Abstract
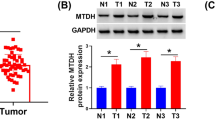
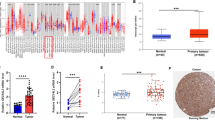
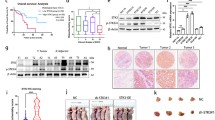
SYF2, also known as CCNDBP1-interactor or p29, is reported in pre-mRNA splicing and cell cycle progression. However, the role of SYF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) development remains elusive. In the present study, Western blot and immunohistochemistry assays demonstrated that SYF2 was overexpressed in ESCC tumor tissues and cell lines. In addition, immunohistochemistry analysis revealed that SYF2 expression was positively correlated with tumor grade and predicted poor prognosis of ESCC. In vitro studies using serum starvation-refeeding experiment and SYF2-siRNA transfection assay demonstrated that SYF2 expression promoted proliferation of ESCC cells, while SYF2 knockdown led to decreased cell growth rate and colony formation resulted from growth arrest of cell cycle at G0/G1 phase. Furthermore, our results indicated that SYF2 can down-regulate the sensitivity of ESCC cells for cisplatin. Our findings for the first time supported that SYF2 might play an important role in the regulation of ESCC proliferation and would provide a novel therapeutic strategy against human ESCC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchanan G, Ricciardelli C, Harris JM, Prescott J, Yu ZC, Jia L, et al. Control of androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer by the cochaperone small glutamine rich tetratricopeptide repeat containing protein alpha. Cancer Res. 2007;67(20):10087–96. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1646.
Ciccarelli RB, Solomon MJ, Varshavsky A, Lippard SJ. In vivo effects of cis- and trans-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) on SV40 chromosomes: differential repair, DNA-protein cross-linking, and inhibition of replication. Biochemistry. 1985;24(26):7533–40.
Hulleman E, Boonstra J. Regulation of G1 phase progression by growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. 2001;58(1):80–93.
Malumbres M, Carnero A. Cell cycle deregulation: a common motif in cancer. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:5–18.
Tashima Y, Hamada H, Okamoto M, Hanai T. Prediction of key factor controlling G1/S phase in the mammalian cell cycle using system analysis. J Biosci Bioeng. 2008;106(4):368–74. doi:10.1263/jbb.106.368.
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7(5):812–21.
Hollstein MC, Metcalf RA, Welsh JA, Montesano R, Harris CC. Frequent mutation of the p53 gene in human esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(24):9958–61.
Adelaide J, Monges G, Derderian C, Seitz JF, Birnbaum D. Oesophageal cancer and amplification of the human cyclin D gene CCND1/PRAD1. Br J Cancer. 1995;71(1):64–8.
Shinozaki H, Ozawa S, Ando N, Tsuruta H, Terada M, Ueda M, et al. Cyclin D1 amplification as a new predictive classification for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, adding gene information. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 1996;2(7):1155–61.
Xu W, Cao M, Zheng H, Tan X, Li L, Cui G, et al. Upregulation of SYF2 is associated with neuronal apoptosis caused by reactive astrogliosis to neuroinflammation. J Neurosci Res. 2014;92(3):318–28. doi:10.1002/jnr.23312.
Chang MS, Chang CL, Huang CJ, Yang YC. p29, a novel GCIP-interacting protein, localizes in the nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279(2):732–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3992.
Ben-Yehuda S, Dix I, Russell CS, McGarvey M, Beggs JD, Kupiec M. Genetic and physical interactions between factors involved in both cell cycle progression and pre-mRNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2000;156(4):1503–17.
Chang MS, Chen CY, Yeh HI, Fan CC, Huang CJ, Yang YC. Cloning, expression, and genomic organization of mouse mp29 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;299(2):241–6.
Chu PC, Yang YC, Lu YT, Chen HT, Yu LC, Chang MS. Silencing of p29 affects DNA damage responses with UV irradiation. Cancer Res. 2006;66(17):8484–91. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3229.
Chu PC, Wang TY, Lu YT, Chou CK, Yang YC, Chang MS. Involvement of p29 in DNA damage responses and Fanconi anemia pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(10):1710–6. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp204.
Dahan O, Kupiec M. Mutations in genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoding pre-mRNA splicing factors cause cell cycle arrest through activation of the spindle checkpoint. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(20):4361–70.
Chen CH, Chu PC, Lee L, Lien HW, Lin TL, Fan CC, et al. Disruption of murine mp29/Syf2/Ntc31 gene results in embryonic lethality with aberrant checkpoint response. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33538. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033538.
Sobin LH, Fleming ID. TNM classification of malignant tumors, fifth edition (1997). Union internationale contre le cancer and the american joint committee on cancer. Cancer. 1997;80(9):1803–4.
Xue Q, Lv L, Wan C, Chen B, Li M, Ni T, et al. Expression and clinical role of small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-containing protein alpha (SGTA) as a novel cell cycle protein in NSCLC. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(9):1539–49. doi:10.1007/s00432-013-1474-5.
Liu Y, Lv L, Xue Q, Wan C, Ni T, Chen B, et al. Vacuolar protein sorting 4B, an ATPase protein positively regulates the progression of NSCLC via promoting cell division. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;381(1–2):163–71. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1699-2.
Liu Y, Chen Y, Lu X, Wang Y, Duan Y, Cheng C, et al. SCYL1BP1 modulates neurite outgrowth and regeneration by regulating the Mdm2/p53 pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23(23):4506–14. doi:10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0362.
Morris GF, Mathews MB. Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(23):13856–64.
Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7265–79. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206933.
Masuda M, Suzui M, Weinstein IB. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on growth, epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways, gene expression, and chemosensitivity in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2001;7(12):4220–9.
Takano S, Shiomoto S, Inoue KY, Ino K, Shiku H, Matsue T. Electrochemical approach for the development of a simple method for detecting cell apoptosis based on caspase-3 activity. Anal Chem. 2014. doi:10.1021/ac403394z.
Fan JH, Feng GG, Huang L, Tang GD, Jiang HX, Xu J. Naofen promotes TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis of hepatocytes by activating caspase-3 in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2014;20(17):4963–71. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.4963.
Yang S, Wang L, Kong Q. Depression of focal adhesion kinase induces apoptosis in rat osteosarcoma OSR-6 cells in a caspase-dependent pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-9979-3.
Zhu H, Wang Q, Hu C, Zhang W, Quan L, Liu M, et al. High expression of survivin predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma following radiotherapy. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2011;32(6):1147–53. doi:10.1007/s13277-011-0217-y.
Vincent K, Wang Q, Jay S, Hobbs K, Rymond BC. Genetic interactions with CLF1 identify additional pre-mRNA splicing factors and a link between activators of yeast vesicular transport and splicing. Genetics. 2003;164(3):895–907.
Witzel II, Koh LF, Perkins ND. Regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010;38(Pt 1):217–22. doi:10.1042/BST0380217.
Ma W, Stafford LJ, Li D, Luo J, Li X, Ning G, et al. GCIP/CCNDBP1, a helix-loop-helix protein, suppresses tumorigenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2007;100(6):1376–86. doi:10.1002/jcb.21140.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272708).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Junya Zhu and Lili Ji contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Ji, L., Zhang, J. et al. Upregulation of SYF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor cell proliferation and predicts poor prognosis. Tumor Biol. 35, 10275–10285 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2305-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2305-2