Abstract
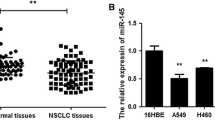
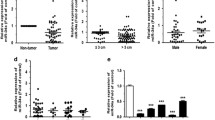
The cases of larynx carcinoma (LC) with poor prognosis largely result from the distal metastases of the primary tumor. Since microRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles during cancer metastases, determination of the involved miRNAs in the regulation of the LC metastases may provide novel therapeutic targets for LC treatment. Here, we studied the LC specimens from the patients and found that the levels of miR-138 were significantly decreased and the levels of ZEB2, a critical factor that regulates cancer cell invasiveness, were significantly increased in LC, compared to the paired normal larynx tissue. Metastatic LC appeared to contained lower levels of miR-138. Moreover, miR-138 and ZEB2 inversely correlated in LC specimens. Bioinformatics analyses showed that miR-138 targeted the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of ZEB2 mRNA to inhibit its translation, which was confirmed in a luciferase reporter assay. Further, miR-138 overexpression inhibited ZEB2-mediated cell invasiveness, while miR-138 depletion increased ZEB2-mediated cell invasiveness in LC cells. Together, our data suggest that miR-138 suppression in LC cells may promote ZEB2-mediated cancer metastases. Thus, miR-138 appears to be an intriguing therapeutic target to prevent metastases of LC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mojica-Manosa P, Reidy J, Wilson K, Douglas W. Larynx squamous cell carcinoma: concepts and future directions. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2004;13:99–112.
Hu Q, Tong S, Zhao X, Ding W, Gou Y, Xu K, et al. Periostin mediates TGF-beta-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:799–809.
Sa Y, Li C, Li H, Guo H. TIMP-1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin in fibroblasts to promote urethral scar formation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:2233–43.
Lan A, Qi Y, Du J. Akt2 mediates TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition by deactivating GSK3beta/snail signaling pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:368–82.
Teng Y, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Chen W, Li X. Id-1, a protein repressed by miR-29b, facilitates the TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:717–30.
Guo Y, Lang X, Lu Z, Wang J, Li T, Liao Y, et al. MiR-10b directly targets ZEB1 and PIK3CA to curb adenomyotic epithelial cell invasiveness via upregulation of E-cadherin and inhibition of Akt phosphorylation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:2169–80.
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T. E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28:151–66.
Di Leva G, Croce CM. MiRNA profiling of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013;23:3–11.
Pereira DM, Rodrigues PM, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CM. Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18:282–9.
Mei Q, Li F, Quan H, Liu Y, Xu H. Busulfan inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma through miR-200 family microRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2014;105:755–62.
Wang F, Xiao W, Sun J, Han D, Zhu Y. MiRNA-181c inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP9 activation via suppressing Akt phosphorylation in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:8653–8.
Liu G, Jiang C, Li D, Wang R, Wang W. MiRNA-34a inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP7 activation in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9801–6.
Mitomo S, Maesawa C, Ogasawara S, Iwaya T, Shibazaki M, Yashima-Abo A, et al. Downregulation of miR-138 is associated with overexpression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase protein in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:280–6.
Zhao X, Yang L, Hu J, Ruan J. MiR-138 might reverse multidrug resistance of leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2010;34:1078–82.
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, Xu S, Hu K, et al. MiR-138 suppressed nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:2495–506.
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H, Qi ZT. MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:1113–20.
Zhou X, Qi Y. PLGF inhibition impairs metastasis of larynx carcinoma through MMP3 downregulation. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9381–6.
Zhou X, Qi Y. Larynx carcinoma regulates tumor-associated macrophages through PLGF signaling. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10071.
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL. In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:329–33.
Xu C, Fu H, Gao L, Wang L, Wang W, Li J, et al. BCR-ABl/GATA1/miR-138 mini circuitry contributes to the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 2014;33:44–54.
Long L, Huang G, Zhu H, Guo Y, Liu Y, Huo J. Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting TWIST2. J Transl Med. 2013;11:275.
Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhao M, Lv Z, Zhang X, Qin X, et al. MiR-138 inhibits tumor growth through repression of EZH2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31:56–65.
Gao Y, Fan X, Li W, Ping W, Deng Y, Fu X. MiR-138-5p reverses gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via negatively regulating G protein-coupled receptor 124. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;446:179–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
For the use of the clinical materials for research purposes, approval from the Institutional Research Ethics Committee was obtained.
Conflicts of interest
None
Informed consent
Patient’s consents were obtained.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Wang, J., Xie, J. et al. Role of miR-138 in the regulation of larynx carcinoma cell metastases. Tumor Biol. 37, 15601–15606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4244-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4244-y