Abstract
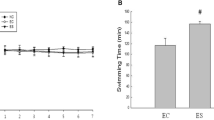
In this study, the anti-fatigue effect of pea peptides in mice was explored. Mice were administrated with pea peptides for 30 days and then anti-fatigue related experiments and assays were performed. Swimming times of mice fed with pea peptides were very significantly longer than those of mice from control group in weight-loaded swimming test. Pea peptides showed very significant effect on decreasing level of blood urea nitrogen and blood lactic acid, increasing content of muscle glycogen and hepatic glycogen. Insulin level and lactate dehydrogenase activity was also improved by pea peptides treatment. Pea peptides demonstrated strong antioxidant activity in vivo test. Moreover, supplementation of pea peptides could improve immunity by increasing phagocyte activity, stimulating sIgA secretion and decreasing the pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice. These findings indicated that pea peptides had strong anti-fatigue effect in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagis S, Tamer L, Sahin G, Bilgin R, Guler H, Ercan B, Erdogan C (2005) Free radicals and antioxidants in primary fibromyalgia: an oxidative stress disorder? Rheumatol Int 25:188–190
Blomstrand B, Newsholme EA (1992) Effect of branched-chain amino acid supplementation on the exercise-induced change in aromatic amino acid concentration in human muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 146:293–298
Calbet JAL, MacLean DA (2002) Plasma glucagon and insulin responses depend on the rate of appearance of amino acids after ingestion of different protein solutions in humans. J Nutr 132:2174–2182
Castell LM (2002) Can glutamine modify the apparent immunodepression observed after prolonged, exhaustive exercise? Nutrition 18:371–375
Chaudhuri A, Behan PO (2004) Fatigue in neurological disorders. Lancet 363:978–988
Childs E, De Wit H (2008) Enhanced mood and psychomotor performance by a caffeine-containing energy capsule in fatigued individuals. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16:13–21
Ding JF, Li YY, Xu JJ, Su XY, Gao X, Yue FP (2011) Study on effect of jellyfish collagen hydrolysate on anti-fatigue and anti-oxidation. Food Hydrocoll. 25:1350–1353
Dohm GL, Tapscott EB, Barakat HA, Kasperek GJ (1983) Influence of fasting on glycogen depletion in rats during exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 55:830–833
Gibson H, Edwards RH (1985) Muscular exercise and fatigue. Sports Med 2:120–132
Hirano T (2010) Interleukin 6 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: a personal memoir. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 86:717–730
Jakubczyk A, Karas M, Baraniak B, Pietrzak M (2013) The impact of fermentation and in vitro digestion on formation angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from pea proteins. Food Chem 141:3774–3780
Jin HM, Wei P (2011) Anti-fatigue properties of tartary buckwheat extracts in mice. Int J Mol Sci 12:4770–4780
Kim J, Hwang H, Park J, Yun HY, Suh H, Lim K (2014) Silk peptide treatment can improve the exercise performance of mice. J Int Soc Sport Nutr 11:35–41
Koo HN, Lee JK, Hong SH, Kim HM (2004) Herbkines increases physical stamina in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 27:117–119
Li D, Ren JW, Zhang T, Liu R, Wu L, Du Q, Li Y (2018) Anti-fatigue effects of small-molecule oligopeptides isolated from Panax quinquefolium L in mice. Food Funct 9:4266–4273
Luo C, Xu X, Wei X, Feng W, Huang H, Liu H, Xu R, Lin J, Han L, Zhang D (2019) Natural medicines for the treatment of fatigue: bioactive components, pharmacology, and mechanisms. Pharmacol Res 148:104409
Marquezi ML, Roschel HA, dos Santa Costa A, Sawada LA, Lancha AH (2003) Effect of aspartate and asparagine supplementation on fatigue determinants in intense exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 13:65–75
Mensah FKF, Bansal AS, Ford B, Cambridge G (2017) Chronic fatigue syndrome and the immune system: Where are we now? Neurophysiol Clin 47:131–138
Miao F, Wu D, Ni G (2016) Evaluation of anti-fatigue activity of flavonoids from tartary buckwheat in mice. Afr J Tradit Compl Altern Med 13:52–60
Miao J, Liao W, Kang M, Jia Y, Wang Q, Duan S, Xiao S, Cao Y, Ji H (2018) Anti-fatigue and anti-oxidant activities of oyster (Ostrea rivularis) hydrolysate prepared by compound protease. Food Funct 9:6577–6585
Monchi M, Rérat AA (1993) Comparison of net protein utilization of milk protein mild enzymatic hydrolysates and free amino acid mixtures with a close pattern in the rat. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 17:355–363
Morifuji M, Kanda A, Koga J, Kawanaka K, Higuchi M (2011) Preexercise ingestion of carbohydrate plus whey protein hydrolysates attenuates skeletal muscle glycogen depletion during exercise in rats. Nutrition 27:833–837
Ndiaye F, Vuong T, Duarte J, Aluko RE, Matar C (2012) Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties of an enzymatic protein hydrolysate from yellow field pea seeds. Eur J Nutr 51:29–37
Niehues M, Euler M, Georgi G, Mank M, Stahl B, Hensel A (2010) Peptides from Pisum sativum L. enzymatic protein digest with anti-adhesive activity against Helicobacter pylori: structure–activity and inhibitory activity against BabA, SabA, HpaA and a fibronectin-binding adhesion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 54:1851–1861
Niepel G, Bibani RH, Vilisaar J, Langley RW, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Constantinescu CS (2013) Association of a deficit of arousal with fatigue in multiple sclerosis: Effect of modafinil. Neuropharmacology 64:380–388
Orzack MH, Taylor CL, Kornetsky C (1968) A research report on the anti-fatigue effects of magnesium pemoline. Psychopharmacologia 13:413–417
Perdigon G, de Macias MEN, Alvarez S, Oliver G, de Ruiz Holgado AAP (1986) Effect of perorally administered lactobacilli on macrophage activation in mice. Infect Immun 53:404–410
Powers SK, Deruisseau KC, Quindry J, Hamilton KL (2004) Dietary antioxidants and exercise. J Sport Sci 22:81–94
Pownall TL, Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE (2010) Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of pea seed (Pisum sativum L.) enzymatic protein hydrolysate fractions. J Agric Food Chem 58:4712–4718
Ren J, Zhao MM, Wang HY, Cui C, You LJ (2011) Effects of supplementation with grass carp protein versus peptide on swimming endurance in mice. Nutrition 27:789–795
Saito K, Jin D, Ogawa T, Muramoto K, Hatakeyama E, Yasuhara T, Nokihara K (2003) Antioxidative properties of tripeptide libraries prepared by the combinatorial chemistry. J Agric Food Chem 51:3668–3674
van Loon LJ, Kruijshoop M, Verhagen H, Saris WH, Wagenmakers AJ (2000) Ingestion of protein hydrolysate and amino acid-carbohydrate mixtures increases postexercise plasma insulin responses in men. J Nutr 130:2508–2513
Villanueva C, Kross RD (2012) Antioxidant-induced stress. Int J Mol Sci 13:2091–2109
Wang J, Li S, Fan Y, Chen Y, Liu D, Cheng H, Gao X, Zhou Y (2010) Anti-fatigue activity of the water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. J Ethnopharmacol 130:421–423
Zheng Z, Yang X, Liu J, Qian P, Hao L, Wang Z, Guo S (2017) Effects of wheat peptide supplementation on antifatigue and immunoregulation during incremental swimming exercise in rats. RSC Adv 7:43345–43355
Zlott DA, Byrne M (2010) Mechanisms by which pharmacologic agents may contribute to fatigue. PM & R 2:451–455
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. 2016GXNSFCA380018, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21702033), and the Start-up Scientific Research Project from the Guangxi University for Nationalities (Grant No. 2016MDQD003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, T., Huang, Y., Tang, Z. et al. Anti-fatigue effects of pea (Pisum sativum L.) peptides prepared by compound protease. J Food Sci Technol 58, 2265–2272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04737-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04737-3