Abstract
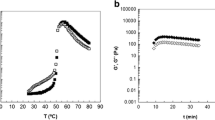
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of different salts (NaF, NaCl, NaBr, NaI, K2SO4, KCl, KNO3, KSCN, LiCl) on freeze–thaw stability, gel strength and rheological properties of potato starch. Addition of the structure-making (salting-out) ions, such as F− and SO4 2−, decreased freeze–thaw stability and increased gel strength, maximal storage modulus (G′) and maximal loss modulus (G″) of potato starch, due to a stronger three-dimensional network by promoting the starch retrogradation and inhibiting starch gelatinization. Shear stress versus shear rate of all samples at 25 °C was well fitted to the simple power-law model with high determination coefficients (R2 = 0.9863–0.9990). Flow behavior index (n), consistency index (K) and apparent viscosities increased with adding salting-out ions. However, the structure-breaking (salting-in) ions had reverse effects on freeze–thaw stability, gel strength and rheological characteristics of potato starch. The addition of structure-breaking ions, such as Br−, NO3 −, I−, SCN−, Na+ and Li+, decreased gel strength, G′ and G″ values and increased freeze–thaw stability. Salts could significantly influence on the retrogradation of potato starch, generally following the ion order: F− > SO4 2− > Cl− > Br− > NO3 − > I− > SCN− for anions and K+ > Na+ > Li+ for cations, consistent with the Hofmeister series.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Jdayil B (2004) Flow properties of sweetened sesame paste (halawa tehineh). Eur Food Res Technol 219:265–272
Ahmad FB, Williams PA (1999) Effect of salts on the gelatinization and rheological properties of sago starch. J Agric Food Chem 47:3359–3366
Arunyanart T, Charoenrein S (2008) Effect of sucrose on the freeze–thaw stability of rice starch gels: correlation with microstructure and freezable water. Carbohydr Polym 74:514–518. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.002
BeMiller JN, Whistler RL (eds) (2009) Starch: chemistry and technology, 3rd edn. Academic Press, NewYork
Ferrero C, Martino M, Zaritzky N (1994) Corn starch–xanthan gum interaction and its effect on the stability during storage of frozen gelatinized suspension. Starch-Stärke 46:300–308
Fredriksson H, Silverio J, Andersson R, Eliasson AC, Åman P (1998) The influence of amylose and amylopectin characteristics on gelatinization and retrogradation properties of different starches. Carbohydr Polym 35:119–134
Hagenimana A, Pu P, Ding X (2005) Study on thermal and rheological properties of native rice starches and their corresponding mixtures. Food Res Int 38:257–266. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2004.05.009
Huang M, Kennedy J, Li B, Xu X, Xie B (2007) Characters of rice starch gel modified by gellan, carrageenan, and glucomannan: a texture profile analysis study. Carbohydr Polym 69:411–418
Jiang X, Li H, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Hou L (2016) Studies of the plasticizing effect of different hydrophilic inorganic salts on starch/poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Int J Biol Macromol 82:223–230. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.046
Julianti E, Rusmarilin H, Ridwansyah Yusraini E (2015) Functional and rheological properties of composite flour from sweet potato, maize, soybean and xanthan gum. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci. doi:10.1016/j.jssas.2015.05.005
Kaur L, Singh J, McCarthy OJ, Singh H (2007) Physico-chemical, rheological and structural properties of fractionated potato starches. J Food Eng 82:383–394
Krystyjan M, Sikora M, Adamczyk G, Tomasik P (2012) Caramel sauces thickened with combinations of potato starch and xanthan gum. J Food Eng 112:22–28. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.03.035
Leberman R (1991) The Hofmeister series and ionic strength. Fed Eur Biochem Soc 284:293–294
Lee CM, Chung KH (1989) Analysis of surimi gel properties by compression and penetration tests. J Text Stud 20:363–377
Li Q, Xie Q, Yu S, Gao Q (2014) Application of digital image analysis method to study the gelatinization process of starch/sodium chloride solution systems. Food Hydrocoll 35:392–402. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.06.017
Li Q, Zhang L, Ye Y, Gao Q (2015) Effect of salts on the gelatinization process of Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita) starch with digital image analysis method. Food Hydrocoll 51:468–475. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.045
Matalanis AM, Campanella OH, Hamaker BR (2009) Storage retrogradation behavior of sorghum, maize and rice starch pastes related to amylopectin fine structure. J Cereal Sci 50:74–81. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2009.02.007
Miles MJ, Morris VJ, Orford PD, Ring SG (1985) The roles of amylose and amylopectin in the gelation and retrogradation of starch. Carbohydr Res 135:271–281
Muadklay J, Charoenrein S (2008) Effects of hydrocolloids and freezing rates on freeze–thaw stability of tapioca starch gels. Food Hydrocoll 22:1268–1272. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.06.008
Razavi S, Karazhiyan H (2009) Flow properties and thixotropy of selected hydrocolloids: experimental and modeling studies. Food Hydrocoll 23:908–912
Rockland LB, Stewart GF (1981) Water activity: influences on food quality. Academic Press, London
Singh J, McCarthy O, Singh H (2006) Physico-chemical and morphological characteristics of New Zealand Taewa (Maori potato) starches. Carbohydr Polym 64:569–581. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.11.013
Singh McCarthy O, Singh H, Moughan PJ, Kaur L (2007) Morphological, thermal and rheological characterization of starch isolated from New Zealand Kamo Kamo (Cucurbita pepo) fruit—a novel source. Carbohydr Polym 67:233–244. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.05.021
Singh N, Isono N, Srichuwong S, Noda T, Nishinari K (2008) Structural, thermal and viscoelastic properties of potato starches. Food Hydrocoll 22:979–988. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.05.010
Sodhi NS, Singh N (2003) Morphological, thermal and rheological properties of starches separated from rice cultivars grown in India. Food Chem 80:99–108
Steffe JF (1996) Rheological methods in food process engineering. Freeman Press, East Lansing
Wang L, Xie B, Xiong G, Wu W, Wang J, Qiao Y, Liao L (2013) The effect of freeze–thaw cycles on microstructure and physicochemical properties of four starch gels. Food Hydrocoll 31:61–67. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.10.004
Wang W, Zhou H, Yang H, Zhao S, Liu Y, Liu R (2017) Effects of salts on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of maize starch and waxy maize starch. Food Chem 214:319–327. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.040
Xie Y, Hu X, Jin Z, Xu X, Chen H (2014) Effect of repeated retrogradation on structural characteristics and in vitro digestibility of waxy potato starch. Food Chem 163:219–225. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.04.102
Yamin F, Lee M, Pollak L, White P (1999) Thermal Properties of Starch in Corn Variants Isolated After Chemical Mutagenesis of Inbred Line B73 1. Cereal Chem 76:175–181
Yuan R, Thompson D (1998) Freeze–thaw stability of three waxy maize starch pastes measured by centrifugation and calorimetry. Cereal Chem 75:571–573
Zeng F, Zhao X, Zhou T, Liu G (2012) Dual-wavelength colorimetric method for measuring amylose and amylopectin contents of potato starch. Mod Food Sci Technol 28:119–122
Zhou Z, Robards K, Helliwell S, Blanchard C (2007) Effect of the addition of fatty acids on rice starch properties. Food Res Int 40:209–214. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2006.10.006
Zhou X, Baik B-K, Wang R, Lim S-T (2010) Retrogradation of waxy and normal corn starch gels by temperature cycling. J Cereal Sci 51:57–65. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2009.09.005
Zhou H, Wang C, Shi L, Chang T, Yang H, Cui M (2014) Effects of salts on physicochemical, microstructural and thermal properties of potato starch. Food Chem 156:137–143. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.015
Zhu F, Cai Y-Z, Sun M, Corke H (2009) Effect of phytochemical extracts on the pasting, thermal, and gelling properties of wheat starch. Food Chem 112:919–923
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledges the financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Project 2013PY096) and the Ministry of Scientific and Technology, China (Grant No. 2012BAD28B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhou, H., Yang, H. et al. Effects of salts on the freeze–thaw stability, gel strength and rheological properties of potato starch. J Food Sci Technol 53, 3624–3631 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2350-5
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2350-5