Abstract
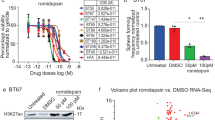
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) play a role in the tumorigenesis of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), whereas the underlying mechanism has not been elucidated. Here, we reported significantly higher HDAC6 levels in GBM from the patients. GBM cell growth was significantly inhibited by ACY-1215, a specific HDAC6 inhibitor. Further analyses show that HDAC6 may promote growth of GBM cells through inhibition of SMAD2 phosphorylation to downregulate p21. Thus, our data demonstrate a previously unrecognized regulation pathway in that HDAC6 increases GBM growth through attenuating transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) receptor signaling.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi G, Jiang G. The molecular mechanism of HDAC inhibitors in anticancer effects. Cell Mol Immunol. 2006;3:285–90.
Secrist JP, Zhou X, Richon VM. HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003;4:1422–7.
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB. Histone deacetylases (HDACS): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 2003;370:737–49.
Chen J, Huang Q, Wang F. Inhibition of FoxO1 nuclear exclusion prevents metastasis of glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:7195–200.
Li S, Gao Y, Ma W, Guo W, Zhou G, et al. EGFR signaling-dependent inhibition of glioblastoma growth by ginsenoside Rh2. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:5593–8.
Wang F, Xiao W, Sun J, Han D, Zhu Y: MiRNA-181c inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP9 activation via suppressing Akt phosphorylation in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol 2014
Bezecny P. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in glioblastoma: pre-clinical and clinical experience. Med Oncol. 2014;31:985.
Adamopoulou E, Naumann U. HDAC inhibitors and their potential applications to glioblastoma therapy. Oncoimmunol. 2013;2:e25219.
Jin H, Liang L, Liu L, Deng W, Liu J. HDAC inhibitor DWP0016 activates p53 transcription and acetylation to inhibit cell growth in U251 glioblastoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114:1498–509.
Asklund T, Kvarnbrink S, Holmlund C, Wibom C, Bergenheim T, Henriksson R, et al. Synergistic killing of glioblastoma stem-like cells by bortezomib and HDAC inhibitors. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:2407–13.
Bajbouj K, Mawrin C, Hartig R, Schulze-Luehrmann J, Wilisch-Neumann A, Roessner A, et al. P53-dependent antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of trichostatin A (TSA) in glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 2012;107:503–16.
Sawa H, Murakami H, Ohshima Y, Murakami M, Yamazaki I, Tamura Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors such as sodium butyrate and trichostatin A inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion from human glioblastoma cells. Brain Tumour Pathol. 2002;19:77–81.
Svechnikova I, Almqvist PM, Ekstrom TJ. HDAC inhibitors effectively induce cell type-specific differentiation in human glioblastoma cell lines of different origin. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:821–7.
Massague J. TGFbeta in cancer. Cell. 2008;134:215–30.
Xiao X, Gaffar I, Guo P, Wiersch J, Fischbach S, Peirish L, et al. M2 macrophages promote beta-cell proliferation by up-regulation of SMAD7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E1211–20.
Yi JJ, Barnes AP, Hand R, Polleux F, Ehlers MD. TGF-beta signaling specifies axons during brain development. Cell. 2010;142:144–57.
Ewen ME, Sluss HK, Whitehouse LL, Livingston DM. TGF beta inhibition of Cdk4 synthesis is linked to cell cycle arrest. Cell. 1993;74:1009–20.
Naka K, Hoshii T, Muraguchi T, Tadokoro Y, Ooshio T, Kondo Y, et al. TGF-beta-FOXO signalling maintains leukaemia-initiating cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2010;463:676–80.
Xiao X, Wiersch J, El-Gohary Y, Guo P, Prasadan K, Paredes J, et al. TGFbeta receptor signaling is essential for inflammation-induced but not beta-cell workload-induced beta-cell proliferation. Diab. 2013;62:1217–26.
Eichhorn PJ, Rodon L, Gonzalez-Junca A, Dirac A, Gili M, Martinez-Saez E, et al. USP15 stabilizes TGF-beta receptor i and promotes oncogenesis through the activation of TGF-beta signaling in glioblastoma. Nat Med. 2012;18:429–35.
Zhang M, Kleber S, Rohrich M, Timke C, Han N, Tuettenberg J. Blockade of TGF-beta signaling by the TGFbetaR-I kinase inhibitor LY2109761 enhances radiation response and prolongs survival in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7155–67.
Grzmil M, Morin Jr P, Lino MM, Merlo A, Frank S, Wang Y, et al. MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 regulates SMAD2-dependent TGF-beta signaling pathway in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2392–402.
Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA, et al. TGF-beta receptor inhibitors target the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:655–68.
Penuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sanchez RM, Folch G, Barba I, Cuartas I, et al. TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating cell self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:315–27.
Emori T, Kitamura K, Okazaki K. Nuclear Smad7 overexpressed in mesenchymal cells acts as a transcriptional corepressor by interacting with HDAC-1 and E2F to regulate cell cycle. Biol Open. 2012;1:247–60.
Ehnert S, Zhao J, Pscherer S, Freude T, Dooley S, Kolk A, et al. Transforming growth factor beta1 inhibits bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-2 and BMP-7 signaling via upregulation of Ski-related novel protein N (SnoN): possible mechanism for the failure of bmp therapy. BMC Med. 2012;10:101.
Cho JS, Moon YM, Park IH, Um JY, Moon JH, Park SJ, et al. Epigenetic regulation of myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix production in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012;42:872–82.
Barter MJ, Pybus L, Litherland GJ, Rowan AD, Clark IM, Edwards DR, et al. HDAC-mediated control of ERK- and PI3K-dependent TGF-beta-induced extracellular matrix-regulating genes. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:602–12.
Glenisson W, Castronovo V, Waltregny D. Histone deacetylase 4 is required for TGFbeta1-induced myofibroblastic differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1572–82.
Qiu P, Ritchie RP, Gong XQ, Hamamori Y, Li L. Dynamic changes in chromatin acetylation and the expression of histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases regulate the SM22alpha transcription in response to Smad3-mediated TGFbeta1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;348:351–8.
Bai S, Cao X. A nuclear antagonistic mechanism of inhibitory Smads in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4176–82.
Santo L, Hideshima T, Kung AL, Tseng JC, Tamang D, Yang M, et al. Preclinical activity, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties of a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, ACY-1215, in combination with bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;119:2579–89.
Huang S, Liao Q, Li L, Xin D. PTTG1 inhibits SMAD3 in prostate cancer cells to promote their proliferation. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6265–70.
Zhang G, Zhao Q, Yu S, Lin R, Yi X: Pttg1 inhibits TGFbeta signaling in breast cancer cells to promote their growth. Tumour Biol 2014 in press
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shun Li and Xiao Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Liu, X., Chen, X. et al. Histone deacetylase 6 promotes growth of glioblastoma through inhibition of SMAD2 signaling. Tumor Biol. 36, 9661–9665 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3747-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3747-x