Abstract
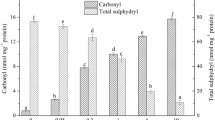
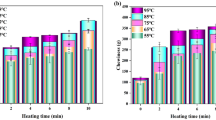
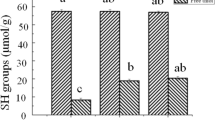
Ultrasonication has been suggested as a new promising technique to improve the quality of meat and other meat products. In this study ultrasonication at low frequency (20 kHz) was carried out to investigate the effect on structural and biochemical properties of myofibril proteins. The possible implications between ultrasonication-induced structural changes and gelation properties were also investigated. Structural changes were investigated by ATPase activity, SDS-PAGE, circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. Microstructural changes in heat induced gels were observed by SEM and water holding capacity was determined by centrifugation. Ultrasonic treatment for 30 min significantly reduced the Ca2+-ATPase activity. Moreover significant change in structure of proteins at secondary level, as indicated by marked decrease in α-helicity, was observed. Marginal change in fluorescence at 10 min was followed by significant increase at 20 and 30 min reflecting exposure of hydrophobic residues on surface during unfolding. Microstructural analyses of gels showed marked improvement in regular three dimensional network at 20 and 30 min of sonication. WHC at 20 min and 30 min were significantly higher than control. Our results suggest that ultrasonication at low frequency (20 kHz) can prove beneficial for improving functional properties of meat and meat products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad R, Hasnain A (2013) Ultrasonication of chicken natural actomyosin: effect on ATPase activity, turbidity and SDS-PAGE profiles at different protein concentrations. Am J Biochem Mol Biol 3(2):240–247
Barany M, Barany K, Oppenheimer H (1963) Effect of ultrasonics on the adenosine triphosphatase activity and actin-binding ability of L-myosin and heavy meromyosin. Nature 199:694–695
Benjakul S, Seymour TA, Morrissey MT, An H (1997) Physicochemical changes in pacific whiting muscle proteins during iced storage. J Food Sci 62(4):729–733
Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Ishizaki S, Tanaka M (2001) Differences in gelation characteristics of natural actomyosin from two species of bigeye snapper, priacanthus tayenus and priacanthus macracanthus. J Food Sci 66(9):1311–1318
Cárcel JA, Benedito J, Bon J, Mulet A (2007) High intensity ultrasound effects on meat brining. Meat Sci 76(4):611–619
Chan JK, Gill TA, Paulson AT (1992) Cross-linking of myosin heavy chains from cod, herring and silver hake during thermal setting. J Food Sci 57(4):906–912
Chemat F, Khan MK (2011) Applications of ultrasound in food technology: processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason Sonochem 18(4):813–835
Choi SM, Ma CY (2007) Structural characterization of globulin from common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) using circular dichroism and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem 102(1):150–160
Dolatowski Z, Stasiak DM, Latoch A (2000) Effect of ultrasound processing of meat before freezing on its texture after thawing. Electron J Pol Agric Univ 3(2):02
Fiske CH, Subarrow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Greenfield NJ (2007) Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc 1(6):2876–2890
Gulseren I, Guzey D, Bruce BD, Weiss J (2007) Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrason Sonochem 14(2):173–183
Hasnain AU, Samejima K, Takahashi K, Yasui T (1979) Molecular adaptability of carp myosin: a study of some physico-chemical properties and their comparison with those of rabbit myosin. Arch Phys Biochem 87:643–662
Hemung BO, Li-Chan EC, Yongsawatdigul J (2008) Thermal stability of fish natural actomyosin affects reactivity to cross-linking by microbial and fish transglutaminases. Food Chem 111(2):439–446
Ito Y, Tatsumi R, Wakamatsu JI, Nishimura T, Hattori A (2003) The solubilization of myofibrillar proteins of vertebrate skeletal muscle in water. Anim Sci J 74(5):417–425
Jayasooriya SD, Bhandari BR, Torley P, D’arcy BR (2004) Effect of high power ultrasound waves on properties of meat: a review. Int J Food Prop 7(2):301–319
Kelly SM, Jess TJ, Price NC (2005) How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1751:119–139
King L, Lehrer SS (1989) Thermal unfolding of myosin rod and light meromyosin: circular dichroism and tryptophan fluorescence studies. Biochemistry 28(8):3498–3502
Kristinsson HG, Hultin HO (2003) Changes in conformation and subunit assembly of cod myosin at low and high pH and after subsequent refolding. J Agric Food Chem 51(24):7187–7196
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li K, Kang ZL, Zhao YY, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2014) Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve functional properties of batter suspensions prepared from PSE-like chicken breast meat. Food Bioprocess Technol 7(12):3466–3477
Li K, Kang ZL, Zou YF, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2015) Effect of ultrasound treatment on functional properties of reduced-salt chicken breast meat batter. J Food Sci Technol 52(5):2622–2633
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maita TE, Yajima S, Nagata T, Miyanishi S, Nakayama G, Matsuda G (1991) The primary structure of skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain: IV. Sequence of the rod, and the complete 1,938-residue sequence of the heavy chain. J Biochem 110:75–87
McClements DJ (1995) Advances in the application of ultrasound in food analysis and processing. Trend Food Sci Technol 6(9):293–299
McDonnell CK, Allen P, Morin C, Lyng JG (2014) The effect of ultrasonic salting on protein and water–protein interactions in meat. Food Chem 147:245–251
Ogawa M, Kanamaru JUN, Miyashita H, Tamiya T, Tsuchiya T (1995) Alpha-helical structure of fish actomyosin: changes during setting. J Food Sci 60(2):297–299
Okada T, Inoue N, Akiba M (1986) Increasing loss of the bound nucleotide contents of carp myosin B during frozen storage. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52(1):121–126
Perry SV (1955) Myosin adenosinetriphosphate. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 582–588
Petracci M, Cavani C (2012) Muscle growth and poultry meat quality issues. Nutr 4(1):1–12
Puolanne E, Halonen M (2010) Theoretical aspects of water-holding in meat. Meat Sci 86(1):151–165
Reynolds JB, Anderson DB, Schmidt GR, Theno DM, Siegel DG (1978) Effects of ultrasonic treatment on binding strength in cured ham rolls. J Food Sci 43(3):866–869
Riebroy S, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Erikson U, Rustad T (2008) Comparative study on acid-induced gelation of myosin from Atlantic cod (Gardus morhua) and burbot (Lota lota). Food Chem 109(1):42–53
Saleem R, Ahmad R (2016) Effect of low frequency ultrasonication on biochemical and structural properties of chicken actomyosin. Food Chem 205:43–51
Saleem R, Hasnain A, Ahmad R (2015a) Solubilisation of muscle proteins from chicken breast muscle by ultrasonic radiations in physiological ionic medium. Cog Food Agric 1(1):1046716
Saleem R, Hasnain A, Ahmad R (2015b) Changes in some biochemical indices of stability of broiler chicken actomyosin at different levels of sodium bicarbonate in presence and absence of sodium chloride. Int J Food Prop 18(6):1373–1384
Samejima K, Ishioroshi M, Yasui T (1981) Relative roles of the head and tail portions of the molecule in heat-induced gelation of myosin. J Food Sci 46(5):1412–1418
Satoh Y, Nakaya M, Ochiai Y, Watabe S (2006) Characterization of fast skeletal myosin from white croaker in comparison with that from walleye pollack. Fish Sci 72(3):646–655
Siró I, Vén C, Balla C, Jónás G, Zeke I, Friedrich L (2009) Application of an ultrasonic assisted curing technique for improving the diffusion of sodium chloride in porcine meat. J Food Eng 91(2):353–362
Vimini RJ, Kemp JD, Fox JD (1983) Effects of low frequency ultrasound on properties of restructured beef rolls. J Food Sci 48(5):1572–1573
Acknowledgments
We thankfully acknowledge UGC for providing Non-NET Fellowship to RS and the Chairman, Department of Zoology for providing necessary facilities. Sonication facility provided by Prof. S.M. Abbas Abidi is deeply appreciated. Electron microscopy facility provided by USIF, AMU; Fluorescent spectroscopy facility by Department of Chemistry (AMU, Aligarh), and CD spectroscopy by AIRF centre (JNU, New Delhi) is greatly acknowledged. Finally, we are extremely obliged to Dr. Absar-ul Hasnain for useful suggestions and cooperation by Dr. Manish Kumar, Faisal Tarique (JNU New Delhi) Imtiyaaz Ahmad and Sheeraz Ahmad (AMU Aligarh).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, R., Ahmad, R. Effect of ultrasonication on secondary structure and heat induced gelation of chicken myofibrils. J Food Sci Technol 53, 3340–3348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2311-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2311-z