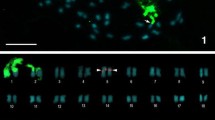
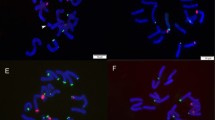
Abstract
Among the nine species of the genus Coix, C. lacrymajobi L. and C. gigantea Koen. have 2n = 20 small chromosomes and C. aquatica Roxb. 2n = 10 large chromosomes, and are widely distributed in South and South East Asia, the first is cultivated and spread to all warmer parts of the world. The other species have restricted localized distribution. C. aquatica originated from a hypothetical diploid ancestor with 2n = 10 small chromosomes, which became longer through accumulation of duplicate segments and heterochromatin and adapted to wet habitats. C. lacrymajobi and C. gigantea originated through the same two small chromosome diploid ancestors, one of which may be common to C. aquatica, through allopolyploidy and adapted to drier conditions. All the three species can survive equally well in wet and dry localities. Aneuploid and polyploid races occurred through chromosome nondisjunction and genome doubling in C. gigantea and C. aquatica, generation of alien-addition and substitution chromosome races appears to be the further course of evolution. Six morphological varieties were differentiated in C. lacrymajobi through accumulation of gene mutations, and chromosome structural changes gave rise to a completely euchromatic chromosome race. Two aneuploid species with 2n = 32 chromosomes, both large and small, must have originated through allopolyploidy, with C. aquatica (n = 6) race as one of the parents in both, C. lacrymajobi and C. gigantea (n = 10) the second parent in Madhya Pradesh form and West Bengal form respectively. From comparison of morphology and their distribution, C. puellarum Balansa, C. ouwehandii Koord. and C. poilanei Mimeur are speculated to have originated from the three established species, through chromosomal changes and gene mutations and adapted to restricted localized areas, and C. gasteenii Simon an allopolyploid form of C. lacrymajobi and C. gigantea. A schematic diagram is presented depicting the origin, evolution and interrelationships in the genus.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora RK. Job’s tears (Coix lacrymajobi) a minor food and fodder crop of North Eastern India. Econ Bot. 1977;31:358–66.
Barve SS, Sangeetha JS. Cytological studies in 2n = 17 Coix gigantea (Maydeae). J Cytol Genet. 2008;9:79–83.
Bor NL. Grasses of Burma Ceylon India and Pakistan. New York: Pergamon Press; 1960.
Christopher J, Jacob B. Cytology of a new hexaploid cytotype of Coix lacrymajobi Linn. Cytologia. 1990;55:57–60.
Christopher J, Jacob B. Cytological studies of Coix gigantea Koen ex Roxb from South India. Cytologia. 1991;56:265–8.
Christopher J, Mini LS. Karyomorphological studies of a new taxon of Coix Linn. J Cytol Genet. 1988;23:113–7.
Christopher J, Mini LS, Omana Kumari N. Cytological evidence for the hybrid origin of Coix taxon (2n = 32). Caryologia. 1995;48:181–8.
Christopher J, Mini LS, Omana Kumari N. Hybridization studies in Coix sps 1 Cytomorphological studies of Coix taxon (2n = 32) C gigantea Koen ex Roxb (2n = 12) and the F1 hybrid. Cytologia. 1995;60:249–56.
Christopher J, Mini LS, Omana Kumari N. Cytotaxonomic studies of the genus Coix L 1 Cytomorpholgoical studies of C gigantea Koenig ex Roxb. Cytologia. 1996;61:41–6.
Christopher J, Mini LS, Omana Kumari N. Cytological studies of interspecific hybrids between C lacrymajobi (2n = 20) and C gigantea (2n = 12) Koenig ex Roxb. Caryologia. 1997;50:175–84.
Christopher J, Mini LS, Pillai TN. Karyomorphological studies of Coix aquatica Roxb. Cytologia. 1989;54:169–72.
Darlington CD, Janaki Ammal EK. Chromosome atlas of cultivated plants. London: Allen and Unwin Ltd; 1945.
Fox I. Conserving Coix gasteenii a rare grass from Cape York Peninsula. Danthonia. 2000;9:6–7.
George AS. Flora of Australia 43 Poaceae—Introduction and Atlas ORCHARD AE Biological Research Study Australia Bureau of Flora and Fauna CSIRO; 1982.
Han YH, Li DY, Li YC, Xue YG, Hu ZI, Song YC. Cytogenetic identification of a new hexaploid Coix aquatica cytotype. Acta Bot Sin. 2004;46:724–9.
Jacob B. Cytomorphological and karyological studies of Coix species (Tribe Maydeae Poaceae) from India. PhD Thesis University of Kerala Thiruvananthapuram India; 1992.
Jacob B, Christopher J. Chromosome behaviour and pachytene morphology of Coix gigantea. Cytologia. 1992;57:303–8.
Koul AK. Interspecific hybridization in Coix 1 Morphological and cytological studies of the hybrids of a new form of Coix with 2n = 32 X C. aquatica Roxb. Genetica. 1965;36:315–34.
Koul AK, Paliwal RL. Morphology and cytology of a new species of Coix with 32 chromosomes. Cytologia. 1964;29:378–86.
Mimeur G. Systematique specific dugenre Coix et systematique varietale de Coix lacrymajobi Morphologie de cette petite cereale et etude de sa plantule. Rev Int Bot Appl Agric Trop. 1951;31:197–211.
Nirmala A. Cytomorphological study of Coix gigantea Koen (2n = 8x = 40) and its interracial and interspecific hybrids. Nucleus. 2003;40:115–9.
Nirmala A, Rao PN. Meiosis in an interchange heterozygote of Coix gigantea. Maydica. 1983;28:77–80.
Nirmala A, Rao PN. Chromosome instability in Coix gigantea Koen (Maydeae). Can J Genet Cytol. 1984;26:334–8.
Nirodi N. Studies in Asiatic relatives of maize. Ann Mo Bot Gard. 1955;42:103–30.
Rao PN. Cytogenetic studies in Coix with some observations on other Oriental Maydeae. Ph D Thesis Andhra University Visakhapatnam India; 1973.
Rao PN. Chromosome elimination in trisomics of Coix aquatica Roxb. Theor Appl Genet. 1976;48:179–84.
Rao PN. Studies on the occurrence cytology fertility and breeding behaviour of aneuploids in induced autotetraploid job’s tears. Cytologia. 1976;41:145–52.
Rao PN. A cytogenetic study of triploids and aneuploids in job’s tears Coix lacrymajobi L. Cytologia. 1977;42:671–9.
Rao PN. Aneuploidy and interchange hybridity in triploid job's tears. In: Manna GK, Sinha U, editors. Perspectives in cytology and genetics. Delhi: Hindasia Publishers; 1981. p. 171–3.
Rao PN, Narayana DS. Occurrence and identification of semigamy in Coix aquatica (tribe Maydeae). J Hered. 1980;71:117–20.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Developmental variation in chromosome number in Coix gigantea (Maydeae). In: Maheswari Devi H, Rao PN, Rao KVM, editors. Recent advances in developmental morphology of crop plants. Dehradun: Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh; 1990. p. 137–43.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Interspecific homologies in Coix lacrymajobi L and C gigantea Koen (Maydeae). Cytologia. 1993;58:355–60.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Cytogenetic study of interspecific hybrids of Coix aquatica Roxb and C gigantea Koen. Cytologia. 1994;59:59–63.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Interspecific hybridization and genome relationships of Coix lacrymajobi L and C aquatica Roxb. Nucleus. 1994;37:10–5.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Inter- and intraspecific chromosome pairing and phylogeny in the genus Coix. Nucleus. 2001;44:52–68.
Rao PN, Nirmala A. Classification of the genus Coix L (Maydeae). J Indian Bot Soc. 2010;89:51–62.
Rao PN, Venkateswarlu J. Studies on the occurrence and relationships of multiple styles double seeds and twin seedlings in Coix aquatica. Maydica. 1976;21:145–55.
Rao PN, Venkateswarlu J. A translocation heterozygote in job’s tears Coix lacrymajobi L. Maydica. 1977;22:119–23.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Cytological studies in a spontaneous autotriploid of Coix aquatica Roxb. Curr Sci. 1982;48:67–9.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Nullisomy to hexasomy in Coix gigantea (Poaceae). Cytologia. 1984;49:345–9.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Cytology of higher polysomics in Coix gigantea (Poaceae) pentasomy and hexasomy. Genetica. 1985;66:73–80.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Typical meiotic nondisjunction and its consequences in Coix gigantea. J Hered. 1985;76:387–9.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Double interchange heterozygote among the nullisomics of Coix gigantea. Curr Sci. 1985;54:519–20.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Monosomic-trisomic Coix gigantea. Curr Sci. 1986;55:363–4.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Cytological studies in tetrasomics of Coix gigantea. Cytologia. 1987;52:323–30.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Nullisomic-trisomic in Coix gigantea (Poaceae). Curr Sci. 1988;57:90–1.
Sapre AB, Barve SS. Cytology of a monosomic-trisomic Coix gigantea (Poaceae). Genetica. 1989;79:63–7.
Sapre AB, Barve SS, Deshpande DS. Cytological report on the spontaneous interspecific hybrids in Coix L involving aneuploids. Cytologia. 1985;50:655–61.
Sapre AB, Deshpande DS. A chromosomal range in the interspecific hybrids and hybrid derivatives of Coix L (Poaceae). Curr Sci. 1986;55:363–4.
Sapre AB, Deshpande DS. Origin of B chromosomes in Coix L through spontaneous interspecific hybridization. J Hered. 1987;78:191–6.
Sapre AB, Deshpande DS. Spontaneous emergence of parents from the F1 interspecific hybrids of Coix L. J Hered. 1987;78:357–60.
Sapre AB, Deshpande DS. Isolation of a series of chromosomal variants (2n = 10–21) from an open pollinated population of interspecific hybrids between Coix gigantea and C aquatica (Poaceae). Genetica. 1987;74:61–8.
Sapre AB, Mishra NS. A quadruple trisomic among the open pollinated progeny of an autotriploid Coix lacrymajobi. Cytologia. 1990;55:539–95.
Sapre AB, Naik AS. Formation of aneuploid gametes through nondisjunction during premeiotic mitoses in Coix gigantea. Cytologia. 1990;55:71–7.
Sapre AB, Naik AS. Occurrence of an octosomic plant among selfed progeny of tetrasomic Coix gigantea Roxb. Cytologia. 1991;56:27–9.
Sapre AB, Naik AS, Barve SS. Spontaneous allotetraploid of Coix gigantea X C aquatica. Curr Sci. 1988;57:191–2.
Simon BK. A new species of Coix L (Poaceae) from Australia. Austrobaileya. 1989;3:1–5.
Thompson WL, Burnham KP. Sampling of rare or elusive species Concepts Designs and Techniques for Estimating Population Parameters. Island Press; 2004.
Venkateswarlu J. Cytological observations on spontaneously occurring ring and chain formation in Coix aquatica. J Indian Bot Soc. 1958;37:329–33.
Venkateswarlu J, Chaganti RSK. Population structure in Coix aquatica Roxb. J Cytol Genet. 1966;1:14–21.
Venkateswarlu J, Chaganti RSK. Job’s tears (Coix lacrymajobi L). Tech Bull 44 ICAR New Delhi; 1973.
Venkateswarlu J, Chaganti RSK, Rao PN. Pachytene chromosome morphology and its bearing on interspecific and intergeneric relationships of Coix. Bot Mus Leaf Harv Univ. 1976;24:205–24.
Venkateswarlu J, Rao PN. Apomixis in Coix aquatica Roxb. Ann Bot. 1975;39:1131–6.
Venkateswarlu J, Rao PN. Divergent meiotic behaviour in tetraploids of Coix aquatica Roxb. Nucleus. 1976;19:150–2.
Venkateswarlu J, Rao PN. Effect of inbreeding and selection for vigour and fertility on meiotic behaviour in autotetraploid job’s tears Coix lacrymajobi L. Theor Appl Genet. 1976;47:165–9.
Venkateswarlu J, Rao PN. Cytogenetic behaviour of a fragment chromosome in job’s tears Coix lacrymajobi L. Curr Sci. 1977;46:120–1.
Venkateswarlu J, Rao PN, Rao MK. Cytomorphological study of induced autotetraploid job’s tears. Nucleus. 1976;19:4–7.
Watt G. Coix spp or Job’s tears A review of all available information. Agric Ledger. 1904;11:189–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P.N., Nirmala, A. Chromosomal basis of evolution in the genus Coix L. (Maydeae): a critical appraisal. Nucleus 53, 13–24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-010-0013-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-010-0013-x