Abstract
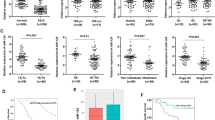
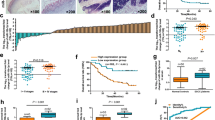
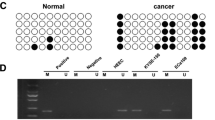
MiRNAs regulate gene expression and play pivotal roles in biological processes. MiRNAs can be inactivated by epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA hypermethylation of CpG sites within CpG islands. Here, we investigated the role and methylation status of miR-203a and miR-203b in esophageal cancer cell lines and primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tumors and further elucidate the role of both miRNAs in the prognosis of ESCC. The present study revealed a strong downregulation of miR-203a and miR-203b in esophageal cancer cell lines and primary ESCC samples. Treatment of esophageal cancer cells with demethylating agent 5-Aza-dC led to increased miR-203a and miR-203b expression, confirming the epigenetic regulation of both miRNAs. The inhibition of proliferation and invasiveness in esophageal cancer cells after treated with 5-Aza-dC or transfected with miR-203a or miR-203b mimics, suggesting the tumor suppressor role of both miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Furthermore, the critical CpG sites of miR-203a and miR-203b were found to be located in proximal promoter region, and the proximal promoter hypermethylation of both miRNAs was found to influence transcriptional activity. Downregulation and hypermethylation of miR-203a and miR-203b were associated with TNM stage, pathological differentiation, and lymph node metastasis. ESCC patients in stages III and IV, with reduced expression of miR-203a or hypermethylation of miR-203a or miR-203b, demonstrated poor patient survival. In summary, our results suggest that miR-203a and miR-203b may function as tumor-suppressive miRNAs that are inactivated through proximal promoter hypermethylation and miR-203a expression and methylation may be useful prognostic marker in ESCC patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose JN, Packham G. MicroRNAs: key players in carcinogenesis and novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35:339–47.
Oom AL, Humphries BA, Yang C. MicroRNAs: novel players in cancer diagnosis and therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:959461.
Xue J, Niu J, Wu J, Wu ZH. MicroRNAs in cancer therapeutic response: friend and foe. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5:730–43.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:15524–9.
Tian L, Li M, Ge J, Guo Y, Sun Y, Liu M, et al. MiR-203 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and can suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of tumours. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:5953–63.
Liu Y, Ren F, Rong M, Luo Y, Dang Y, Chen G. Association between underexpression of microrna-203 and clinicopathological significance in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:62.
Lee SA, Kim JS, Park SY, Kim HJ, Yu SK, Kim CS, et al. miR-203 downregulates Yes-1 and suppresses oncogenic activity in human oral cancer cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015.
Xu M, Gu M, Zhang K, Zhou J, Wang Z, Da J. miR-203 inhibition of renal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting of FGF2. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10:24.
Liao H, Bai Y, Qiu S, Zheng L, Huang L, Liu T, et al. MiR-203 downregulation is responsible for chemoresistance in human glioblastoma by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via SNAI2. Oncotarget. 2015;6:8914–28.
Mao L, Zhang Y, Mo W, Yu Y, Lu H. BANF1 is downregulated by IRF1-regulated microRNA-203 in cervical cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0117035.
Qu Y, Li WC, Hellem MR, Rostad K, Popa M, McCormack E, et al. MiR-182 and miR-203 induce mesenchymal to epithelial transition and self-sufficiency of growth signals via repressing SNAI2 in prostate cells. Int J Cancer. 2013;133:544–55.
Tang G, Wu J, Xiao G, Huo L. miR-203 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide and inhibits glioma cell invasion by targeting E2F3. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:2838–44.
Chang X, Sun Y, Han S, Zhu W, Zhang H, Lian S. MiR-203 inhibits melanoma invasive and proliferative abilities by targeting the polycomb group gene BMI1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456:361–6.
Zhou X, Xu G, Yin C, Jin W, Zhang G. Down-regulation of miR-203 induced by Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting CASK. Oncotarget. 2014;5:11631–40.
Zhou M, Chen J, Zhou L, Chen W, Ding G, Cao L. Pancreatic cancer derived exosomes regulate the expression of TLR4 in dendritic cells via miR-203. Cell Immunol. 2014;292:65–9.
Wang N, Liang H, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhang S, Pan Y, et al. miR-203 suppresses the proliferation and migration and promotes the apoptosis of lung cancer cells by targeting SRC. PLoS One. 2014;9, e105570.
Chen Z, Li D, Cheng Q, Ma Z, Jiang B, Peng R, et al. MicroRNA-203 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of U251 glioblastoma cells by directly targeting PLD2. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9:503–8.
Ralfkiaer U, Hagedorn PH, Bangsgaard N, Løvendorf MB, Ahler CB, Svensson L, et al. Diagnostic microRNA profiling in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood. 2011;118:5891–900.
Wang S, Zhao X, Wang J, Wen Y, Zhang L, Wang D, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-203 is associated with advanced tumor progression and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30:681.
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V, Petrocca F, Casalini P, et al. MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8699–707.
Li Z, Du L, Dong Z, Yang Y, Zhang X, Wang L, et al. MiR-203 suppresses ZNF217 upregulation in colorectal cancer and its oncogenicity. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0116170.
Yantiss RK, Goodarzi M, Zhou XK, Rennert H, Pirog EC, Banner BF, et al. Clinical, pathologic, and molecular features of early-onset colorectal carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:572–82.
Taipaleenmäki H, Browne G, Akech J, Zustin J, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, et al. Targeting of Runx2 by miR-135 and miR-203 impairs progression of breast cancer and metastatic bone disease. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1433–44.
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C, Shi Y. MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31:58.
Zhang Z, Zhang B, Li W, Fu L, Fu L, Zhu Z, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-203 upregulates SNAI2 and contributes to the invasiveness of malignant breast cancer cells. Genes Cancer. 2011;2:782–91.
Saini S, Arora S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Chen Y, Deng G, et al. Curcumin modulates microRNA-203-mediated regulation of the Src-Akt axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011;4:1698–709.
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Calin GA, Fassan M, Bassi P, et al. Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol. 2007;25:387–92.
Joyce CE, Zhou X, Xia J, Ryan C, Thrash B, Menter A, et al. Deep sequencing of small RNAs from human skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis miRNAome. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20:4025–40.
Yan B, Guo JT, Zhu CD, Zhao LH, Zhao JL. miR-203b: a novel regulator of MyoD expression in tilapia skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol. 2013;216:447–51.
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S, Imoto I, Inazawa J. miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:766–76.
Chim CS, Wan TS, Wong KY, Fung TK, Drexler HG, Wong KF. Methylation of miR-34a, miR-34b/c, miR-124-1 and miR-203 in Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. J Transl Med. 2011;9:197.
Huang YW, Kuo CT, Chen JH, Goodfellow PJ, Huang TH, Rader JS, et al. Hypermethylation of miR-203 in endometrial carcinomas. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;133:340–5.
Diao Y, Guo X, Jiang L, Wang G, Zhang C, Wan J, et al. miR-203, a tumor suppressor frequently down-regulated by promoter hypermethylation in rhabdomyosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:529–39.
Botezatu A, Goia-Rusanu CD, Iancu IV, Huica I, Plesa A, Socolov D, et al. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between microRNA-124a, −34b and −203 gene methylation and cervical oncogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2011;4:121–8.
Chim CS, Wong KY, Leung CY, Chung LP, Hui PK, Chan SY, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of the hsa-miR-203 in haematological malignancies. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:2760–7.
Jamali Z, Asl Aminabadi N, Attaran R, Pournagiazar F, Ghertasi Oskouei S, Ahmadpour F. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:321–31.
Nagaraja V, Eslick GD. Forthcoming prognostic markers for esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;5:67–76.
Guohong Z, Min S, Duenmei W, Songnian H, Min L, Jinsong L, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of oesophageal cancer in high-incidence areas of southern and northern China. PLoS One. 2010;5, e9668.
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Srovnal J, Zemanova M, Harustiak T, Ehrmann J, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of miR-21, miR-29c, miR-148 and miR-203 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10:42.
Chen X, Hu H, Guan X, Xiong G, Wang Y, Wang K, et al. CpG island methylation status of miRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:1607–13.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Sasaki M, Anast J, Bassett W, Kawakami T, Sakuragi N, Dahiya R. Bisulfite conversion-specific and methylation-specific PCR: a sensitive technique for accurate evaluation of CpG methylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;309:305–9.
Yu L, Liu C, Vandeusen J, Becknell B, Dai Z, Wu YZ, et al. Global assessment of promoter methylation in a mouse model of cancer identifies ID4 as a putative tumor-suppressor gene in human leukemia. Nat Genet. 2005;37:265–74.
Zhang K, Dai L, Zhang B, Xu X, Shi J, Fu L, et al. miR-203 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F1 and causes G1 arrest in esophageal cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230:903–10.
Okumura T, Shimada Y, Moriyama M, Takei Y, Omura T, Sekine S, et al. MicroRNA-203 inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with restored epithelial tissue architecture in vivo. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:1923–32.
Zhang F, Yang Z, Cao M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen X, et al. MiR-203 suppresses tumor growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through repressing Ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;342:121–9.
Takeshita N, Mori M, Kano M, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Hanari N, et al. miR-203 inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating LASP1. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:1653–61.
He J, Deng Y, Yang G, Xie W. MicroRNA-203 down-regulation is associated with unfavorable prognosis in human glioma. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108:121–5.
Ikenaga N, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J, Kayashima T, Sakai H, et al. MicroRNA-203 expression as a new prognostic marker of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:3120–8.
Chen HY, Han ZB, Fan JW, Xia J, Wu JY, Qiu GQ, et al. miR-203 expression predicts outcome after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic liver. Med Oncol. 2012;29:1859–65.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients for taking part in this study. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (no. 81472335).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81472335)
Yibing Liu and Zhiming Dong contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Clinicopathologic characteristics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cases (DOCX 15 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Primer sequences and reaction conditions of miR-203a and miR-203b used in this study (DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Dong, Z., Liang, J. et al. Methylation-mediated repression of potential tumor suppressor miR-203a and miR-203b contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development. Tumor Biol. 37, 5621–5632 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4432-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4432-9