Abstract
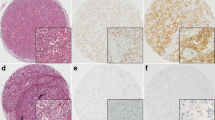
The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, glucose transporter 1 (Glut-1), carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), and monocarboxylate transporter (MCT)4, which are metabolism-related proteins in phyllodes tumors (PTs), and clinicopathologic factors and its implication. We used tissue microarrays to analyze 207 PTs and performed immunohistochemical staining against the glycolysis-related molecules HIF-1α, IGF-1, Glut-1, CAIX, and MCT4. We then compared the immunohistochemical results and clinicopathologic parameters. The expressions of HIF-1α, Glut-1, CAIX, and MCT4 in the stromal component of PTs increased (P = 0.019, P < 0.001, P = 0.045, and P < 0.001, respectively) with increasing tumor grade. According to univariate analysis, factors associated with shorter disease-free survival were Glut-1 expression (P = 0.001) and MCT4 expression (P < 0.001) in the stromal component, and the factors associated with shorter overall survival were IGF-1 expression (P = 0.012), Glut-1 expression (P < 0.001), CAIX expression (P = 0.039), and MCT4 expression (P < 0.001) in the stromal component. Our investigation of stromal expression of the metabolism-related proteins HIF-1α, IGF-1, Glut-1, CAIX, and MCT4 revealed that, as the PT grade increased, the stromal expression of HIF-1α, Glut-1, CAIX, and MCT4 significantly increased. This result suggested that increasing PT grade is associated with increased glycolysis in the stromal component.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–14.
Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:891–9.
Kim JW, Gao P, Dang CV. Effects of hypoxia on tumor metabolism. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:291–8.
Shaw RJ. Glucose metabolism and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:598–608.
Swietach P, Vaughan-Jones RD, Harris AL. Regulation of tumor pH and the role of carbonic anhydrase 9. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:299–310.
Alo PL, Visca P, Botti C, Galati GM, Sebastiani V, Andreano T, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of human erythrocyte glucose transporter and fatty acid synthase in infiltrating breast carcinomas and adjacent typical/atypical hyperplastic or normal breast tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001;116:129–34.
Brown RS, Wahl RL. Overexpression of Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 1993;72:2979–85.
Grover-McKay M, Walsh SA, Seftor EA, Thomas PA, Hendrix MJ. Role for glucose transporter 1 protein in human breast cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 1998;4:115–20.
Ravazoula P, Batistatou A, Aletra C, Ladopoulos J, Kourounis G, Tzigounis B. Immunohistochemical expression of glucose transporter Glut1 and cyclin D1 in breast carcinomas with negative lymph nodes. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2003;24:544–6.
Stackhouse BL, Williams H, Berry P, Russell G, Thompson P, Winter JL, et al. Measurement of Glut-1 expression using tissue microarrays to determine a race specific prognostic marker for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;93:247–53.
Chia SK, Wykoff CC, Watson PH, Han C, Leek RD, Pastorek J, et al. Prognostic significance of a novel hypoxia-regulated marker, carbonic anhydrase IX, in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3660–8.
Pinheiro C, Sousa B, Albergaria A, Paredes J, Dufloth R, Vieira D, et al. GLUT1 and CAIX expression profiles in breast cancer correlate with adverse prognostic factors and MCT1 overexpression. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26:1279–86.
Trastour C, Benizri E, Ettore F, Ramaioli A, Chamorey E, Pouyssegur J, et al. HIF-1alpha and CA IX staining in invasive breast carcinomas: prognosis and treatment outcome. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1451–8.
Anderson BO, Lawton TJ, Lehman CD, Moe RE. Phyllodes tumor. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Osborne KC, editors. Disease of the breast. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott & Wilkins; 2004. p. 991–1006.
Tavassoli FA, Devilee P, International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the breast and female genital organs. Lyon: IAPS; 2003.
Ben Hassouna J, Damak T, Gamoudi A, Chargui R, Khomsi F, Mahjoub S, et al. Phyllodes tumors of the breast: a case series of 106 patients. Am J Surg. 2006;192:141–7.
Kwon JE, Jung WH, Koo JS. Molecules involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and epithelial-stromal interaction in phyllodes tumors: implications for histologic grade and prognosis. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:787–98.
Chen CL, Chu JS, Su WC, Huang SC, Lee WY. Hypoxia and metabolic phenotypes during breast carcinogenesis: expression of HIF-1alpha, GLUT1, and CAIX. Virchows Arch. 2010;457:53–61.
Kawamura T, Kusakabe T, Sugino T, Watanabe K, Fukuda T, Nashimoto A, et al. Expression of glucose transporter-1 in human gastric carcinoma: association with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and patient survival. Cancer. 2001;92:634–41.
Mineta H, Miura K, Takebayashi S, Misawa K, Araki K, Misawa Y, et al. Prognostic value of glucose transporter 1 expression in patients with hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:3489–94.
Schonberger J, Ruschoff J, Grimm D, Marienhagen J, Rummele P, Meyringer R, et al. Glucose transporter 1 gene expression is related to thyroid neoplasms with an unfavorable prognosis: an immunohistochemical study. Thyroid. 2002;12:747–54.
Younes M, Brown RW, Mody DR, Fernandez L, Laucirica R. GLUT1 expression in human breast carcinoma: correlation with known prognostic markers. Anticancer Res. 1995;15:2895–8.
Younes M, Brown RW, Stephenson M, Gondo M, Cagle PT. Overexpression of Glut1 and Glut3 in stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor survival. Cancer. 1997;80:1046–51.
Brennan DJ, Jirstrom K, Kronblad A, Millikan RC, Landberg G, Duffy MJ, et al. CA IX is an independent prognostic marker in premenopausal breast cancer patients with one to three positive lymph nodes and a putative marker of radiation resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6421–31.
Colpaert CG, Vermeulen PB, Fox SB, Harris AL, Dirix LY, Van Marck EA. The presence of a fibrotic focus in invasive breast carcinoma correlates with the expression of carbonic anhydrase IX and is a marker of hypoxia and poor prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;81:137–47.
Hussain SA, Ganesan R, Reynolds G, Gross L, Stevens A, Pastorek J, et al. Hypoxia-regulated carbonic anhydrase IX expression is associated with poor survival in patients with invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:104–9.
Robertson N, Potter C, Harris AL. Role of carbonic anhydrase IX in human tumor cell growth, survival, and invasion. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6160–5.
Rademakers SE, Lok J, van der Kogel AJ, Bussink J, Kaanders JH. Metabolic markers in relation to hypoxia; staining patterns and colocalization of pimonidazole, HIF-1alpha, CAIX, LDH-5, GLUT-1, MCT1 and MCT4. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:167.
Witkiewicz AK, Whitaker-Menezes D, Dasgupta A, Philp NJ, Lin Z, Gandara R, et al. Using the “reverse Warburg effect” to identify high-risk breast cancer patients: stromal MCT4 predicts poor clinical outcome in triple-negative breast cancers. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:1108–17.
Kuijper A, van der Groep P, van der Wall E, van Diest PJ. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and its downstream targets in fibroepithelial tumors of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:R808–18.
Noguchi S, Motomura K, Inaji H, Imaoka S, Koyama H. Clonal analysis of fibroadenoma and phyllodes tumor of the breast. Cancer Res. 1993;53:4071–4.
Sawyer EJ, Hanby AM, Ellis P, Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Boyle S, et al. Molecular analysis of phyllodes tumors reveals distinct changes in the epithelial and stromal components. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:1093–8.
Chang H, Shyu KG, Lee CC, Tsai SC, Wang BW. Hsien Lee Y, et al. GL331 inhibits HIF-1alpha expression in a lung cancer model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;302:95–100.
Yeo EJ, Chun YS, Cho YS, Kim J, Lee JC, Kim MS, et al. YC-1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:516–25.
Mohanti BK, Rath GK, Anantha N, Kannan V, Das BS, Chandramouli BA, et al. Improving cancer radiotherapy with 2-deoxy-D-glucose: phase I/II clinical trials on human cerebral gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;35:103–11.
Aft RL, Zhang FW, Gius D. Evaluation of 2-deoxy-d-glucose as a chemotherapeutic agent: mechanism of cell death. Br J Cancer. 2002;87:805–12.
Vullo D, Franchi M, Gallori E, Pastorek J, Scozzafava A, Pastorekova S, et al. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: inhibition of the tumor-associated isozyme IX with aromatic and heterocyclic sulfonamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003;13:1005–9.
Gallagher SM, Castorino JJ, Wang D, Philp NJ. Monocarboxylate transporter 4 regulates maturation and trafficking of CD147 to the plasma membrane in the metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4182–9.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A1A1002886).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, J.E., Jung, WH. & Koo, J.S. The expression of metabolism-related proteins in phyllodes tumors. Tumor Biol. 34, 115–124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0518-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0518-9