Abstract
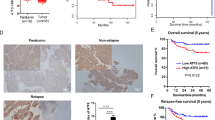
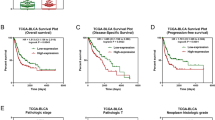
CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling plays important roles in tumor cell metastasis in many types of cancers, and CXCR4 is the key regulator of cell motility in bladder cancer. Emerging evidence suggests that transcription-3 (Stat3) activation is associated with bladder cancer cell growth and survival, while the relationship between CXCL12/CXCR4 signal and Stat3 activation remains unclear. In this study, expression analysis of bladder cancer and adjacent normal tissues showed that higher CXCR4 expression was associated with Stat3 phosphorylation. CXCR4 knockdown in bladder cancer T24 cells impaired CXCL12-induced cell invasion and Stat3 activation. Furthermore, blocking Stat3 activity with the chemical inhibitor Stattic inhibited CXCL12-triggered Stat3 phosphorylation and cell invasion in T24 cells, suggesting that Stat3 activation is required for CXCL12 function in the mobility of bladder cancer. Taken together, CXCR4 is necessary for CXCL12 signal transduction in bladder cancer, and CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes invasion of bladder cancer cells through activation of Stat3 transcriptional activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, et al. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology. 2005;66:4–34.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU, Feldman AS. Bladder cancer. Lancet. 2009;374:239–49.
Lehmann J, Retz M, Stockle M. Is there standard chemotherapy for metastatic bladder cancer? Quality of life and medical resources utilization based on largest to date randomized trial. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;47:171–9.
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM, Homey B. Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:597–606.
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM. CXC chemokines in cancer angiogenesis and metastases. Adv Cancer Res. 2010;106:91–111.
Strieter RM, Belperio JA, Burdick MD, et al. CXC chemokines: angiogenesis, immunoangiostasis, and metastases in lung cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1028:351–60.
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O. Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity. 2000;12:121–7.
Chiu HY, Sun KH, Chen SY, et al. Autocrine CCL2 promotes cell migration and invasion via PKC activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin in bladder cancer cells. Cytokine. 2012;59:423–32.
Singh S, Singh UP, Grizzle WE, et al. CXCL12-CXCR4 interactions modulate prostate cancer cell migration, metalloproteinase expression and invasion. Lab Invest. 2004;84:1666–76.
Dewan MZ, Ahmed S, Iwasaki Y, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:273–6.
Teicher BA, Fricker SP. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2927–31.
Eisenhardt A, Frey U, Tack M, et al. Expression analysis and potential functional role of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor in bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2005;47:111–7.
Retz MM, Sidhu SS, Blaveri E, et al. CXCR4 expression reflects tumor progression and regulates motility of bladder cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2005;114:182–9.
Rigo A, Gottardi M, Damiani E, et al. CXCL12 and [N33A]CXCL12 in 5637 and HeLa cells: regulating HER1 phosphorylation via calmodulin/calcineurin. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34432.
Greten FR, Karin M. Peering into the aftermath: JAKi rips STAT3 in cancer. Nat Med. 2010;16:1085–7.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Chen CL, Cen L, Kohout J, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation is associated with bladder cancer cell growth and survival. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:78.
Chen RJ, Ho YS, Guo HR, et al. Rapid activation of Stat3 and ERK1/2 by nicotine modulates cell proliferation in human bladder cancer cells. Toxicol Sci. 2008;104:283–93.
Ho PL, Lay EJ, Jian W, Parra D, Chan KS. Stat3 activation in urothelial stem cells leads to direct progression to invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3135–42.
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, et al. Stattic: a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol. 2006;13:1235–42.
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS, et al. Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science. 1995;269:81–3.
Saxman SB, Propert KJ, Einhorn LH, et al. Long-term follow-up of a phase III intergroup study of cisplatin alone or in combination with methotrexate, vinblastine, and doxorubicin in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a cooperative group study. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2564–9.
Molyneaux KA, Zinszner H, Kunwar PS, et al. The chemokine SDF1/CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 regulate mouse germ cell migration and survival. Development. 2003;130:4279–86.
Zhou Y, Larsen PH, Hao C, et al. CXCR4 is a major chemokine receptor on glioma cells and mediates their survival. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:49481–7.
Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F, et al. CXCR4 and CXCL12 are inversely expressed in colorectal cancer cells and modulate cancer cell migration, invasion and MMP-9 activation. Exp Cell Res. 2005;310:117–30.
Brule S, Friand V, Sutton A, et al. Glycosaminoglycans and syndecan-4 are involved in SDF-1/CXCL12-mediated invasion of human epitheloid carcinoma HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790:1643–50.
Friand V, Haddad O, Papy-Garcia D, et al. Glycosaminoglycan mimetics inhibit SDF-1/CXCL12-mediated migration and invasion of human hepatoma cells. Glycobiology. 2009;19:1511–24.
Tan CT, Chu CY, Lu YC, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through MMP-13-dependent invasion via the ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1519–27.
Ahr B, Denizot M, Robert-Hebmann V, et al. Identification of the cytoplasmic domains of CXCR4 involved in Jak2 and STAT3 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:6692–700.
Pfeiffer M, Hartmann TN, Leick M, et al. Alternative implication of CXCR4 in JAK2/STAT3 activation in small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1949–56.
Wang M, Chen GY, Song HT, et al. Significance of CXCR4, phosphorylated STAT3 and VEGF-A expression in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2011;2:517–22.
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–6.
Scozzafava A, Mastrolorenzo A, Supuran CT. Non-peptidic chemokine receptors antagonists as emerging anti-HIV agents. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2002;17:69–76.
Wang Z, Ma Q, Liu Q, et al. Blockade of SDF-1/CXCR4 signalling inhibits pancreatic cancer progression in vitro via inactivation of canonical Wnt pathway. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1695–703.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (10ZR1420500).
Conflict of interests
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Hb., Gu, Zq., Jian, K. et al. CXCR4-mediated Stat3 activation is essential for CXCL12-induced cell invasion in bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 34, 1839–1845 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0725-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0725-z