Abstract
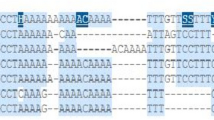
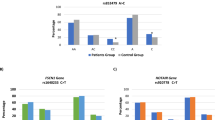
Accumulating evidence has identified that polymorphism residing in the microRNA (miRNA) binding site of target genes can affect the strength of miRNA binding and influence individual susceptibility to cancer. Recently, an insertion/deletion polymorphism (rs3783553 ttca/-) at miRNA-122 binding site in the interleukin-1A 3′ untranslated region has been demonstrated to be functional. We aimed to investigate the association between the rs3783553 polymorphism and the risk of gastric cancer (GC). We genotyped the rs3783553 polymorphism in 207 GC patients and 381 healthy controls by using a polymerase chain reaction method. We found that the ins/ins (ttca/ttca) genotype of the rs3783553 polymorphism was associated with a significantly decreased risk of GC (P = 0.02, odds ratio = 0.48, 95 % confidence interval 0.26–0.90). This finding suggests that the rs3783553 polymorphism may be a protective factor for the development of GC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:784–9.
Crew KD, Neugut AI. Epidemiology of upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:450–64.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature. 2010;466:835–40.
Yu Z, Li Z, Jolicoeur N, Zhang L, Fortin Y, Wang E, et al. Aberrant allele frequencies of the SNPs located in microRNA target sites are potentially associated with human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:4535–41.
Sethupathy P, Borel C, Gagnebin M, Grant GR, Deutsch S, Elton TS, et al. Human microRNA-155 on chromosome 21 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the AGTR1 3′ untranslated region: a mechanism for functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:405–13.
Mishra PJ, Humeniuk R, Longo-Sorbello GS, Banerjee D, Bertino JR. A miR-24 microRNA binding-site polymorphism in dihydrofolate reductase gene leads to methotrexate resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13513–8.
Gao Y, He Y, Ding J, Wu K, Hu B, Liu Y, et al. An insertion/deletion polymorphism at miRNA-122-binding site in the interleukin-1alpha 3′ untranslated region confers risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:2064–9.
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR, de la Chapelle A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7269–74.
Chin LJ, Ratner E, Leng S, Zhai R, Nallur S, Babar I, et al. A SNP in a let-7 microRNA complementary site in the KRAS 3′ untranslated region increases non-small cell lung cancer risk. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8535–40.
Landi D, Moreno V, Guino E, Vodicka P, Pardini B, Naccarati A, et al. Polymorphisms affecting micro-RNA regulation and associated with the risk of dietary-related cancers: a review from the literature and new evidence for a functional role of rs17281995 (CD86) and rs1051690 (INSR), previously associated with colorectal cancer. Mutat Res. 2011;717:109–15.
Landi D, Gemignani F, Naccarati A, Pardini B, Vodicka P, Vodickova L, et al. Polymorphisms within micro-RNA-binding sites and risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:579–84.
Yang ZH, Dai Q, Zhong L, Zhang X, Guo QX, Li SN. Association of IL-1 polymorphisms and IL-1 serum levels with susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50:208–14.
Deng H, Guo Y, Song H, Xiao B, Sun W, Liu Z, et al. MicroRNA-195 and microRNA-378 mediate tumor growth suppression by epigenetical regulation in gastric cancer. Gene. 2013;518:351–9.
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, Liu LY, Tian T, Ni L, et al. MicroRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2009;2:963–70.
Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z, Meng D, et al. Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:652–7.
Liu H, Zhu L, Liu B, Yang L, Meng X, Zhang W, et al. Genome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378 as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;316:196–203.
Apte RN, Voronov E. Is interleukin-1 a good or bad ‘guy’ in tumor immunobiology and immunotherapy? Immunol Rev. 2008;222:222–41.
Pantschenko AG, Pushkar I, Anderson KH, Wang Y, Miller LJ, Kurtzman SH, et al. The interleukin-1 family of cytokines and receptors in human breast cancer: implications for tumor progression. Int J Oncol. 2003;23:269–84.
Elaraj DM, Weinreich DM, Varghese S, Puhlmann M, Hewitt SM, Carroll NM, et al. The role of interleukin 1 in growth and metastasis of human cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:1088–96.
Sakamoto K, Hikiba Y, Nakagawa H, Hayakawa Y, Yanai A, Akanuma M, et al. Inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta regulates gastric carcinogenesis via interleukin-1alpha expression. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(226–238):e226.
Nicklin MJ, Weith A, Duff GW. A physical map of the region encompassing the human interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genes. Genomics. 1994;19:382–4.
Uefuji K, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H. Increased expression of interleukin-1alpha and cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric cancer: a possible role in tumor progression. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:3225–30.
Kemik O, Kemik AS, Begenik H, Erdur FM, Emre H, Sumer A, et al. The relationship among acute-phase response proteins, cytokines, and hormones in various gastrointestinal cancer types patients with cachectic. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2012;31:117–25.
Ma J, Sawai H, Matsuo Y, Ochi N, Yasuda A, Takahashi H, et al. Interleukin-1alpha enhances angiogenesis and is associated with liver metastatic potential in human gastric cancer cell lines. J Surg Res. 2008;148:197–204.
Tomimatsu S, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H. Significant correlation between expression of interleukin-1alpha and liver metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;91:1272–6.
Furuya Y, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H. Interleukin-1alpha concentration in tumors as a risk factor for liver metastasis in gastric cancer. Surg Today. 1999;29:288–9.
Hata Y, Nakaoka H, Yoshihara K, Adachi S, Haino K, Yamaguchi M, et al. A nonsynonymous variant of IL1A is associated with endometriosis in Japanese population. J Hum Genet. 2013. doi:10.1038/jhg.2013.32.
Lu D, Chen L, Shi X, Zhang X, Ling X, Chen X, et al. A functional polymorphism in interleukin-1alpha (IL1A) gene is associated with risk of alopecia areata in Chinese populations. Gene. 2013;521:282–6.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, XF., Li, J. & Li, SB. A functional polymorphism in IL-1A gene is associated with a reduced risk of gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 265–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1034-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1034-2