Abstract
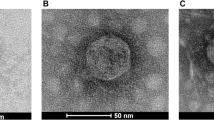
Nine table olive fermentation brines were analysed to demonstrate the presence of lytic bacteriophages active against Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Five brines, out of the nine studied, were added to selected strains of L. plantarum as starter cultures, while the other four brines were left to ferment spontaneously. Turbidity tests with different host strains inoculated in growth medium with added filter-sterilized brines demonstrated the presence of phages able to lyse the sensitive strains. Phages were isolated from fermented brines and their presence was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. A subsequent phage characterization based on host range, restriction analysis and protein profiles was performed. This study reported for the first time the isolation and characterization of L. plantarum phages from table olive fermentation. This demonstrated presence of lytic phages active against L. plantarum could represent a serious obstacle in the regular table olive fermentation process. For these reasons, the search for phage-resistant strains, to use as starter cultures, could be important to counteract the development of fermentation problems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brito MD, Delgado AM, Catulo L, Quintans F, Perese C (2004) The role of bacteriocin producers in table-olive fermentation. In: 5th International Symposium on Olive Growing, Izmir, Turkey
Caso JL, de los Reyes-Gavilàn CG, Herrero M, Montilla A, Rodriguez A, Suarez JE (1995) Isolation and characterization of temperate and virulent bacteriophage of Lactobacillus plantarum. J Dairy Sci 78:741–750
Chibanni-Chennoufi S, Dillmann ML, Marvin-Guy L, Rami-Shojaei S, Brussow H (2004) Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage LP65: a new member of the SPO1-like genus of the family Myoviridae. J Bacteriol 186:7069–7083
Ciafardini G, Marsilio V, Lanza B, Pozzi N (1994) Hydrolysis of oleuropein by Lactobacillus plantarum strains associated with olive fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4142–4147
Cogan TM, Peitersen N, Sellars RL (1991) Starter systems. In: Bulletin International Dairy Federation (FIL-IDF), Practical phage control, 263: 16–23
De Antoni G, Zago M, Vasek O, Giraffa G, Carminati D, Briggiler M, Reinheimer J, Suarez V (2010) Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophages isolated from Kefir grains: phenotypic and molecular characterization. J Dairy Res 77:7–12
Doi K, Zhang Y, Nishizaki Y, Umeda A, Ohmomo S, Ogata S (2003) A comparative study and phage typing of silage-making Lactobacillus bacteriophages. J Biosci Bioeng 95:518–525
Garrido Fernandez A, Fernandez Diaz MJ, Adams RM (1997) Table olives: production and processing. Chapman & Hall, London
Giraffa G (2004) Studying the dynamics of microbial populations during food fermentation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:251–260
IOOC (2004) Trade Standard Applying to Table Olives, COI/OT/NC No 1 December 2004 (Resolution No. RES-2/91-IV/04). International Olive Oil Council, Madrid, Spain
Lanza B, Rossetti L, Zago M, Carminati D, Russi F, Iannucci E, Di Serio MG, Mucciarella MR, Giraffa G (2009) Presenza di fagi nelle salamoie di fermentazione di olive da tavola, In: Proceedings of Convegno Internazionale RIOM, Rende (CS), Italy, 11–12 giugno, pp. 447–449
Leal-Sanchez MV, Ruiz-Barba JL, Sanchez AH, Rejano L, Jimenez-Diaz R, Garrido A (2002) Fermentation profile and optimization of green olive fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum LPCO10 as a starter culture. Food Microbiol 20:421–430
Leroy F, De Vuyst L (2004) Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:67–78
Lillehaug D (1997) An improved plaque assay for poor plaque-producing temperate lactococcal bacteriophages. J Appl Microbiol 83:85–90
Lu Z, Breidt F, Fleming HP, Altermann E, Klaenhammer TR (2003a) Isolation and characterization of a Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage, Φ JL-1, from a cucumber fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 84:225–235
Lu Z, Breidt F, Plengvidhya V, Fleming HP (2003b) Bacteriophage ecology in commercial sauerkraut fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3192–3202
Marsilio V, Lanza B (1998) Characterization of an oleuropein degrading strain of Lactobacillus plantarum. Combined effect of compounds present in olive fermenting brines (phenols, glucose and NaCl) on bacterial activity. J Sci Food Agric 76:520–524
Marsilio V, Lanza B, Pozzi N (1996) Progress in table olives debittering: degradation in vitro of oleuropein and its derivatives by L. plantarum. J Am Oil Chem Soc 73:593–597
Marsilio V, Seghetti L, Iannucci E, Russi F, Lanza B, Felicioni M (2005) Use of a lactic acid bacteria starter culture during green olive (Olea europaea L., cv. Ascolana tenera) processing. J Sci Food Agric 85:1084–1090
Panagou RZ, Tassou CC, Katsaboxakis CZ (2003) Induced lactic acid fermentation of untreated green olives of the Conservolea cultivar by Lactobacillus pentosus. J Agric Food Sci 83:667–674
Rubia-Soria A, Abriouel H, Lucas R, Ben Omar N, Martinez-Canamero M, Galvez A (2006) Production of antimicrobial substances by bacteria isolated from fermented table olives. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:765–768
Ruiz-Barba JL, Cathcart DP, Warner PJ, Jimenez-Diaz R (1994) Use of Lactobacillus plantarum LPCO10, a bacteriocin producer, as a starter culture in Spanish-Style green olive fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2059–2064
Sanders ME (1987) Bacteriophages of industrial importance. In: Goyal SM, Gerba CP, Bitton G (eds) Phage ecology. Wiley, New York, pp 211–244
Servili M, Settanni L, Veneziani G, Esposto S, Massitti O, Taticchi A, Urbani S, Montedoro GF, Corsetti A (2006) The use of Lactobacillus pentosus 1MO to shorten the debittering process time of black table olives (cv. Itrana and Leccino): a pilot-scale application. J Agric Food Chem 54:3869–3875
Svensson V, Christiansson A (1991) Methods for phage monitoring. In: Bulletin International Dairy Federation (FIL-IDF), Practical phage control, 263: 29–39.
Trevors KE, Holley RA, Kempton AG (1983) Isolation and characterization of a Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage isolated from a meat starter culture. J Appl Bacteriol 54:281–288
Yoon SS, Kim JW, Breidt F, Fleming HP (2001) Characterization of a lytic Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage and molecular cloning of a lysin gene in Escherichia coli. Int J Food Microbiol 65:63–74
Yoon SS, Barrangou-Poueys R, Breidt F, Klaenhammer TR, Fleming HP (2002) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from fermenting sauerkraut. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:973–976
Zago M, Carminati D, Giraffa G (2003) Characterization of Streptococcus thermophilus phages from cheese. Ann Microbiol 53:171–178
Zago M, De Lorentiis A, Carminati D, Comaschi L, Giraffa G (2006a) Detection and identification of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis bacteriophages by PCR. J Dairy Res 73:146–153
Zago M, Rossetti L, Fornasari ME, De Lorentiis A, Bonioli A, Perrone A, Giraffa G, Carminati D (2006b) Identificazione e caratterizzazione di batteriofagi di lattobacilli termofili isolati da innesti naturali. Sci Tec Latt Cas 57:525–534
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the Italian Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Forestry - Project ASER-COLMIA "Collection of Microorganisms of interest in agriculture, industry and environment". Strains used in this study belong to ASER-COLMIA collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lanza, B., Zago, M., Carminati, D. et al. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophages from table olive fermentation. Ann Microbiol 62, 1467–1472 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0400-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0400-9