Abstract
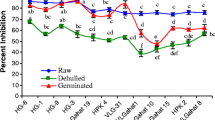
The changes in chemical composition, antioxidant activity and fatty acid composition of lentil flour after dehulling, germination and cooking of seeds were investigated. Dehulling showed no significant effect on protein content, however, protein content decreased in most of the varieties after germination and cooking. Total soluble sugars (TSS) content increased significantly after dehulling (2.0–41.64 %) and cooking (2.08–31.07 %) whereas, germination had no significant effect on TSS content. Total lipids increased significantly after dehulling (21.56–42.86 %) whereas, it decreased significantly after germination (2.97–26.52 %) and cooking (23.05–58.63 %). Cooking was more effective than other methods in reducing trypsin inhibitors (80.51–85.41 %). Dehulling was most effective in reducing tannins (89.46–92.99 %) and phytic acid (52.63–60.00 %) content over raw seed. Myristic, palmitic, stearic, oleic and linoleic acid content decreased while linolenic acid content increased after dehulling. Dehulling, germination and cooking decreased the content of antioxidant metabolite (gallic acid, catechin and quercetin) and also antioxidant activities. Raw samples followed by germinated samples showed the highest concentrations of phytochemicals responsible for antioxidant activity and also the antioxidant capacities. Present study showed germination and cooking would be useful in formulation and development of lentil based functional foods for human health benefits.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adsule RN, Kadam SS (1989) Proteins. In: Salunkhe DK, Kadam SS (eds) Handbook of world food legumes 1. CRC Press, Florida, pp 76–91
Aguilera Y, Dueñas M, Estrella I, Hernández T, Benitez V, Esteban RM, Martín-Cabrejas MA (2010) Evaluation of phenolic profile and antioxidant properties of Pardina lentil as affected by industrial dehydration. J Agric Food Chem 58:10101–10108
Ajayi OB, Ajayi DD (2009) Effect of oilseed diets on plasma lipid profile in albino rats. Pak J Nutr 8:116–118
AOAC (2005) Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Benzie I, Strain J (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of antioxidant power: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Phys 37(8):911–917
Borhade VP, Kadam SS, Salunke DK (1984) Solubilization and functional properties of mothbean (Vigna aconitifolia marechal) and horse gram (Macrotyloma uniflorum L. Verdc.). J Food Biochem 8:229–235
Frias J, Fornal J, Ring SG, Vidal-Valverde C (1998) Effect of germination on physico-chemical properties of lentil starch and its components. LWT Food sci Technol 31(3):228–236
Ghadge SV, Raheman H (2005) Biodiesel production from mahua (Madhuca indica) oil having high free fatty acids. Biomass Bioenergy 28(6):601–605
Ghavidel RA, Prakash J (2007) The impact of germination and dehulling on nutrients, antinutrients, in vitro iron and calcium bioavailability and in vitro starch and protein digestibility of some legume seeds. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:1292–1299
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Sing N (2016) Impact of germination on flour, protein and starch characteristics of lentil (Lens culinaris) and horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum L.) lines. LWT Food Sci Technol 65:137–144
Haug W, Lantzsch HJ (1983) Sensitive method for the rapid determination of phytate in cereals and cereal products. J Sci Food Agr 34:1423–1426
Hedge JE, Hofreiter BT (1962) Determination of reducing sugars and carbohydrate. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN (eds) Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, vol 17. Academic Press, New York, p 420
Huda-Faujan N, Noriham A, Norrakiah AS, Babji AS (2009) Antioxidant activity in plants methanol extract containing phenolic compounds. Afr J Biotechnol 8:484–489
Kaur M, Sandhu KS (2010) Functional, thermal and pasting characteristics of fl ours from different lentil (Lens culinaris) cultivars. J Food Sci Technol 47(3):273–278
Lopez A, Montano A, Garcia P, Garrido A (2006) Fatty acid profile of table olives and its multivariate characterization using unsupervised (PCA) and supervised (DA) chemometrics. J Agric Food Chem 54:6747–6753
Mishra KK, Pal RS, Arun KR, Chandrashekara C, Jain SK, Bhatt JC (2013) Antioxidant properties of different edible mushroom species and increased bioconversion efficiency of Pleurotus eryngii using locally available casing materials. Food Chem 138:1557–1563
Moongngarm A, Saetung N (2010) Comparison of chemical compositions and bioactive compounds of germinated rough rice and brown rice. Food Chem 122(3):782–788
Pal RS, Bhartiya A, ArunKumar R, Kant L, Aditya JP, Bisht JK (2016) Impact of dehulling and germination on nutrients, antinutrients, and antioxidant properties in horsegram. J Food Sci Technol 53(1):337–347
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341
Randhir R, Kwon YI, Shetty K (2008) Effect of thermal processing on phenolics, antioxidant activity and health-relevant functionality of select grain sprouts and seedlings. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 9:355–364
Rao BSN, Prabhavathi T (1982) Tannin content of foods commonly consumed in India and its influence on ionisable iron. J Sci Food Agr 33:89–96
Reddy NR, Pierson MD, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1984) Chemical, nutritional and physiological aspects of dry bean carbohydrates: a review. Food Chem 13:25–68
Sangronis E, Machado CJ (2007) Influence of germination on the nutritional quality of Phaseolus vulgaris and Cajanus cajan. J Food Sci Agri Technol 40(1):116–120
Smith C, Megen WV, Twaalfhoven L, Hitchcock C (1980) The determination of trypsin inhibitor levels in foodstuffs. J Sci Food Agric 31:321–350
Torres A, Frias J, Granito M, Vidal-Valverde C (2007) Germinated Cajanus cajan seeds as ingredients in pasta products: chemical, biological and sensory evaluation. Food Chem 101(1):202–211
Vasishtha H, Srivastava RP, Verma P (2014) Effect of dehusking and cooking on protein and dietary fibre of different genotypes of desi, kabuli and green type chickpeas (Cicer arietinum). J Food Sci Technol 51(12):4090–4095
Vidal-Valverde C, Frias J, Sierra I, Blazquez I, Lambien F, Kuo YH (2002) New functional legume food by germination: effect on the nutritive value of beans, lentils and peas. Eur Food Res Technol 215:472–476
Wang N (2008) Effect of variety and crude protein content on dehulling quality and on the resulting chemical composition of red lentil (Lens culinaris). J Sci Food Agric 88:885–890
Wang N, Daun JK (2004) Eff ect of variety and crude protein content on nutrients and certain anti-nutrients in field pea (Pisum sativum). J Sci Food Agric 84:1021–1029
Wang N, Lewis MJ, Brennan JG, Westby A (1997) Effect of processing methods on nutrients and antinutritional factors in cowpea. Food Chem 58:59–68
Wang N, Hatcher DW, Toews R, Gawalko EJ (2009) Influence of cooking and dehulling on nutritional composition of several varieties of lentils (Lens culinaris). LWT Food Sci Technol 42:842–848
Xu B, Chang SK (2008) Effect of soaking, boiling, and steaming on total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of cool season food legumes. Food Chem 110:1–13
Zhang B, Deng Z, Tang Y, Chen P, Liu R, Ramdath DD, Liu Q, Hernandez M, Tsao R (2014) Fatty acid, carotenoid and tocopherol compositions of 20 Canadian lentil cultivars and synergistic contribution to antioxidant activities. Food Chem 161:296–304
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), for financial support to carry out this work at Vivekanand Parvatiya Krishi Anusandhan Sansthan (VPKAS), Almora (Uttarakhand) 263601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, R.S., Bhartiya, A., Yadav, P. et al. Effect of dehulling, germination and cooking on nutrients, anti-nutrients, fatty acid composition and antioxidant properties in lentil (Lens culinaris). J Food Sci Technol 54, 909–920 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2351-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2351-4