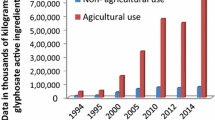
Abstract
Silver is one of the most popular metals for use in synthesizing metal-based nanoparticles. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are intensively applied within many industrial sectors. Previously, we observed unusual avoidance behavior in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to AgNPs. To understand the molecular basis of this abnormality, earthworms were exposed to AgNPs (1, 10, 100 mg/kg) or AgNO3 (100 mg/kg, positive control) via the soil to evaluate reactive oxygen species generation, genotoxicity, and transcriptional levels of stress-related genes (catalase, glutathione-Stransferase, heat shock protein 70, metallothionein, and superoxide dismutase). Earthworms exhibited a low propensity to accumulate silver, indicating a reduced mobility of AgNPs in the soil environment. Although abnormal behaviors were not found at low AgNPs concentrations, oxidative stress-related indicators were present, illustrating the importance of molecular responses as sensitive initial biomarkers of AgNP terrestrial contamination. The current study suggests that AgNPs may regulate oxidative stress-related mechanisms and provides an improved understanding of the environmental health effects of AgNPs on species in soil ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlich, K., Klawonn, T., Terytze, K. & Hund-Rinke, K. Effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate in the earworm reproduction test. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:181–188 (2013).
Mueller, N. C. & Nowack, B. Exposure modeling of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 42:4447–4453 (2008).
Tourinho, P. S. et al. Metal-based nanoparticles in soil: fate behavior, and effects on soil invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1679–1692 (2012).
Sagee, O., Dror, I. & Berkowitz, B. Transport of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in soil. Chemosphere 88:670–675 (2012).
Spurgeon, D. J. et al. Review of subtethalecotoxicological tests for measuring harm in terrestrial ecosystems. Technical Report P5-063/TR1, Environment Agency, Bristol, UK. (2002)
Klobucar, G. et al. Aporrectodea caliginosa, a suitable earthworm species for field based genotoxicity assessment? Environ Pollut 159:841–849 (2011).
Roh, J. Y. et al. Ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using functional ecotoxicogenomics. Environ Sci Technol 43:3933–3940 (2009).
Lim, D. et al. Oxidative stress-related PMK-1 P38 MAPK activation as a mechanism for toxicity of silver nanoparticles to reproduction in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:585–592 (2012).
Shoults-Wilson, W. A. et al. Effect of silver nanoparticle surface coating on bioaccumulation and reproductive toxicity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Nanotoxicology 5:432–444 (2011).
Heckmann, L. H. et al. Limit-test toxicity screening of selected inorganic nanoparticles to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicology 20:226–233 (2011).
Shoults-Wilson, W. A. et al. Evidence for avoidance of Ag nanoparticles by earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicology 20:385–396 (2011).
Tsyusko, O. V. et al. Short-term molecular-level effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 171:249–255 (2012).
Lapied, E., Moudilou, E., Exbrayat, J. M., Oughton, D. H. & Joner, E. J. Silver nanoparticle exposure causes apoptotic response in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta). Nanomedicine 5:975–984 (2010).
Asare, N. et al. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanaoparticles in testicular cells. Toxicology 291: 65–72 (2012).
Nymark, P. et al. Genotoxicity of polyvinylpyrrolidonecoated silver nanoparticles in BEAS 2B cells. Toxicology 313:38–48 (2013).
Hayashi, Y. et al. Earthworms and humans in vitro: characterizing evolutionarily conserved stress and immune responses to silver nanoparticls. Environ Sci Technol 46:4166–4173 (2012).
Coutris, C., Hertel-Aas, T., Lapied, E., Joner, E. J. & Oughton, D. H. Bioavailability of cobalt and silver nanoparticle to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Nanotoxicology 6:186–195 (2012).
Fabrega, J., Luoma, S. N., Tyler, C. R., Galloway, T. S. & Lead, J. R. Silver nanoparticles: Behaviour and effects in the aquatic environment. Environ Int 37:517–531 (2011).
Cornelis, G. et al. Retention and dissolution of engineered silver nanoparticles in natural soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:891–902 (2012).
Darlington, T. K., Neigh, A. M., Spencer, M. T., Nguyen, O. T. & Oldenburg, S. J. Nanoparticle characteristics affecting environmental fate and transport through soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1191–1199 (2009).
Unrine, J. M. et al. Evidence for bioavailability of Au nanoparticles from soil and biodistribution within earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Sci Technol 44: 8308–8313 (2010).
Nair, P. M. G., Park, S. Y., Lee, S. & Choi, J. Differential expression of ribosomal protein gene, gonadotrophin releasing hormone gene and Balbiani ring protein gene in silver nanoparticles exposed Chironomus riparius. Aquatic Toxicol 101:31–37 (2011).
Vijayavel, K. & Balasubramanian, M. P. DNA damage and cell necrosis induced by naphthalene due to the modulation of biotransformation enzymes in an estuarine crab Scylla serrate. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 22:1–7 (2008).
Tomasello, B. et al. Biochemical and bioaccumulation approaches for investigating marine pollution using Mediterranean rainbow wrasse, Coris julis (Linneaus 1798). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 86:168–175 (2012).
Long, T. C. et al. Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ Health Perspect 115:1631–1637 (2007).
Lin, D., Zhou, Q., Xu, Y., Chen, C. & Li, Y. Physiological and molecular responses of the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to soil chlortetracycline contamination. Environ Pollut 171:46–51 (2012).
Rinna, A. et al. Effect of silver nanoparticles on mitogen-activated protein kinases activation: role of reactive oxygen species and implication in DNA damage. Mutagenesis 30:59–66 (2015).
Bigorgne, E. et al. Ecotoxicological assessment of TiO2 byproducts on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 159:2698–2705 (2011).
Lee, K. W. et al. Expression of glustathione S. transferase (GST) genes in marine copepod Tigriopus japonicas exposed to trace metals. Aquat Toxicol 89:158–166 (2008).
Nair, P. M. G., Park, S. Y. & Choi, J. Evaluation of the effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions using stress responsive gene expression in Chironomus riparius. Chemosphere 92:592–599 (2013).
Hayashi, Y., Heckmann, L. H., Simonsen, V. & Scott-Fordsmand, J. J. Time-course profiling of molecular stress responses to silver nanoparticles in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:219–226 (2013).
Gomes, S. I., Soares, A. M., Scott-Fordsmand, J. J. & Amorim, M. J. Mechanisms of response to silver nanoparticles on Enchytraeus albidus (Oligochaeta): survival, reproduction and gene expression profile. J Hazard Mater 254-255:336–344 (2013).
Hou, W. C., Westerhoff, P. & Posner, J. D. Biological accumulation of engineered nanomaterials: a review of current knowledge. Environ Sci 15:103–122 (2013).
OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. No. 207. Earthworm Acute Toxicity Test. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris 1984. wwwoecd-ilibraryorg/OECD207pdf (1984).
Eyambe, G. S., Goven, A. J., Fitzpatrick, L. C., Venables, B. J. & Cooper, E. L. A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25:61–67 (1991).
Diogene, J., Dufour, M., Poirier, G. G. & Nadeau, D. Extrusion of earthworm coelomocytes: comparison of the cell populations recovered from the species Lumbricus terrestris, Eisenia fetida and Octolasiontyrtaeum. Lab Anim 31:326–336 (1997).
Olive, P. L., Wlodek, D. & Banath, J. P. DNA doublestrand breaks measured in individual cells subjected to gel electrophoresis. Cancer Res 51:4671–4676 (1991).
Barja, G. The quantitative measurement of H2O2 generation in isolated mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomem 34:227–233 (2002).
Julian, D., April, K. L., Patel, S., Stein, J. R. & Wohlgemuth, S. E. Mitochondrial depolarization following hydrogen sulfide exposure in erythrocytes from a sulfide-tolerant marine invertebrate. J Exp Biol 208:4109–4122 (2005).
Chen, C., Zhou, Q., Liu, S. & Xiu, Z. Acute toxicity, biochemical and gene expression responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to polycyclic musks. Chemosphere 83:1147–1154 (2011).
Livak, K. J. & Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408 (2001).
Park, J. W., Heah, T. P., Gouffon, J. S., Henry, T. B. & Sayler, G. S. Global gene expression in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine and sertraline) reveals unique expression profiles and potential biomarkers of exposure. Environ Pollut 167:163–170 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.S., Park, JW. Molecular characterization and toxicological effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in a terrestrial invertebrate, the earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 11, 423–431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-015-0045-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-015-0045-z