Abstract
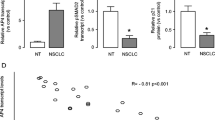
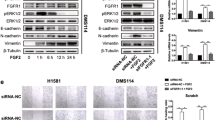
The molecular regulation of metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains not completely defined. Here we showed significant higher MMP26 in the resected NSCLC than adjacent healthy tissue from the patients. Moreover, a strong correlation between MMP26 and the phosphorylated fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) was detected. To examine the causal relationship between activated FGFR signaling and MMP26, we studied a human NSCLC cell line, A549. We found that FGF1-induced FGFR1 phosphorylation in A549 cells activated MMP26, resulting in an increase in cancer invasiveness. Inhibition of FGFR1 phosphorylation abolished FGF1-stimulated MMP26 activation, suggesting that activation of FGFR signaling pathway in NSCLC promotes cancer metastasis through MMP26. To define the signal transduction cascades downstream of FGFR1 activation for MMP26 activation, we used specific inhibitors for PI3K, ERK/MAPK, and JNK, respectively, to the FGF1-stimulated A549 cells. We found that only inhibition of JNK significantly decreased the activation of MMP26 in response to FGF1 stimulation, suggesting that activation of FGFR1 signaling may activate JNK to activate MMP26 in NSCLC. Our study thus highlights FGFR signaling pathway and MMP26 as novel therapeutic targets for NSCLC therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarogoulidis K, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Boutsikou E, Machairiotis N, Tsakiridis K, et al. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (nsclc). J Thorac Dis. 2013;5:S389–96.
Mitsudomi T, Suda K, Yatabe Y. Surgery for nsclc in the era of personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:235–44.
Pallis AG, Syrigos KN. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of nsclc. Lung Cancer. 2013;80:120–30.
Jian H, Zhao Y, Liu B, Lu S. Sema4b inhibits mmp9 to prevent metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11051–6.
Pei J, Lou Y, Zhong R, Han B. Mmp9 activation triggered by epidermal growth factor induced foxo1 nuclear exclusion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6673–8.
Takaishi H, Kimura T, Dalal S, Okada Y, D’Armiento J. Joint diseases and matrix metalloproteinases: a role for mmp-13. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2008;9:47–54.
Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (mmp-1, mmp-13) genes in arthritis: integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. 2002;4:157–64.
Balbin M, Pendas AM, Uria JA, Jimenez MG, Freije JP, Lopez-Otin C. Expression and regulation of collagenase-3 (mmp-13) in human malignant tumors. APMIS. 1999;107:45–53.
Li D. Peaking of mmp-26 and timp-4 marks invasive transition in prostate cancer. Cell Res. 2006;16:741.
Yamamoto H, Vinitketkumnuen A, Adachi Y, Taniguchi H, Hirata T, Miyamoto N, et al. Association of matrilysin-2 (mmp-26) expression with tumor progression and activation of mmp-9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:2353–60.
Zhang Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Lin Y, Tan Y, Fang X, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer invasion and metastasis promoted by mmp-26. Mol Med Rep. 2011;4:1201–9.
Li L, Mei TH, Zhou XD, Zhang XG. Expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase (mmp)-26 protein in non-small cell lung cancer. Ai Zheng. 2009;28:60–3.
Friesel R, Maciag T. Fibroblast growth factor prototype release and fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:748–54.
Jaye M, Schlessinger J, Dionne CA. Fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases: molecular analysis and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1135:185–99.
Fujimoto J, Hori M, Ichigo S, Tamaya T. Expressions of the fibroblast growth factor family (fgf-1, −2 and −4) mrna in endometrial cancers. Tumour Biol. 1996;17:226–33.
Soundararajan P, Fawcett JP, Rafuse VF. Guidance of postural motoneurons requires mapk/erk signaling downstream of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. J Neurosci. 2010;30:6595–606.
Kuslak SL, Marker PC. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling through mek-erk is required for prostate bud induction. Differentiation. 2007;75:638–51.
Williamson AJ, Dibling BC, Boyne JR, Selby P, Burchill SA. Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced cell death is effected through sustained activation of p38mapk and up-regulation of the death receptor p75ntr. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47912–28.
Kan M, Wu X, Wang F, McKeehan WL. Specificity for fibroblast growth factors determined by heparan sulfate in a binary complex with the receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15947–52.
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Prat A, Perez-Garcia J, Adamo B, Felip E, et al. Genomic aberrations in the fgfr pathway: Opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:552–63.
Parker BC, Engels M, Annala M, Zhang W. Emergence of fgfr family gene fusions as therapeutic targets in a wide spectrum of solid tumours. J Pathol. 2014;232:4–15.
Wu YM, Su F, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Khazanov N, Ateeq B, Cao X, et al. Identification of targetable fgfr gene fusions in diverse cancers. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:636–47.
Beau-Faller M, Gaub MP, Schneider A, Guerin E, Meyer N, Ducrocq X, et al. Allelic imbalance at loci containing fgfr, fgf, c-met and hgf candidate genes in non-small cell lung cancer sub-types, implication for progression. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:2538–47.
Ren M, Hong M, Liu G, Wang H, Patel V, Biddinger P, et al. Novel fgfr inhibitor ponatinib suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells overexpressing fgfr1. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:2181–90.
Volm M, Koomagi R, Mattern J, Stammler G. Prognostic value of basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor (fgfr-1) in patients with non-small cell lung carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 1997;33:691–3.
Lieber M, Smith B, Szakal A, Nelson-Rees W, Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type ii alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1976;17:62–70.
Kang M, Choi S, Jeong SJ, Lee SA, Kwak TK, Kim H, et al. Cross-talk between tgfbeta1 and egfr signalling pathways induces tm4sf5 expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem J. 2012;443:691–700.
Xiao X, Gaffar I, Guo P, Wiersch J, Fischbach S, Peirish L, et al. M2 macrophages promote beta-cell proliferation by up-regulation of smad7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E1211–20.
Xu Y, Xia W, Baker D, Zhou J, Cha HC, Voorhees JJ, et al. Receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase beta (rptp-beta) directly dephosphorylates and regulates hepatocyte growth factor receptor (hgfr/met) function. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:15980–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (81001036) and Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (2010Y066).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Deping Zhao and Yi Lu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Lu, Y., Yang, C. et al. Activation of FGF receptor signaling promotes invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 3637–3642 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3001-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3001-y