Abstract
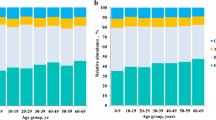
The gut microbial diversity of Thai people was investigated between two large cohorts, adult and elderly subjects, from the middle region of Thailand; the cohorts were divided into different age groups of healthy adult (73) and elderly subjects (47). The diversities of the groups were characterized using a pyrosequencing technique with primers targeting the V6–V8 region of the 16S rRNA gene, and a significant decrease in the Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes ratio from 7.3 to 4.5 was observed with increased age. The microbiota of the adult and elderly groups had a significantly higher abundance of the phylum Actinobacteria, including the three species Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum, and the phylum Bacteroidetes containing the four species Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides caccae and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Firmicutes showed no significant differences between the two groups. Eleven species belonging to Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria were shared by at least 90% of all subjects and defined as core gut microbiota of healthy Thai, among which a high abundance of Escherichia coli was particularly characterized in Thai elderly individuals. Multiple linear regression analysis of age, gender, BMI and diet consumption frequency showed the correlation of age with Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium. Rice consumption frequency showed a significant positive correlation with Bacteroides, while no correlation was found for other factors. Taken together, in the gut of Thai adults, Bifidobacterium decreased and Bacteroides increased with age, while rice consumption increased the abundance of Bacteroides. These link of age and food, especially rice carbohydrate, to gut microbiota and health could be ultimately proposed as the Thai feature.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert C, Scheel J, Engst W, Loh G, Blaut M (2009) Adaptation of protein expression by Escherichia coli in the gastrointestinal tract of gnotobiotic mice. Environ Microbiol 11(4):751–761
Bartosch S, Fite A, Macfarlane GT, McMurdo ME (2004) Characterization of bacterial communities in feces from healthy elderly volunteers and hospitalized elderly patients by using real-time PCR and effects of antibiotic treatment on the fecal microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(6):3575–3581
Becker C, Neurath MF, Wirtz S (2015) The intestinal microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. ILAR J 56(2):192–204
Bentley R, Meganathan R (1982) Biosynthesis of vitamin K (menaquinone) in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 46(3):241–280
Biagi E, Candela M, Fairweather-Tait S, Franceschi C, Brigidi P (2012) Ageing of the human metaorganism: the microbial counterpart. Age 34(1):247–267
Biagi E, Nylund L, Candela M, Ostan R, Bucci L, Pini E, Nikkïla J, Monti D, Satokari R, Franceschi C, Brigidi P, De Vos W (2010) Through ageing, and beyond: gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10667
Brüssow H (2013) Microbiota and healthy ageing: observational and nutritional intervention studies. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):326–334
Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Stat 11(4):265–270
Claesson MJ, Cusack S, O’Sullivan O, Greene-Diniz R, Weerd H, Flannery E (2011) Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(Suppl 1):4586–4591
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power SE, O’Connor EM, Cusack S (2012) Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 488:178–184
Clemente Jose C, Ursell Luke K, Parfrey Laura W, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148(6):1258–1270
Conlon AM, Bird RA (2015) The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 7(1):17–44
Darfeuille-Michaud A, Boudeau J, Bulois P, Neut C, Glasser A-L, Barnich N, Bringer M-A, Swidsinski A, Beaugerie L, Colombel J-F (2004) High prevalence of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli associated with ileal mucosa in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 127(2):412–421
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(33):14691–14696
De Palma G, Nadal I, Collado MC, Sanz Y (2009) Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult human subjects. Br J Nutr 102(8):1154–1160
Duncan SH, Hold GL, Barcenilla A, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2002) Roseburia intestinalis sp. nov., a novel saccharolytic, butyrate-producing bacterium from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52(5):1615–1620
Favier CF, Vaughan EE, De Vos WM, Akkermans ADL (2002) Molecular monitoring of succession of bacterial communities in human neonates. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):219–226
Gavini F, Cayuela C, Antoine J-M, Lecoq C, Lefebvre B, Membré J-M, Neut C (2001) Differences in the distribution of bifidobacterial and enterobacterial species in human faecal microflora of three different (children, adults, elderly) age groups. Microb Ecol Health Dis 13(1):40–45
Geirnaert A, Steyaert A, Eeckhaut V, Debruyne B, Arends JBA, Van Immerseel F, Boon N, Van de Wiele T (2014) Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum, a butyrate producer with probiotic potential, is intrinsically tolerant to stomach and small intestine conditions. Anaerobe 30:70–74
Hayashi H, Sakamoto M, Kitahara M, Benno Y (2003) Molecular analysis of fecal microbiota in elderly individuals using 16S rDNA library and T-RFLP. Microbiol Immunol 47(8):557–570
He F, Ouwehand AC, Isolauri E, Hosoda M, Benno Y, Salminen S (2001) Differences in composition and mucosal adhesion of bifidobacteria isolated from healthy adults and healthy seniors. Curr Microbiol 43(5):351–354
Hopkins MJ, Macfarlane GT (2002) Changes in predominant bacterial populations in human faeces with age and with Clostridium difficile infection. J Med Microbiol 51(5):448–454
Hosseini E, Grootaert C, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T (2011) Propionate as a health-promoting microbial metabolite in the human gut. Nutr Rev 69(5):245–258
Huse SM, Ye Y, Zhou Y, Fodor AA (2012) A core human microbiome as viewed through 16S rRNA sequence clusters. PLoS ONE 7(6):e34242
Kadner RJ (1978) Repression of synthesis of the vitamin B12 receptor in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 136(3):1050–1057
Koenig JE, Spor A, Scalfone N, Fricker AD, Stombaugh J, Knight R, Angenent LT, Ley RE (2011) Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(Suppl 1):4578–4585
La-ongkham O, Nakphaichit M, Leelavatcharamas V, Keawsompong S, Nitisinprasert S (2015) Distinct gut microbiota of healthy children from two different geographic regions of Thailand. Arch Microbiol 197(4):561–573
Léké A, Romond M, Mullié C (2007) Insights in the human bifidobacterial flora through culture-dependent and independent techniques. Commun Curr Res Educ Top Trends Appl Microbiol 2:758–765
Li M, Wang B, Zhang M, Rantalainen M, Wang S, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Shen J, Pang X, Zhang M, Wei H, Chen Y, Lu H, Zuo J, Su M, Qiu Y, Jia W, Xiao C, Smith LM, Yang S, Holmes E, Tang H, Zhao G, Nicholson JK, Li L, Zhao L (2008) Symbiotic gut microbes modulate human metabolic phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):2117–2122
Lindstedt B-A, Finton MD, Porcellato D, Brandal LT (2018) High frequency of hybrid Escherichia coli strains with combined intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (IPEC) and extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) virulence factors isolated from human faecal samples. BMC Infect Dis 18(1):544
Lopetuso LR, Scaldaferri F, Petito V, Gasbarrini A (2013) Commensal Clostridia: leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog 5(1):23
Mäkivuokko H, Tiihonen K, Tynkkynen S, Paulin L, Rautonen N (2009) The effect of age and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on human intestinal microbiota composition. Br J Nutr 103(2):227–234
Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, Guimarăes V, Sokol H, Doré J (2009) The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol 9(1):123
Martínez I, Muller CE, Walter J (2013) Long-Term Temporal analysis of the human fecal microbiota revealed a stable core of dominant bacterial species. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69621
Miquel S, Martín R, Bridonneau C, Robert V, Sokol H, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Thomas M, Langella P (2014) Ecology and metabolism of the beneficial intestinal commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Gut Microbes 5(2):146–151
Mueller S, Saunier K, Hanisch C, Norin E, Alm L, Midtvedt T (2006) Differences in fecal microbiota in different European study populations in relation to age, gender, and country: a cross-sectional study. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1027–1033
Nakayama J (2010) Pyrosequence-based 16S rRNA profiling of gastro-intestinal microbiota. Biosci Microflora 29(2):83–96
Nakayama J, Jiang J, Watanabe K, Chen K, Ninxin H, Matsuda K, Kurakawa T, Tsuji H, Sonomoto K, Lee Y-K (2013) Up to species-level community analysis of human gut microbiota by 16S rRNA amplicon pyrosequencing. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 32(2):69–76
Nakayama J, Watanabe K, Jiang J, Matsuda K, Chao SH, Haryono P (2015) Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci Rep 5:8397
Nam YD, Jung MJ, Roh SW, Kim MS, Bae JW (2011) Comparative analysis of Korean human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 6(7):e22109
Odamaki T, Kato K, Sugahara H, Hashikura N, Takahashi S, Xiao J-z, Abe F, Osawa R (2016) Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: a cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol 16(1):90
Ottman N, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Belzer C (2012) The function of our microbiota: who is out there and what do they do? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:104
Ouwehand AC, Isolauri E, Kirjavainen PV, Salminen SJ (1999) Adhesion of four Bifidobacterium strains to human intestinal mucus from subjects in different age groups. FEMS Microbiol Lett 172(1):61–64
Palmer C, Bik EM, DiGiulio DB, Relman DA, Brown PO (2007) Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol 5(7):e177
Park S-K, Kim M-S, Roh SW, Bae J-W (2012) Blautia stercoris sp. Nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(4):776–779
Power SE, O'Toole PW, Stanton C, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF (2013) Intestinal microbiota, diet and health. Br J Nutr 111(3):387–402
Pryde SE, Duncan SH, Hold GL, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2002) The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217(2):133–139
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, Mende DR, Li J, Xu J, Li S, Li D, Cao J, Wang B, Liang H, Zheng H, Xie Y, Tap J, Lepage P, Bertalan M, Batto J-M, Hansen T, Le Paslier D, Linneberg A, Nielsen HB, Pelletier E, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Turner K, Zhu H, Yu C, Li S, Jian M, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Qin N, Yang H, Wang J, Brunak S, Dore J, Guarner F, Kristiansen K, Pedersen O, Parkhill J, Weissenbach J, Bork P, Ehrlich SD, Wang J (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464(7285):59–65
Ruengsomwong S, Korenori Y, Sakamoto N, Wannissorn B, Nakayama J, Nitisinprasert S (2014) Senior Thai fecal microbiota comparison between vegetarians and non-vegetarians using PCR-DGGE and real-time PCR. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(8):1026–1033
Ruengsomwong S, La-Ongkham O, Jiang J, Wannissorn B, Nakayama J, Nitisinprasert S (2016) Microbial community of healthy Thai vegetarians and non-vegetarians, their core gut microbiota and pathogens risk. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(10):1723–1735
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 90(3):859
Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, Lakhdari O, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Gratadoux J-J, Blugeon S, Bridonneau C, Furet J-P, Corthier G, Grangette C, Vasquez N, Pochart P, Trugnan G, Thomas G, Blottière HM, Doré J, Marteau P, Seksik P, Langella P (2008) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(43):16731–16736
Tap J, Mondot S, Levenez F, Pelletier E, Caron C, Furet J-P, Ugarte E, Muñoz-Tamayo R, Paslier DLE, Nalin R, Dore J, Leclerc M (2009) Towards the human intestinal microbiota phylogenetic core. Environ Microbiol 11(10):2574–2584
Taras D, Simmering R, Collins MD, Lawson PA, Blaut M (2002) Reclassification of Eubacterium formicigenerans Holdeman and Moore 1974 as Dorea formicigenerans gen. nov., comb. nov., and description of Dorea longicatena sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52(2):423–428
Tiihonen K, Ouwehand AC, Rautonen N (2010) Human intestinal microbiota and healthy ageing. Ageing Res Rev 9(2):107–116
Van Tongeren SP, Slaets JPJ, Harmsen HJM, Welling GW (2005) Fecal microbiota composition and frailty. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(10):6438–6442
Vrieze A, Holleman F, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JBL, Nieuwdorp M (2010) The environment within: how gut microbiota may influence metabolism and body composition. Diabetologia 53(4):606–613
Weiskopf D, Weinberger B, Grubeck-Loebenstein B (2009) The aging of the immune system. Transpl Int 22(11):1041–1050
Wexler HM (2007) Bacteroides: the good, the bad, and the Nitty–Gritty. Clin Microbiol Rev 20(4):593–621
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51(2):221–271
Woodmansey EJ, McMurdo MET, Macfarlane GT, Macfarlane S (2004) Comparison of compositions and metabolic activities of fecal microbiotas in young adults and in antibiotic-treated and non-antibiotic-treated elderly subjects. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):6113–6122
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen Y-Y, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334(6052):105–108
Yang Y, Jobin C (2014) Microbial imbalance and intestinal pathologies: connections and contributions. Dis Model Mech 7(10):1131–1142
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M (2012) Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486(7402):222–227
Zhang J, Guo Z, Xue Z, Sun Z, Zhang M, Wang L, Wang G, Wang F, Xu J, Cao H, Xu H, Lv Q, Zhong Z, Chen Y, Qimuge S, Menghe B, Zheng Y, Zhao L, Chen W, Zhang H (2015) A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J 9(9):1979–1990
Zhao L, Qiao X, Zhu J, Zhang X, Jiang J, Hao Y, Ren F (2011) Correlations of fecal bacterial communities with age and living region for the elderly living in Bama, Guangxi. China J Microbiol 49(2):186–192
Zwielehner J, Liszt K, Handschur M, Lassl C, Lapin A, Haslberger AG (2009) Combined PCR-DGGE fingerprinting and quantitative-PCR indicates shifts in fecal population sizes and diversity of Bacteroides, bifidobacteria and Clostridium cluster IV in institutionalized elderly. Exp Gerontol 44(6–7):440–446
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their thanks to all the volunteers who were willing to provide fecal samples for this research. This work was supported by the Royal Golden Jubilee PhD. Scholarship Grant (RGJ-PhD) of the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) and Kasetsart University (PHD/0318/2552), partially supported by the Center for Advanced Studies for Agriculture and Food, Institute for Advanced Studies, Kasetsart University Under the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission, Ministry of Education, Thailand (CASAF PD011), by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) No. 25304006 from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (to Jiro Nakayama) and performed under the Core-to-Core Program, which was financially supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT), Vietnam Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), the National University of Laos, Beuth University of Applied Sciences and Brawijaya University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Ethical statements
This study was approved by the Institute for the Development of Human Research Protection (IHRP) Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand with ethical approval number IHRP 311, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Accession numbers Sequences obtained in this present study have been deposited in the DDBJ Sequence Read Archive (DRA) (BioProject accession number PRJDB5860, PSUB007333 and DRA accession number DRA005889).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La-ongkham, O., Nakphaichit, M., Nakayama, J. et al. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota and the core gut microbiome of healthy Thai humans. 3 Biotech 10, 276 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02265-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02265-7