokochi L, et al. Serum CRP and IL-6, genetic variants and risk of colorectal adenoma in a multiethnic population. Canc Cause Contr CCC. 2010;21(7):1131–8. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9540-7.
Abuli A, Fernandez-Rozadilla C, Alonso-Espinaco V, Munoz J, Gonzalo V, Bessa X, et al. Case-control study for colorectal cancer genetic susceptibility in EPICOLON: previously identified variants and mucins. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:339. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-339.
Azimzadeh P, Romani S, Mohebbi SR, Kazemian S, Vahedi M, Almasi S, et al. Interleukin-16 (IL-16) gene polymorphisms in Iranian patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis JGLD. 2011;20(4):371–6.
Azimzadeh P, Romani S, Mohebbi SR, Mahmoudi T, Vahedi M, Fatemi SR, et al. Association of polymorphisms in microRNA-binding sites and colorectal cancer in an Iranian population. Canc Genet. 2012;205(10):501–7. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2012.05.013.
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA, Bondurant KL, Wolff RK. JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2013;52(2):155–66. doi:10.1002/mc.21841.
Blauvelt A, Prinz JC, Gottlieb AB, Kingo K, Sofen H, Ruer-Mulard M, et al. Secukinumab administration by pre-filled syringe: efficacy, safety and usability results from a randomized controlled trial in psoriasis (FEATURE). Br J Dermatol. 2015;172(2):484–93. doi:10.1111/bjd.13348.
Li Y, de Haar C, Chen M, Deuring J, Gerrits MM, Smits R, et al. Disease-related expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 signalling pathway in ulcerative colitis and ulcerative colitis-related carcinogenesis. Gut. 2010;59(2):227–35. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.184176.
Chung YC, Chang YF. Serum interleukin-6 levels reflect the disease status of colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2003;83(4):222–6. doi:10.1002/jso.10269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary table 1
Characteristics of included SNPs in IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway. (DOCX 35 kb)
Supplementary table 2
The quality assessment of included trials. (DOCX 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, W. Genetic variants in IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and the risk of CRC. Tumor Biol. 37, 6561–6569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4529-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4529-1