Abstract
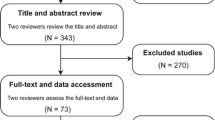
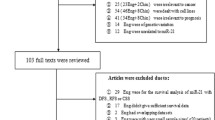
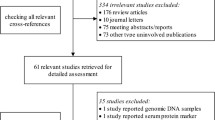
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) exhibit altered expression in patients with cancer and could be considered as potential prognostic biomarker of cancer. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to summarize all the results from available studies, aiming to analyze the prognostic role of circulating microRNA-21 (miR-21) in human cancers. Eligible studies were identified from PubMed and EMBASE through multiple search strategies. We extracted and estimated the hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS), which compared the high and low expression levels of circulating miR-21 in patients with a variety of carcinomas. Pooled HRs and 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Eleven studies with a total of 1,224 patients with various carcinomas were included this meta-analysis. For OS, higher circulating miR-21expression could significantly predict worse outcome with the pooled HR of 2.11 (95 % CI 1.36–3.26, P = 0.0009). The subgroup analysis suggested that the elevated circulating miR-21 expression was correlated with worse OS in Asian population with the pooled HR of 2.36 (95 % CI 1.61–3.48, P < 0.0001) and digestive system cancers with the pooled HR of 2.19 (95 % CI 1.01–4.75, P = 0.05). The present meta-analysis suggests that circulating miR-21 expression is associated with poor survival in patients with cancer and could be a prognostic biomarker for those patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Bartel DP. Micrornas: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54.
Ferracin M, Veronese A, Negrini M. Micromarkers: miRNAs in cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010;10:297–308.
Nana-Sinkam P, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis in cancer: what does the future hold? Pharmacogenomics. 2010;11:667–9.
Madhavan D, Cuk K, Burwinkel B, Yang R. Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating microrna signatures. Front Genet. 2013;4:116.
Shen J, Stass SA, Jiang F. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors. Cancer Lett. 2013;329:125–36.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Konishi H, Nagata H, Hirajima S, et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 and miR-375 in plasma of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12 Suppl 1:S53–9.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Tsujiura M, Konishi H, Takeshita H, Nagata H, et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 in the plasma of patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:271–6.
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang C, et al. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 2012;58:610–8.
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, et al. High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29:618–26.
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, et al. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:849–59.
Wang ZX, Bian HB, Wang JR, Cheng ZX, Wang KM, De W. Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104:847–51.
Xu YZ, Xi QH, Ge WL, Zhang XQ. Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and prognosis in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:1057–60.
Yuan J, Chen L, Chen X, Sun W, Zhou X. Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemosensitivity and prognosis in human osteosarcoma. J Int Med Res. 2012;40:2090–7.
Liu GH, Zhou ZG, Chen R, Wang MJ, Zhou B, Li Y, et al. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2175–81.
Menendez P, Padilla D, Villarejo P, Palomino T, Nieto P, Menendez JM, et al. Prognostic implications of serum microRNA-21 in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108:369–73.
Song J, Bai Z, Zhang J, Meng H, Cai J, Deng W, et al. Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis. Oncol Lett. 2013;6:1733–7.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (moose) group. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–12.
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17:2815–34.
Chen W, Wang H, Chen H, Liu S, Lu H, Kong D, et al. Clinical significance and detection of microRNA-21 in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in chinese population. Eur J Haematol. 2014.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2008;141:672–5.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mrnas. Nature. 2005;433:769–73.
Kent OA, Mendell JT. A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes. Oncogene. 2006;25:6188–96.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302:1–12.
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H, Schetter AJ, Nykter M, et al. Circulating plasma miR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17745.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ. Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2010;251:499–505.
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:118–26.
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY, Yu J, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 2009;58:1375–81.
Pu XX, Huang GL, Guo HQ, Guo CC, Li H, Ye S, et al. Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1674–80.
Wang LG, Gu J. Serum microRNA-29a is a promising novel marker for early detection of colorectal liver metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012;36:e61–7.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10513–8.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, et al. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1046–54.
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim JH, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2690–5.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2257–61.
Wang B, Zhang Q. The expression and clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five solid tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1659–66.
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G. Mir-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13:39–53.
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH, et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene. 2008;27:4373–9.
Yang CH, Yue J, Pfeffer SR, Handorf CR, Pfeffer LM. Microrna miR-21 regulates the metastatic behavior of B16 melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:39172–8.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–36.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microrna miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1026–33.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the pten tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–58.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F. Mo YY: miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26:2799–803.
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A, Tomko Jr RJ, et al. MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25a and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:8157–65.
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S, Esau CC, Burchard J, Linsley PS, et al. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:5369–80.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14328–36.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yinlong Yang and Jinxian Qian contributed equally to this work and are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Qian, J., Chen, Y. et al. Prognostic role of circulating microRNA-21 in cancers: evidence from a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 35, 6365–6371 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1846-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1846-8