Abstract
Background
Synonymous codon usage bias is noticed in the genome of every organism, influenced by mutation pressure and natural selection. The analysis of codon usage pattern in Porphyra umbilicalis chloroplast genome are inferred while previous study focused on codon bias in nuclear genome.
Objective
To develop a better understanding of the factors affecting synonymous codon usage, codon usage patterns and nucleotide composition of 150 genes in P. umbilicalis cp genome, and provide a theoretical basis for genetic modification of chloroplast genome.
Methods
In this study, all codon usage bias parameters and nucleotide compositions were calculated by Python script, Codon W, DNA Star, CUSP of EMBOSS and Microsoft Excel.
Results
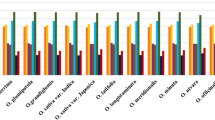
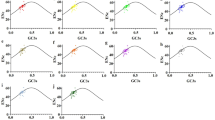
It shows that codon usage models are mainly influenced by compositional constraints under mutational pressure and synonymous codon prefers to use codons ending with A/T, comparing to C/G. The ENC value is slight low which shows the weak codon bias. For all coding genes of P. umbilicalis chloroplast genome except Photosystem I genes, a weak correlation between GC3 and GC12 suggests natural selection might play a significant role in synonymous codon usage bias.
Conclusion
The codon usage bias in P. umbilicalis cp genome is low and in some way or other, influenced by natural selection, mutation pressure, nucleotide composition. Our results can provide a theoretical basis for codon modification of exogenous genes, accuracy of prediction about new members of chloroplast gene family and identification of unknown genome.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisalputra T, Bisalputra AA (1969) The ultrastructure of chloroplast of a brown alga Sphacelaria sp. I. Plastid DNA configuration—the chloroplast genophore. J Ultrastruct Res 29:151–170
Blunden G (1992) Seaweed resources in europe: uses and potential, vol 2. Wiley, Chichester, pp 178–198 (Issue 2)
Brawley SH, Blouin NA, Fickoblean E, Wheeler GL (2017) Insights into the red algae and eukaryotic evolution from the genome of Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiophyceae, Rhodophyta). P Natl Acad Sci USA 114:E6361–E6370
Brodie JA, Irvine LM (2003) Seaweeds of the British Isles: Volume 1 Part 3b Bangiophycidae. Natural History Museum, London, ISBN 1-898298-87-4, XIII, pp 167
Cai MS, Cheng AC, Wang MS, Zhao LC (2009) Characterization of synonymous codon usage bias in the duck plague virus UL35 gene. Karger 52:266–278
Chen X, Cai X, Chen Q, Zhou H (2011) Factors affecting synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of oncidium gower ramsey. Evol Bioinform 7:271–278
He S, Zhang SJ, Xiu LS, Xing ZB (2013) Codon usage analysis in squalene synthase gene. Genom Appl Biol 32:232–239
He L, Qian J, Li X, Sun Z (2017) Complete chloroplast genome of medicinal plant lonicera japonica: genome rearrangement, intron gain and loss, and implications for phylogenetic studies. Molecules 22:249
Kh LVB, Kowallik KV (1992) Structural organization of the chloroplast genome of the chromophytic alga Vaucheria bursata. Plant Mol Biol 18:83–95
Li J, Shulian X, Jia F (2010) Progress in chloroplast genome of algae. J Northwest Bot 30:208–214
Li ZZ, Saina JK, Gichira AW, Kyalo CM (2018) comparative genomics of the balsaminaceae sister genera Hydrocera triflora and Impatiens pinfanensis. Int J Mol Sci 19:319
Lohse M, Drechsel O, Kahlau S, Bock R (2013) OrganellarGenomeDRAW—a suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res 41:W575–W581
Long S, Yao H, Wu Q, Li G (2018) Analysis of compositional bias and codon usage pattern of the coding sequence in Banna virus genome. Virus Res 258:68–72
Monisha N, Arif U, Supriyo C (2017) Codon usage bias and its influencing factors for Y-linked genes in human. Comput Biol Chem 69:77–86
Parks M, Cronn R, Liston A (2009) Increasing phylogenetic resolution at low taxonomic levels using massively parallel sequencing of chloroplast genomes. BMC Biol 7:84
Romero H, Zavala A, Musto H (2000) Codon usage in Chlamydia trachomatis is the result of strand-specific mutational biases and a complex pattern of selective forces. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2084–2090
Sharp PM, Li WH (1986) An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J Mol Evol 24:28–38
Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T (1986) The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J 5:2043–2049
Snawar H, Sahibzada TR (2017) Analysis of synonymous codon usage in Zika virus. Acta Trop 173:136–146
Wang H, Meng T, Wei W (2018) Analysis of synonymous codon usage bias in helicase gene from Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. Genes Genom 40:767–780
Wei L, He J, Jia X, Qi Q (2014) Analysis of codon usage bias of mitochondrial genome in Bombyx mori and its relation to evolution. BMC Biol 14:262
Wright F (1990) The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 87:23
Yu T, Li J, Yang Y, Qi L (2012) Codon usage patterns and adaptive evolution of marine unicellular cyanobacteria Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus. Mol Phylogenet Evol 62:206–213
Zhang R, Zhang L, Wang W, Zhang Z (2018) Differences in codon usage bias between photosynthesis-related genes and genetic system-related genes of chloroplast genomes in cultivated and wild solanum species. Int J Mol Sci 19:3142
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research grants from Discipline construction Double Support Project of Sichuan Agricultural University (Grant No. 00770114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GLL and HPY identified the research topic and designed the experiments. YYH, QYX and YJ collected the data. GLL and SCG performed the experiments and analyzed the data. GLL and ZLP wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Pan, Z., Gao, S. et al. Analysis of synonymous codon usage of chloroplast genome in Porphyra umbilicalis. Genes Genom 41, 1173–1181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00847-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00847-1