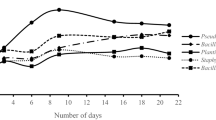
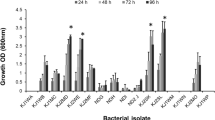
Abstract
An efficient hydrocarbon-degrading native bacterial strain Bacillus pumilus KS2 (identified by partial 16S rDNA gene sequencing) was isolated from crude oil-contaminated soil collected from oil fields of Lakowa, Sivasagar district of Assam, India. Experiments were conducted under laboratory conditions to determine the efficiency of this biosurfactant-producing strain to degrade polycyclicaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Quantification of the capacity of the biosurfactant to reduce the surface tension (ST) of the culture medium was used as a measure of biosurfactant production. In terms of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) degradation, strain KS2 was able to degrade 80.44 % of the TPH by 4 weeks of incubation. It also demonstrated efficient degradation of PAHs, completely degrading nine of the 16 major PAHs present in the crude oil sample. Strain KS2 also produced biosurfactant which, based on biochemical and FTIR analyses, was glycolipid in nature. To our knowledge, this is the first report showing the potential of a native strain of the North-East region of India for efficient degradation of TPH and PAHs and, consequently, in the remediation of hydrocarbons from contaminated sites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas RM (1981) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev 45(1):180–209
Bamforth SM, Singleton I (2005) Bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: current knowledge and future directions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:723–736
Banat IM (1995) Biosurfactant production and possible uses in microbial enhanced oil recovery and oil pollution remediation: review. Bioresour Technol 55:1–12
Bodour AA, Miller-Maier RM (1998) Application of a modified drop-collapse technique for surfactant quantitation and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 32:273–280
Bordoloi NK, Konwar BK (2009) Bacterial biosurfactant in enhancing solubility and metabolism of petroleum hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mater 170:495–505
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R (2008) Improved bioavailability and biodegradation of a model polyaromatic hydrocarbon by a biosurfactant producing bacterium of marine origin. Chemosphere 72:1229–1234
Déziel E, Paquette G, Villemur R, Lepine F, Bisaillon J (1996) Biosurfactant production by a soil Pseudomonas strain growing on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1908–1912
Francy DS, Thomas JM, Raymond RL, Ward CH (1991) Emulsification of hydrocarbons by subsurface bacteria. J Ind Microbiol 8:237–246
Ganeshalingam S, Legge RL, Anderson WA (1994) Surfactant enhanced leaching of poly aromatic hydrocarbons from soil. Trans Inst Chem Eng 72:247–251
George S, Jayachandran K (2009) Analysis of Rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced through submerged fermentation using orange fruit peelings as sole carbon source. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158:694–705
Georgiou G, Lin S, Sharma MM (1992) Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Biotechnology 10:60–65
Gilewicz M, Ni'matuzahroh T, Nadalig H, Budzinski H, Doumenq P, Michotey V, Bertrand JC (1997) Isolation and characterization of a marine bacterium capable of utilizing 2-methylphenanthrene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:528–533
Harayama S (1997) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon bioremediation design. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:268–273
Hickey AM, Gordon L, Dobson AD, Kelly CT, Doyle EM (2007) Effect of surfactants on fluoranthene degradation by Pseudomonas alcaligenes PA-10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(4):851–856
Jacques RJS, Okeke BC, Bento FM, Peralba MCR, Camargo FAO (2007) Characterization of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading microbial consortium from a petrochemical sludge land farming site. Biorem J 11:1–11
Kelley I, Cernigilia CE (1995) Degradation of a mixture of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons by a Mycobacterium strain PYR-1. J Soil Contam 4:77–91
Khanna P, Goyal D, Khanna S (2011) Pyrene degradation by Bacillus pumilus isolated from crude oil contaminated soil. Polycycl Aromat Compd 31(1):1–15
Klug MJ, Markovetz AJ (1971) Utilization of aliphatic hydrocarbons by microorganism. Adv Microb Physiol 5:1–4
Kumari B, Singh SN, Singh DP (2012) Characterization of two biosurfactant producing strains in crude oil degradation. Process Biochem 47:2463–2471
Ma B, Chen H, He Y, Xu JM (2010) Isolations and consortia of PAH-degrading bacteria from the rhizosphere of four crops in PAH contaminated field. In: 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World. Brisbane, pp 63–66 (published on DVD)
Mandri T, Lin J (2007) Isolation and characterization of engine oil degrading indigenous microorganisms in Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr J Biotechnol 6(1):23–27
Mittal A, Singh P (2009) Isolation of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria from soils contaminated with crude oil spills. Indian J Exp Biol 47:760–765
Mulligan CN, Gibbs BF (2004) Types, production and applications of biosurfactants. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 70:31–55
Nguyen TT, Youssef NH, Mclnerney MJ, Sabatini DA (2008) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant mixtures for environmental remediation. Water Res 42:1735–1743
Nie M, Yin X, Ren C, Wang Y, Xu F, Shen Q (2010) Novel rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NY3. Biotechnol Adv 28(5):635–643
Nievas ML, Commendatore MG, Estevas JL, Bucalá V (2008) Biodegradation pattern of hydrocarbons from a fuel oil-type complex residue by an emulsifier producing microbial consortium. J Hazard Mater 154:96–104
Nilsson WB, Strom MS (2002) Detection and identification of bacterial pathogens of fish in kidney tissue using terminal restriction length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Dis Aquat Org 48:175–185
Oberbremer A, Müller-Hurtig R, Wagner F (1990) Effect of the addition of microbial surfactants on hydrocarbon degradation in a soil population in a stirred reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32(4):485–489
Olivera NL, Commendatore MG, Delgado O, Esteves JL (2003) Microbial characterization and hydrocarbon biodegradation potential of natural bilge waste microflora. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30(9):542–548
Pacwa-Plociniczak M, Plaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. J Mol Sci 12:633–654
Phan CW, Bakar NFA, Hamzah A (2013) A comparative study on biosurfactant activity of crude oil-degrading bacteria and its correlation to total petroleum hydrocarbon degradation. Biorem J 17(4):240–251
Rahman KSM, Banat IM, Thahira J, Thayumanavan T, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P (2002) Bioremediation of gasoline contaminated soil by a bacterial consortium amended with poultry litter, coir pith and rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Bioresour Technol 81:25–32
Saikia RR, Deka S, Deka M, Banat IM (2012) Isolation of biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa RS29 from oil-contaminated soil and evaluation of different nitrogen sources in biosurfactant production. Ann Microbiol 62:753–763
Samanta SK, Singh OV, Jain RK (2002) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: environmental pollution and bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol 20(6):243–248
Sawhney SK, Singh R (2000) Introductory practical biochemistry. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 16–17
Singh C, Lin J (2008) Isolation and characterization of diesel oil degrading indigenous microorganisms in Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr J Biotechnol 7(12):1927–1932
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Thenmozhi R, Sornalaksmi AN, Nagasathya A, Praveenkumar D, Thajuddin N (2011) Characterisation of biosurfactant produced by bacterial isolates from engine oil contaminated soil. Adv Environ Biol 5(8):2402–2408
Toledo FL, Calvo C, Rodelas B, Lez-Lopez GJ (2006) Selection and identification of bacteria isolated from waste crude oil with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal capacities. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:244–252
Viramontes-Ramos S, Portillo-Ruiz MC, Ballinas-Casarrubias ML, Torres-Muñoz JV, Rivera-Chavira BE, Nevárez-Moorillón GV (2010) Selection of biosurfactant/bioemulsifier-producing bacteria from hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 41:668–675
Wong JWC, Fang M, Zhao Z, Xing B (2004) Effect of surfactants on solubilization and degradation of phenanthrene under thermophilic conditions. J Environ Qual 33:2015–2025
Ye D, Siddiqi MA, Maccubbin AE, Kumar S, Sikka HC (1996) Degradation of polynuclear aromatic hydro-carbons by Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Environ Sci Technol 30:136–142
Yuliani H, Sahlan M, Hermansyah H, Wijanarko A (2012) Selection and identification of polyaromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria. World Appl Sci J 20(8):1133–1138
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Director, Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), Guwahati, India for providing laboratory facilities and encouraging the research. Kaustuvmani Patowary is also grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India for providing assistance as a Junior Research Fellow (JRF) to carry out the research work. We also thank Dr. N. Sen Sarma, Associate Professor, and Dr. A. Devi, Assistant Professor, IASST, for their assistance with the FTIR and GC analysis, respectively, at IASST, Guwahati. We expression our appreciation to Dr. Hemen Deka, RA, IASST, for the statistical analysis and Rajeev K. Brahma, Tezpur University, for the phylogenetic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patowary, K., Saikia, R.R., Kalita, M.C. et al. Degradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons employing biosurfactant-producing Bacillus pumilus KS2. Ann Microbiol 65, 225–234 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0854-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0854-7