Abstract
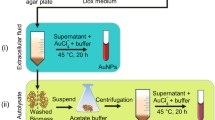
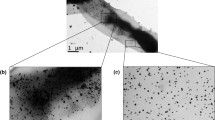
A biogenic route was adopted towards the synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the extract of a novel strain, Talaromyces flavus. Reduction of chloroauric acid by the fungal extract resulted in the production of gold nanoparticle, which was further confirmed by the concordant results obtained from UV–visible spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis. Morphology and the crystal nature of the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED). A direct correlation was observed between nanoparticle formation and the concentration of reducing agent present in the fungal extract. The time-dependent kinetic study revealed that the bioreduction process follows an autocatalytic reaction. Crystalline, irregular, and mostly flower-shaped gold nanoparticles with a mean hydrodynamic radius of 38.54 ± 10.34 nm were obtained. pH played a significant role on production of mono-dispersed nanoparticle. FTIR analysis partially deciphered the involvement of –NH2, −SH, and –CO groups as the probable molecules in the bio-reduction and stabilization process. Compared to the conventional methods, a time-resolved, green, and economically viable method for floral-shaped nanoparticle synthesis was developed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Mukherjee P, Mandal D, Senapati S, Khan MI, Kumar R, Sastry M (2002) Enzyme mediated extracellular synthesis of CdS nanoparticles by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Am Chem Soc 124:12108
Beveridge TJ, Murray RG (1980) Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 141:876–87
Boca S, Rugina D, Pintea A, Barbu-Tudoran L, Astilean S (2011) Flower-shaped gold nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and their application as SERS-active tags inside living cells. Nanotechnology 22: 055702 (7 pp)
Boosalis MG (1956) Effect of soil temperature and green-manure amendment of unsterilized soil on parasitism of Rhizoctonia solani by Penicillium vermiculatum and Trichoderma sp. Phytopathology 46:473–478
Chandran PR, Naseer M, Udupa N, Sandhyarani N (2012) Size controlled synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles and their activity in the oxidation of NADH. Nanotechnology 23:015602
Dong S, Zhou S (2007) Photochemical synthesis of colloidal gold nanoparticles. Mat Sci Eng B 140:153–159
Dykman L, Khlebtsov N (2012) Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: recent advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 41:2256–2282. doi:10.1039/c1cs15166e
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: Noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev 35:209–217
Fravel DR, Davis JR, Sorenson LH (1986) Effect of Talaromyces flavus and metham on Verticillum wilt incidence and potato yield. Biol Cult Tests 1:17
Ghosh S, Patil S, Ahire M, Kitture R, Gurav DD, Jabgunde AM, Kale S, Pardesi K, Shinde V, Bellare J, Dhavale DD, Chopade BA (2012) Gnidia glauca flower extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its chemocatalytic potential. J Nanobiotechnol 10:17
Haiss W, Thanh NTK, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of Size and Concnetration of Gold Nanoparticles from UV–vis Spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–221
Hong X, Hall EAH (2012) Contribution of gold nanoparticles to the signal amplification in surface Plasmon resonance. Analyst 137:4712–719. doi:10.1039/c2an35742a
Huang ZY, Mills G, Hajek B (1993) Spontaneous formation of Silver Particles in Basic 2-Propanaol J. Phys Chem 97:11542–11550
Huang J, Liu Z, Liu X, He C, Chow SY, Pan J (2005) Platinum nanoparticles from hydrosilylation reaction: capping agents, physical characterizations and electrochemical properties. Langmuir 21:699–704
Kim JH, Kang T, Yoo SM, Lee SY, Kim B, Choi YK (2009) A well-ordered flower-like gold nanostructure for integrated sensors via surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nanotechnology 20:235302. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/23/235302
Liangwei D, Xian L, Feng J (2011) Rapid extra-/intracellular biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Penicillium sp. J Nanopart Res 13:921–930. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0165-2
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-Phenol reagents. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luangpipat T, Beattie IR, Chisti Y, Haverkamp RG (2011) Gold nanoparticles produced in a microalga. J Nanopart Res. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0397-9
Mclaren DL, Huang HC, Kozub GC, Rimmer SR (1994) Biological control of sclerotinia wilt of sunflower with Talaromyces flavus and Coniothyrium minitans. Plant Dis 78:231–235
Mukherjee P et al (2001) Bioreduction of AuCl4 –Ions by the Fungus, Verticillium sp. and surface trapping of the gold nanoparticles formed. Angew Chem Int Ed 40:3585–3588
Nayak RR, Pradhan N, Behera D, Pradhan KM, Mishra S, Sukla LB, Mishra BK (2010) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle by Penicillium purpurogenum NPMF: the process and optimization. J Nanopart Res. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0208-8
Nehl LH, Liao H, Hafner JH (2006) Synthesis and Optical properties of Star- shaped gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 6:683. doi:10.1021/nl052409y
Prusinkiewicz MA, Farazkhorasani F, Dynes JJ, Wang J, Gough KM, Kaminskyj SGW (2012) Proof-of-principle for SERS imaging of Aspergillus nidulans hyphae using in vivo synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Analyst. doi:10.1039/c2an35620a
Sanghi R, Verma P (2010) pH dependent fungal proteins in the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Adv Mat Lett 1(3):193–199. doi:10.5185/amlett.2010.5124
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW (2009) Gold nanoparticle: past, present and future. Langmuir 25(24):13840–51. doi:10.1021/la9019475
Sastry M, Ahmad A, Khan MI, Kumar R (2003) Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles using fungi and actinomycete. Curr Sci 85:162–170
Scampicchio M, Wang J, Blasco AJ, Arribas AS, Mannino S, Escarpa A (2006) Nanoparticle-based assays of antioxidant activity. Anal Chem 78:2060–2063
Schmid G, Simon U (2005) Gold nanoparticles: assembly and electrical properties in 1–3 dimensions. Chem Commun,p 697–710. doi:10.1039/b411696h
Serwas AH, Delplancke JL, Jerome R, Jerome C, Canet L (2008) Preparation of stable suspensions of gold nanoparticles in water by sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrason Sonochem 15:1055–1061
Sharma VK, Yngard RA, Lin Y (2009) Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 145:83–96. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2008.09.002
Silverstain RM, Webster FX (1998) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds, 6th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 71–143
Soni N, Prakash S (2012) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Aspergillus niger and its efficacy against mosquito larvae. Rep Parasitol 2:1–7. doi:10.2147/RIP.S29033
Stratakis M, Garcia H (2012) Catalysis by supported gold nanoparticles: beyond aerobic oxidative processes. Chem Rev 112:446–4506. doi:10.1021/cr3000785
Sylvestre JP, Kabashin AV, Sacher E, Meunier M, Luong JHT (2004) Stabilization and size control of gold nanoparticles during laser ablation in aqueous cyclodextrins. J Am Chem Soc 126:7176–7177
Turkevitch J, Stevenson PC, Hiller J (1951) Nucleation and growth process in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Wang L, Wei G, Guo C, Sun L, Sun Y, Song Y, Yang T, Li Z (2008) Photochemical synthesis and self assembly of gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A 312:148–153. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.06.043
Xie H, Tkachenko AG, Glomm WR, Ryan JA, Brennaman MK, Papanikolas JM, Franzen S, Feldheim DL (2003) Critical flocculation concentrations, binding isotherms, and ligand exchange properties of peptide-modified gold nanoparticles studied by UV–Visible, fluorescence, and time-correlated single photon counting spectroscopies. Anal Chem 75:5797–805
Yu Y, Chnag SS, Lee CL, Wang CRC (1997) Gold nanorods: elecrochemical synthesis and optical properties. J Phys Chem B 101:6661. doi:10.1021/jp971656q
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions in improving the manuscript. E. Priyadarshini would like to express her sincere thanks to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India, for fellowship under the DST-Inspire Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
The X-ray diffractogram of GNPs synthesized from T. flavus extract (ECF) using 1mM HAuCl4 (PDF 35 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
(a) Energy dispersive X-ray spectrum SAED pattern of GNP synthesized with (b) ECF (c) BECF (PDF 151 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
DLS analysis representing the size distribution of biosynthesized GNP (a) ECF (b) BECF (c) BBF (PDF 41.1 KB)
Supplementary Fig. 4
FTIR Spectra of fungal extract (ECF) before and after GNP formation (PDF 80.3 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priyadarshini, E., Pradhan, N., Sukla, L.B. et al. Biogenic synthesis of floral-shaped gold nanoparticles using a novel strain, Talaromyces flavus . Ann Microbiol 64, 1055–1063 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0744-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0744-4