Abstract
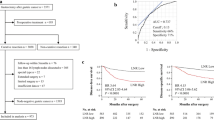
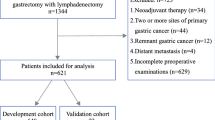
The aim of our study was to develop a new score system that might predict the probability of lymph node of gastric carcinoma. We studied the clinicopathological variables of 932 patients with gastric carcinoma admitted to the Department of Surgical Oncology at the First Hospital of China Medical University. Logistic analysis was performed to identify predictors. The hazard risk (HR) of variables obtained from logistic regression was used to construct a simple scoring system determined by an aggregate of the points assigned for each selected variable. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was created to analyze the specificity. Lymph node metastases were found in 644 (69.1 %) of 932 patients. After multivariate logistic regression analysis, tumor size, depth of invasion, and macroscopic types (P < 0.001) were selected as viable predictors to establish the scoring system. ROC curves were plotted to verify the accuracy of predicting score and other variables for both Lymph node stage (N stage) prediction. It showed that the predicting score system had a better specificity and sensitivity (65.71 % and 83.54 %, respectively). The current study suggests that a preoperative prediction system to identify the risk of lymph node metastasis is feasible. This model may be useful in preoperative counseling about the cost and benefit of systemic lymph node dissection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang L, Yang KH, Guan QL, Zhao P, Chen Y, Tian JH. Survival and recurrence free benefits with different lymphadenectomy for resectable gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2013;107(8):807–14. doi:10.1002/jso.23325.
Kunisaki C, Shimada H, Takahashi M, Nomura M, Matsuda G, Otsuka Y, etal. Implication of extended lymph node dissection stratified for advanced gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(5b):4181–6.
Deng J, Zhang R, Pan Y, Wang B, Wu L, Hao X, etal. N stages of the seventh edition of TNM classification are the most intensive variables for predictions of the overall survival of gastric cancer patients who underwent limited lymphadenectomy. Tumour Biol. 2013. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1428-1.
Kim SH, Ha TK, Kwon SJ. Evaluation of the 7th AJCC TNM Staging System in Point of Lymph Node Classification. J Gastric Cancer. 2011;11(2):94–100. doi:10.5230/jgc.2011.11.2.94.
Sierra A, Regueira FM, Hernandez-Lizoain JL, Pardo F, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Cienfuegos JA. Role of the extended lymphadenectomy in gastric cancer surgery: experience in a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10(3):219–26.
Enestvedt BK, Chandrasekhara V, Ginsberg GG. Endoscopic ultrasonographic assessment of gastric polyps and endoscopic mucosal resection. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2012;14(6):497–503. doi:10.1007/s11894-012-0292-2.
Ren G, Cai R, Zhang WJ, Ou JM, Jin YN, Li WH. Prediction of risk factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(20):3096–107. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3096.
Bollschweiler E, Boettcher K, Hoelscher AH, Sasako M, Kinoshita T, Maruyama K, etal. Preoperative assessment of lymph node metastases in patients with gastric cancer: evaluation of the Maruyama computer program. Br J Surg. 1992;79(2):156–60.
Bozzetti F. D2 lymphadenectomy (over-D1 dissection) for advanced gastric cancer is an evidence-based procedure. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15(11):2122–3. doi:10.1007/s11605-011-1612-9.
Degiuli M, Sasako M, Ponti A, Vendrame A, Tomatis M, Mazza C, etal. Randomized clinical trial comparing survival after D1 or D2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2014;101(2):23–31. doi:10.1002/bjs.9345.
Seevaratnam R, Bocicariu A, Cardoso R, Mahar A, Kiss A, Helyer L, etal. A meta-analysis of D1 versus D2 lymph node dissection. Gastric Cancer. 2012;15 Suppl 1:S60–9. doi:10.1007/s10120-011-0110-9.
Schwarz RE, Smith DD. Clinical impact of lymphadenectomy extent in resectable gastric cancer of advanced stage. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(2):317–28. doi:10.1245/s10434-006-9218-2.
Caletti G, Fusaroli P. The rediscovery of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in gastric cancer staging. Endoscopy. 2012;44(6):553–5. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1309770.
Bentrem D, Gerdes H, Tang L, Brennan M, Coit D. Clinical correlation of endoscopic ultrasonography with pathologic stage and outcome in patients undergoing curative resection for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(6):1853–9. doi:10.1245/s10434-006-9037-5.
Sendler A, Dittler HJ, Feussner H, Nekarda H, Bollschweiler E, Fink U, etal. Preoperative staging of gastric cancer as precondition for multimodal treatment. World J Surg. 1995;19(4):501–8.
Aurello P, Catracchia V, Petrucciani N, D'Angelo F, Leonardo G, Picchetto A, etal. What is the role of nodal ratio as a prognostic factor for gastric cancer nowadays? Comparison with new TNM staging system and analysis according to the number of resected nodes. Am Surg. 2013;79(5):483–91.
Medina-Franco H, Cabrera-Mendoza F, Almaguer-Rosales S, Guillen F, Suarez-Bobadilla YL, Sanchez-Ramon A. Lymph node ratio as a predictor of survival in gastric carcinoma. Am Surg. 2013;79(3):284–9.
Wang X, Appleby DH, Zhang X, Gan L, Wang JJ, Wan F. Comparison of three lymph node staging schemes for predicting outcome in patients with gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2013;100(4):505–14. doi:10.1002/bjs.9014.
Frindt G, Windhager EE. Ca2(+)-dependent inhibition of sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1990;258(3 Pt 2):F568–82.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81302129), Social Development Plan of Liaoning Province (2009412001_7), and the General Project of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (L2013291). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yanjun Zhang and Zhi Zhu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhu, Z., Sun, Z. et al. Preoperative predicting score of lymph node metastasis for gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 10437–10442 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2363-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2363-5