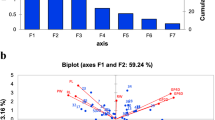
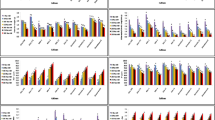
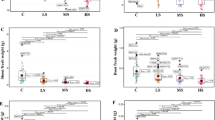
Abstract
Durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) is one of the main species of cultivated wheat. In arid and semi-arid areas, salinity stress reduces durum wheat productivity. This study used 26 durum wheat accessions from semi-arid regions in Tunisia to analyze plant tolerance to salt stress. Salt stress was experimentally applied by regularly submerging pots in NaCl solution. The salt tolerance trait index (STTI) and salt tolerance index (STI) of various growth parameters were used as criteria to select for salt tolerance. Analysis of genetic relationships was carried out to determine the genetic distance between durum wheat accessions. Based on simple sequence repeats analysis, a molecular marker for salt stress resistance in durum wheat was developed. Salt-treated plants had reduced morphological traits compared to control plants. Most STTIs in all genotypes were below 100 %. Based on STI, 8 accessions were found to be salt-resistant, 16 were salt-moderate, two were salt-susceptible. Analysis of the genetic relationships among 28 Tunisian durum wheat accessions revealed that landraces of the same nominal type are closely related. Of the 94 SSR primers investigated, three were selected and used to design sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) primers. One SCAR primer pair, KUCMB_Xgwm403_2, produced a 207 bp band that was present in salt-resistant durum wheat lines but absent in salt-susceptible lines. The results suggest that KUCMB_Xgwm403_2 could be a potential genetic tag for salt-tolerant durum wheats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Shahzad A, Iqbal M, Asif M, Hirani AH (2013) Morphological and molecular genetic variation in wheat for salinity tolerance at germination and early seedling stage. Aust J Crop Sci 7:66
Ali Z, Salam A, Azhar FM, Khan IA (2007) Genotypic variation in salinity tolerance among spring and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) accessions. S Afr J Bot 73:70–75
Amar SB, Brini F, Sentenac H, Masmoudi K, Véry A-A (2014) Functional characterization in Xenopus oocytes of Na+ transport systems from durum wheat reveals diversity among two HKT1; 4 transporters. J Exp Bot 65:213–222
Arabbeigi M, Arzani A, Majidi MM, Kiani R, Tabatabaei BES, Habibi F (2014) Salinity tolerance of Aegilops cylindrica genotypes collected from hyper-saline shores of Uremia Salt Lake using physiological traits and SSR markers. Acta Physiol Plant 36:2243–2251
Arora A, Kundu S, Dilbaghi N, Sharma I, Tiwari R (2014) Population structure and genetic diversity among Indian wheat varieties using microsatellite (SSR) markers. Aust J Crop Sci 8:1281–1289
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2013) Crop breeding for salt tolerance in the era of molecular markers and marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 132:10–20
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic-linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Brini F, Amara I, Feki K, Hanin M, Khoudi H, Masmoudi K (2009) Physiological and molecular analyses of seedlings of two Tunisian durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. subsp. Durum [Desf.]) varieties showing contrasting tolerance to salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 31:145–154
Burdon JJ, Barrett LG, Rebetzke G, Thrall PH (2014) Guiding deployment of resistance in cereals using evolutionary principles. Evol Appl 7:609–624
Cao W, Hughes GR, Ma H, Dong Z (2001) Identification of molecular markers for resistance to Septoria nodorum blotch in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102:551–554
Che Y, Yang Y, Yang X, Li X, Li L (2015) Phylogenetic relationship and diversity among Agropyron Gaertn. germplasm using SSRs markers. Plant Syst Evol 301:163–170
Ciuca M, Petcu E (2009) SSR markers associated with membrane stability in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Rom Agric Res 26:21–24
Doyle J, Doyle JL (1987) Genomic plant DNA preparation from fresh tissue-CTAB method. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
El-Hendawy SE, Hu YC, Yakout GM, Awad AM, Hafiz SE, Schmidhalter U (2005) Evaluating salt tolerance of wheat genotypes using multiple parameters. Eur J Agron 22:243–253
El-Hendawy SE, Hu Y, Schmidhalter U (2007) Assessing the suitability of various physiological traits to screen wheat genotypes for salt tolerance. J Integr Plant Biol 49:1352–1360
Gholizadeh A, Dehghani H, Dvorak Y (2014) Determination of the most effective traits on wheat yield under saline stress. Agric Adv 3:103–110
Hachicha MJOJ, Job JO, Mtimet A (1994) Les sols salés et la salinisation en Tunisie. Sols de Tunisie 5:271–341
Jogaiah S, Sharathchandra RG, Raj N, Vedamurthy AB, Shetty HS (2014) Development of SCAR marker associated with downy mildew disease resistance in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.). Mol Biol Rep 41:7815–7824
Khoufi S, Khamassi K, da Silva JAT, Chaabane R, Naceur MBB (2012) Morphological and molecular characterization of six of the most frequently cultivated hard wheat varieties in Tunisia. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 4:106–114
Kim SH, Kim DY, Yacoubi I, Seo YW (2014) Phenotypic and genotypic analyses of drought tolerance in Korean and tunisian wheat cultivars. Plant Breed Biotechnol 2:139–150
Kumla S, Doolgindachbaporn S, Sudmoon R, Sattayasai N (2012) Genetic variation, population structure and identification of yellow catfish, Mystus nemurus (C&V) in Thailand using RAPD, ISSR and SCAR marker. Mol Biol Rep 39:5201–5210
Latiri K, Lhomme JP, Annabi M, Setter TL (2010) Wheat production in Tunisia: progress, inter-annual variability and relation to rainfall. Eur J Agron 33:33–42
Liu K, Muse S (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Mansour M, Hachicha M (2014) The vulnerability of tunisian agriculture to climate change. In: Ahmad P, Rasool S (eds) Emerging technologies and management of crop stress tolerance. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 485–500
Moghaieb REA, Abdel-Hadi A-HA, Talaat NB (2013) Molecular markers associated with salt tolerance in Egyptian wheats. Afr J Biotechnol 10:18092–18103
Munns R, James RA (2003) Screening methods for salinity tolerance: a case study with tetraploid wheat. Plant Soil 253:201–218
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Munns R, James RA, Xu B, Athman A, Conn SJ, Jordans C, Byrt CS, Hare RA, Tyerman SD, Tester M, Plett D, Gilliham M (2012) Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene. Nat Biotechnol 30:360–364
Munoz-Pajares AJ, Martinez-Rodriguez L, Teruel M, Cabrero J, Camacho JP, Perfectti F (2011) A single, recent origin of the accessory B chromosome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Genetics 187:853–863
Ouni Y, Lakhdar A, Rabhi M, Smaoui A, Maria AR, Chedly A (2013) Effects of the halophytes Tecticornia indica and Suaeda fruticosa on soil enzyme activities in a Mediterranean Sabkha. Int J Phytoremediat 15:188–197
Paran I, Michelmore RW (1993) Development of reliable PCR-based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85:985–993
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 60:324–349
Pradhan GP, Prasad PVV, Fritz AK, Kirkham MB, Gill BS (2012) High temperature tolerance in Aegilops species and its potential transfer to wheat. Crop Sci 52:292–304
Rengasamy P (2010) Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct Plant Biol 37:613–620
Roy S, Chakraborty U (2014) Salt tolerance mechanisms in salt tolerant grasses (STGs) and their prospects in cereal crop improvement. Bot Stud 55:31
Salem KFM, Mattar MZ (2014) Identification of microsatellite alleles for salt tolerance at seedling stage in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Life Sci J 11:1064–1073
Samdur MY, Singh AL, Mathur RK, Manivel P, Chikani BM, Gor HK, Khan MA (2000) Field evaluation of chlorophyll meter for screening groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes tolerant to iron-deficiency chlorosis. Curr Sci (India) 79:211–213
Saqib ZA, Akhtar J, Ul-Haq MA, Ahmad I (2012) Salt induced changes in leaf phenology of wheat plants are regulated by accumulation and distribution pattern of Na+ ion. Pak J Agr Sci 49:141–148
Sardouie-Nasab S, Mohammadi-Nejad G, Zebarjadi A (2013) Haplotype analysis of QTLs attributed to salinity tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol Biol Rep 40:4661–4671
Schroeder JI, Delhaize E, Frommer WB, Guerinot ML, Harrison MJ, Herrera-Estrella L, Horie T, Kochian LV, Munns R, Nishizawa NK, Tsay YF, Sanders D (2013) Using membrane transporters to improve crops for sustainable food production. Nature 497:60–66
Shahzad A, Ahmad M, Iqbal M, Ahmed I, Ali GM (2012) Evaluation of wheat landrace genotypes for salinity tolerance at vegetative stage by using morphological and molecular markers. Genet Mol Res 11:679–692
Shtereva L, Vassilevska-Ivanova R, Kartzeva T, Kraptchev B (2015) Salt tolerance of two sunflower genotypes: Helianthus annuus and interspecific line Helianthus anuus × Helianthus mollis. Genet Plant Physiol 5:61–73
Son J-H, Kim K-H, Shin S, Choi I, Kim H-S, Cheong Y-K, Lee C-K, Lee S-I, Choi J-Y, Park K-G (2014) Development of SCAR Markers for Korean Wheat Cultivars Identification. Plant Breed Biotechnol 2:224–230
Sonmezoglu OA, Bozmaz B, Yildirim A, Kandemir N, Aydin N (2012) Genetic characterization of Turkish bread wheat landraces based on microsatellite markers and morphological characters. Turk J Biol 36:589–597
Turki N, Shehzad T, Harrabi M, Okuno K (2015) Detection of QTLs associated with salinity tolerance in durum wheat based on association analysis. Euphytica 201:29–41
Vaillancourt A, Nkongolo KK, Michael P, Mehes M (2008) Identification, characterisation, and chromosome locations of rye and wheat specific ISSR and SCAR markers useful for breeding purposes. Euphytica 159:297–306
Van Bueren ETL, Backes G, De Vriend H, Østergård H (2010) The role of molecular markers and marker assisted selection in breeding for organic agriculture. Euphytica 175:51–64
Yang L, Fu S, Khan MA, Zeng W, Fu J (2013) Molecular cloning and development of RAPD-SCAR markers for Dimocarpus longan variety authentication. SpringerPlus 2:501
Yıldırım M, Kılıç H, Kendal E, Karahan T (2010) Applicability of chlorophyll meter readings as yield predictor in durum wheat. J Plant Nutr 34:151–164
Zhu M, Shabala S, Shabala L, Fan Y, Zhou MX (2016) Evaluating predictive values of various physiological indices for salinity stress tolerance in wheat. J Agron Crop Sci 202:115–124
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of “Next-Generation BioGreen21 Program for Agriculture & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01103501)” Rural Development Administration. Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Kim, J.Y., Kim, D.Y. et al. Development of a SCAR marker associated with salt tolerance in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) from a semi-arid region. Genes Genom 38, 939–948 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0438-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0438-y