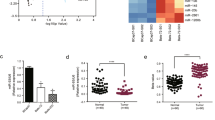
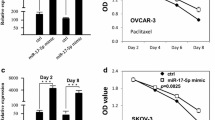
Abstract
Patients with cervical cancer show minimal clinical response to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib, which targets the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The molecular mechanisms underlying sensitivity to gefitinib are unknown. The purpose of this study was to investigate the possible mechanism by which microRNA-221 (miR-221) affects sensitivity to gefitinib. We showed that miR-221 expression was significantly increased in cervical cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. Upregulation of miR-221 expression in cervical cancer cells decreased PTEN expression levels, resulting in increased pAkt and BCL-2 expression. Importantly, gefitinib sensitivity was decreased by the upregulation of miR-221, which was blocked by pcDNA-PTEN co-transfection or by the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002. These data suggest that miR-221 can reduce the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to gefitinib through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. miR-221 represents a potential target to increase the sensitivity to gefitinib in cervical cancer treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NCCN:
-
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
- TKIs:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancers
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- MMP-2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 2
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MET:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Rose PG, Bundy BN, Watkins EB, Thigpen JT, Deppe G, Maiman MA, et al. Concurrent cisplatin-based radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(15):1144–53.
Thomas GM. Improved treatment for cervical cancer—concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(15):1198–200.
Zighelboim I, Wright JD, Gao F, Case AS, Massad LS, Mutch DG, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of topotecan, cisplatin and bevacizumab for recurrent or persistent cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130(1):64–8.
Wang CC, Chou HH, Yang LY, Lin H, Liou WS, Tseng CW, et al. A randomized trial comparing concurrent chemoradiotherapy with single-agent cisplatin versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced cervical cancer: an Asian Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;137(3):462–7.
Lorusso D, Petrelli F, Coinu A, Raspagliesi F, Barni S. A systematic review comparing cisplatin and carboplatin plus paclitaxel-based chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;133(1):117–23.
Manci N, Marchetti C, Di Tucci C, Giorgini M, Esposito F, Palaia I, et al. A prospective phase II study of topotecan (Hycamtin®) and cisplatin as neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;122(2):285–90.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–39.
Kersemaekers AM, Fleuren GJ, Kenter GG, Van den Broek LJ, Uljee SM, Hermans J, et al. Oncogene alterations in carcinomas of the uterine cervix: overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor is associated with poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5(3):577–86.
Mathur SP, Mathur RS, Rust PF, Young RC. Human papilloma virus (HPV)-E6/E7 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) protein levels in cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Am J Reprod Immunol. 2001;46(4):280–7.
Goncalves A, Fabbro M, Lhommé C, Gladieff L, Extra JM, Floquet A, et al. A phase II trial to evaluate gefitinib as second- or third-line treatment in patients with recurring locoregionally advanced or metastatic cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;108(1):42–6.
An J, Zhu X, Wang H, Jin X. A dynamic interplay between alternative polyadenylation and microRNA regulation: implications for cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. 2013;43(4):995–1001.
Ke J, Zhao Z, Hong SH, Bai S, He Z, Malik F, et al. Role of microRNA221 in regulating normal mammary epithelial hierarchy and breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(6):3709–21.
Fu X, Wang Q, Chen J, Huang X, Chen X, Cao L, et al. Clinical significance of miR-221 and its inverse correlation with p27Kip1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(5):3029–35.
Sarkar S, Dubaybo H, Ali S, Goncalves P, Kollepara SL, Sethi S, et al. Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2), and PUMA. Am J Cancer Res. 2013;3(5):465–77.
Lau MT, Klausen C, Leung PC. E-cadherin inhibits tumor cell growth by suppressing PI3K/Akt signaling via β-catenin-Egr1-mediated PTEN expression. Oncogene. 2011;30(24):2753–66.
Ruan K, Fang X, Ouyang G. MicroRNAs: novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009;285(2):116–26.
Song X, Shi B, Huang K, Zhang W. miR-133a inhibits cervical cancer growth by targeting EGFR. Oncol Rep. 2015. doi:10.3892/or.2015.4101.
Wang LQ, Zhang Y, Yan H, Liu KJ, Zhang S. MicroRNA-373 functions as an oncogene and targets YOD1 gene in cervical cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;459(3):515–20.
Yang F, Wang W, Zhou C, Xi W, Yuan L, Chen X, et al. MiR-221/222 promote human glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis by targeting TIMP2. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3763–73.
Bae HJ, Jung KH, Eun JW, Shen Q, Kim HS, Park SJ, et al. MicroRNA-221 governs tumor suppressor HDAC6 to potentiate malignant progression of liver cancer. J Hepatol. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.03.019.
Gocze K, Gombos K, Juhasz K, Kovacs K, Kajtar B, Benczik M, et al. Unique microRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(6):2561–7.
Sun Y, St Clair DK, Fang F, Warren GW, Rangnekar VM, Crooks PA, et al. The radiosensitization effect of parthenolide in prostate cancer cells is mediated by nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition and enhanced by the presence of PTEN. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6(9):2477–86.
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(8):627–44.
Cui B, Zheng B, Zhang X, Stendahl U, Andersson S, Wallin KL. Mutation of PIK3CA: possible risk factor for cervical carcinogenesis in older women. Int J Oncol. 2009;34(2):409–16.
Shultz JC, Goehe RW, Wijesinghe DS, Murudkar C, Hawkins AJ, Shay JW, et al. Alternative splicing of caspase 9 is modulated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway via phosphorylation of SRp30a. Cancer Res. 2010;70(22):9185–96.
Siddiqa A, Long LM, Li L, Marciniak RA, Kazhdan I. Expression of HER-2 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells modulates anti-apoptotic proteins survivin and Bcl-2 via the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) and phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) signalling pathways. BMC Cancer. 2008. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-8-129.
Zhang Z, Song T, Jin Y, Pan J, Zhang L, Wang L, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates MT1-MMP and MMP-2 synthesis in SiHa cells via both PI3-K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009;19(6):998–1003.
Chun-Zhi Z, Lei H, An-Ling Z, Yan-Chao F, Xiao Y, Guang-Xiu W, et al. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:367.
Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G, Nuovo G, Suh SS, Ngankeu A, et al. miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell. 2009;16(6):498–509.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(8):786–92.
Shih JY, Gow CH, Yang PC. EGFR mutation conferring primary resistance to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(2):207–8.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316(5827):1039–43.
Garofalo M, Romano G, Di Leva G, Nuovo G, Jeon YJ, Ngankeu A, et al. EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat Med. 2011;18(1):74–82.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a foundation of the Heilongjiang Provincial Educational Department, China (Grant No. 11551163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients prior to participation in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Wang, L., Li, C. et al. MicroRNA-221 targets PTEN to reduce the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to gefitinib through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Tumor Biol. 37, 3939–3947 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4247-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4247-8