Abstract
Background
Upregulation of human enhancer filamentation 1 (HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L) and Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is closely correlated with metastasis of human cancer. However, the mechanism by which the overexpression of HEF1 or Plk1 stimulates cancer metastasis and induces tumorigenesis remains enigmatic. In addition, the accumulation of HEF1 at the focal adhesion (FA) is known to be an essential event in cancer cell migration, but the mechanism of how HEF1 is targeted to the FA remains yet to be unveiled.
Objective
This study was performed to elucidate the FA docking mechanism of HEF1 and to determine its effect on tumorigenesis.
Methods
To confirm the effect of the kinase on HEF1 translocation, various expression-knockdown stable cell lines were generated using a lentivirus system, and the effect of the HEF1-Plk1 complex on tumorigenesis was confirmed using a xenograft mouse model.
Results
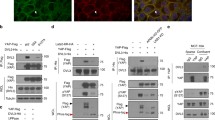
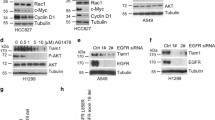
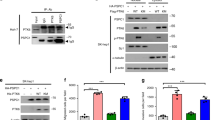
Here, we show that Wnt5a-dependent Plk1 binding to HEF1 is critically required for HEF1 translocation to the FA. We also confirmed that Plk1 and CK1δ activities essential for HEF1 translocation are induced by Wnt5a. Finally, we confirmed the induction of tumorigenesis by the HEF1-Plk1 complex in the xenograft mouse model.
Conclusion
Our data collectively unveil the Wnt5a-CK1δ-HEF1-Plk1-FA remodeling pathway that governs HEF1 transportation to the FA to induce cell migration and tumorigenesis. This study sheds light on a mechanism underlying tumorigenesis and provides new strategies for anticancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr FA, Silljé HH, Nigg EA (2004) Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:429–440
Bryja V, Schulte G, Rawal N, Grahn A, Arenas E (2007) Wnt-5a induces Dishevelled phosphorylation and dopaminergic differentiation via a CK1-dependent mechanism. J Cell Sci 120:586–595
Ishida-Takagishi M, Enomoto A, Asai N, Ushida K, Watanabe T, Hashimoto T, Kato T, Weng L, Matsumoto S, Asai M, Murakumo Y, Kaibuchi K, Kikuchi A, Takahashi M (2012) The Dishevelled-associating protein Daple controls the non-canonical Wnt/Rac pathway and cell motility. Nat Commun 3:859
Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B, Brennan C, Hahn WC, Cordon-Cardo C, Wagner SN, Flotte TJ, Duncan LM, Granter SR, Chin L (2006) Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell 125:1269–1281
Kurayoshi M, Oue N, Yamamoto H, Kishida M, Inoue A, Asahara T, Yasui W, Kikuchi A (2006) Expression of Wnt-5a is correlated with aggressiveness of gastric cancer by stimulating cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res 66:10439–10448
Kyun ML, Kim SO, Lee HG, Hwang JA, Hwang J, Soung NK, Cha-Molstad H, Lee S, Kwon YT, Kim BY, Lee KH (2020) Wnt3a stimulation promotes primary ciliogenesis through β-catenin phosphorylation-induced reorganization of centriolar satellites. Cell Rep 30:1447–1462
Law SF, Zhang YZ, Klein-Szanto AJ, Golemis EA (1998) Cell cycle-regulated processing of HEF1 to multiple protein forms differentially targeted to multiple subcellular compartments. Mol Cell Biol 18:3540–3551
Lee KS, Erikson RL (1997) Plk is a functional homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc5, and elevated Plk activity induces multiple septation structures. Mol Cell Biol 17:3408–3417
Lee KH, Johmura Y, Yu LR, Park JE, Gao Y, Bang JK, Zhou M, Veenstra TD, KimLee BYKS (2012) Identification of a novel Wnt5a-CK1ɛ-Dvl2-Plk1-mediated primary cilia disassembly pathway. EMBO J 31:3104–3117
Lee KH, Hwang JA, Kim SO, Kim JH, Shin SC, Kim EE, Lee KS, Rhee K, Jeon BH, Bang JK, Cha-Molstad H, Soung NK, Jang JH, Ko SK, Lee HG, Ahn JS, Kwon YT, Kim BY (2018) Phosphorylation of human enhancer filamentation 1 (HEF1) stimulates interaction with Polo-like kinase 1 leading to HEF1 localization to focal adhesions. J Biol Chem 293:847–862
Lénárt P, Petronczki M, Steegmaier M, Di Fiore B, Lipp JJ, Hoffmann M, Rettig WJ, Kraut N, Peters JM (2007) The small-molecule inhibitor BI 2536 reveals novel insights into mitotic roles of Polo-like kinase 1. Curr Biol 17:304–315
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436:518–524
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A (2004) WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 5:691–701
Natarajan M, Stewart JE, Golemis EA, Pugacheva EN, Alexandropoulos K, Cox BD, Wang W, Grammer JR, Gladson CL (2006) HEF1 is a necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 25:1721–1732
Oakes PW, Gardel ML (2014) Stressing the limits of focal adhesion mechanosensitivity. Curr Opin Cell Biol 30C:68–73
Rena G, Bain J, Elliott M, Cohen P (2004) D4476, a cell-permeant inhibitor of CK1, suppresses the site-specific phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of FOXO1a. EMBO Rep 5:60–65
Rizki A, Mott JD, Bissell MJ (2007) Polo-like kinase 1 is involved in invasion through extracellular matrix. Cancer Res 67:11106–11110
Singh M, Cowell L, Seo S, O’Neill G, Golemis E (2007) Molecular basis for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L action as a multifunctional co-ordinator of invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle. Cell Biochem Biophys 48:54–72
Strebhardt K, Ullrich A (2006) Targeting polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 6:321–330
Tikhmyanova N, Little JL, Golemis EA (2010) CAS proteins in normal and pathological cell growth control. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:1025–1048
Weeraratna AT, Jiang Y, Hostetter G, Rosenblatt K, Duray P, Bittner M, Trent JM (2002) Wnt5a signaling directly affects cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma. Cancer Cell 1:279–288
Zaidel-Bar R, Itzkovitz S, Ma’ayan A, Iyengar R, Geiger B (2007) Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome. Nat Cell Biol 9:858–867
Acknowledgements
We thank Kyung S. Lee, Sean B. Lee, Chou-Zen Giam, Michael B. Yaffe, and Joel Raingeaud for reagents. This work was supported by Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C1004854), R&D Convergence Program (CAP-16-03-KRIBB) of National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST) of Republic of Korea, and KRIBB Research Initiative Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animal studies were carried out in accordance with the institutional guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of KRIBB (KRIBB-AEC-14082).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, JA., Yu, J.E., Kim, SO. et al. Wnt5a-induced docking of Plk1 on HEF1 promotes HEF1 translocation and tumorigenesis. Genes Genom 43, 567–575 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01088-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01088-x