Abstract
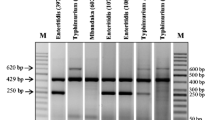
In Tunisia, Salmonella is the most common bacterial agent responsible for childhood diarrhoea. Currently, isolation of the bacterium by microbiological and biochemical methods and confirmation of the serotype by serological method remain as the "gold standard". This study aimed to differentiate among the most common serotypes of Salmonella spp. via two rapid five-plex PCRs assay (MPCR) to evaluate the molecular serotyping method compared with the gold standard serotyping technique. The two five-plex PCRs assays were designed for the simultaneous detection of six genetic loci from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and four from S. enterica serovar Typhi. Sixty-one Tunisian strains (46 collected from patients and 15 from food) were isolated during the period 2002–2007. The STM and STY primers were able to discriminate all tested Salmonella serotypes that represent the most common clinical and food strains of S. enterica subsp. enterica in our laboratory. All strains belonged to 19 different serotypes: 15 serotypes gave unique amplification patterns compared each other and the other 4 serotypes were grouped into two pairs that gave the same molecular profile. We resolved this problem through the addition of a monoplex PCR. Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028 consistently produced the same molecular profile as S. typhimurium laboratory isolates. Interestingly, seven strains of Anatum serovar produced two different PCR profiles with these primers: five strains had the same amplification pattern STM 2,4,5 and STY 2; however, two strains had another molecular profile STM 2,3,5 and STY 2; so the reproducibility of this method was reduced to 93%. The MPCR system is a rapid, specific, and cost-effective molecular method that gas been proved to have efficient discrimination in serotyping of the most common isolates of S. enterica subsp. enterica.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Makker A, Goel SK (2002) Application of the PCR technique for a rapid, specific and sensitive detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Mol Cell Probes 16:243–250
Altwegg M, Hickman-Brenner FW, Farmer JJ (1989) Ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns provide increased sensitivity for typing Salmonella typhi strains. J Infect Dis 160:145–149
Bopp CA, Brenner FW, Fields PI, Wells JG, Stockbine NA (2003) Escherichia, Shigella, and Salmonella. In: Murray PR, Baron EJ, Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Yolken RH (eds) Manual of clinical microbiology, vol 1, 8th edn. ASM Press, Washington D.C,, pp 654–671
Chan K, Baker S, Kim CC, Detweiler CS, Dougan G, Falkow S (2003) Genomic comparison of Salmonella enterica serovars and Salmonella bongori by use of an S. enterica serovar Typhimurium DNA microarray. J Bacteriol 185:553–563
Echeita MA, Herrera S, Garaizar J, Usera MA (2002) Multiplex PCR-based detection and identification of the most common Salmonella second-phase flagellar antigens. Res Microbiol 153:107–113
Esteban E, Snipes K, Hird D, Kasten R, Kinde H (1993) Use of ribotyping for characterization of Salmonella serotypes. J Clin Microbiol 31:233–237
Ezquerra E, Burnens AP, Frith K, Costas M, Stanley J (1993) Molecular genotype analysis of Salmonella bovismorbificans. Mol Cell Probes 7:45–54
Garaizar J, Porwollik S, Echeita A, Rementeria A, Herrera S, Wong RM, Frye J, Usera MA, McClelland M (2002) DNA microarraybased typing of an atypical monophasic Salmonella enterica serovar. J Clin Microbiol 40:2074–2078
Herrera-Leon S, McQuiston JR, Usera MA, Fields PI, Garaizar J, Echeita MA (2004) Multiplex PCR for distinguishing the most common phase 1 flagellar antigens of Salmonella spp. J Clin Microbiol 42:2581–2586
Kim S, Frye JG, Hu J, Fedorka-Cray PJ, Gautom R, Boyle DS (2006) Multiplex PCR-based method for identification of common clinical serotypes of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica. J Clin Microbiol 44:3608–3615
Martinez-Urtaza J, Liebana E, Garcia-Migura L, Perez-Pineiro P, Saco M (2004) Characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium from marine environments in costal waters of Galicia (Spain). Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4030–4034
Nair S, Schreiber E, Thong KL, Pang T, Altwegg M (2000) Genotypic characterization of Salmonella typhi by amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting provides increased discrimination as compared to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and ribotyping. J Microbiol Methods 41:35–43
Nair S, Lin TK, Pang T, Altwegg M (2002) Characterization of Salmonella serovars by PCR-single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. J Clin Microbiol 40:2346–2351
O'Regan E, McCabe E, Burgess C, McGuinness S, Barry T, Duffy G, Whyte P, Fanning S (2008) Development of a real-time multiplex PCR assay for the detection of multiple Salmonella serotypes in chicken samples. BMC Microbiol 8:156
Pang T, Altwegg M, Martinetti G, Koh CL, Puthucheary S (1992) Genetic variation among Malaysian isolates of Salmonella typhi as detected by ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns. Microbiol Immunol 36:539–543
Perch M., Braden C.R., Bishop R., Fields P., Plikaytis R., Tauxe R.V. (2003). Salmonella surveillance summary, 2003. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Ga.
Popoff MY, Bockemuhl J, McWhorter-Murlin A (1992) Supplement 1991 (no. 35) to the Kauffmann-White scheme. Res Microbiol 143:807–811
Porwollik S, Wong RM, McClelland M (2002) Evolutionary genomics of Salmonella: gene acquisitions revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8956–8961
Porwollik S, Boyd EF, Choy C, Cheng P, Florea L, Proctor E, McClelland M (2004) Characterization of Salmonella enterica subspecies I genovars by use of microarrays. J Bacteriol 186:5883–5898
Porwollik S, Santiviago CA, Cheng P, Florea L, McClelland M (2005) Differences in gene content between Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates and comparison to closely related serovars Gallinarum and Dublin. J Bacteriol 187:6545–6555
Shangkuan YH, Lin HC (1998) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis to differentiate different strains of Salmonella typhi and other Salmonella species. J Appl Microbiol 85:693–702
Torpdahl M, Ahrens P (2004) Population structure of Salmonella investigated by amplified fragment length polymorphism. J Appl Microbiol 97:566–573
Uzzau S, Hovi M, Stocker BA (1999) Application of ribotyping and IS200 fingerprinting to distinguish the five Salmonella serotype O6, 7:c:1, 5 groups: Choleraesuis sensu stricto, Choleraesuis var. Kunzendorf, Choleraesuis var. Decatur, Paratyphi C, and Typhisuis. Epidemiol Infect 123:37–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Salem, I., Aouni, M. & Mzoughi, R. Two five-plex PCRs methods for identification of common Salmonella spp. serotypes. Ann Microbiol 60, 135–141 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0021-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0021-8