Abstract
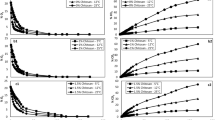
The respiratory behaviour of baby corn - whole and end-cut, under different temperatures and gas conditions was evaluated to study its respiratory dynamics based upon enzyme kinetics. The dependence of respiration rate on the O2 and CO2 concentrations has been described assuming the enzyme kinetics model for combined type of inhibition caused by CO2. Various respiratory parameters viz. maximal O2 consumption rate Michaelis-Menten constants, Inhibition constants under the specified environmental conditions of 5, 12.5, 20°C and 75% relative humidity (RH) were estimated using non-linear regression technique. The enzyme kinetics parameters were analyzed according to Arrhenius law to study their temperature dependence. Based upon the overall analysis, it was found that storage temperature had substantial affect on the partial pressures within the closed containers and subsequently the respiration rates. The concentration of O2 inside the container and surrounding temperature had synergistic effect on the rate of respiration and respiratory parameters. Though the inhibition by evolved CO2 was observed to be of combined type, it changed from predominantly competitive at 5°C to predominantly uncompetitive at 12.5 and 20°C. This study can be utilized for design of modified atmosphere packages for storage of fresh and minimally processed baby corn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Zur A, Saadi H (1990) Prolific maize hybrids for baby corn. J Hort Sci 65(1):97–100
Benkeblia N (2004) Effect of maleic hydrazide on respiratory parameters of stored onion bulbs (Allium cepa L.) Braz. J Plant Physiol 16(1):47–52
Brar JK, Rai DR, Singh A, Kaur N (2011) Biochemical and physiological changes in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum- graecumL.) leaves during storage under modified atmosphere packaging. J Fd. Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0390-4
Charles F, Sanchez J, Gontard N (2005) Modeling of active modified atmosphere packaging of endives exposed to several postharvest temperatures. J Fd Sci 70:443–449
Copeland RA (2000) Enzymes - a practical introduction to structure, mechanism and data analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH, Germany
Emond JP, Castaigne F, Toupin CJ, Desilets D (1991) Mathematical modeling of gas exchange in modified atmosphere packaging. Trans ASAE 34:239–245
Fishman S, Rodov V, Peretz J, Ben-Yehoshua S (1995) Model for gas exchange dynamics in modified atmosphere packages. J Fd Sci 61:956–961
Fonseca SC, Oliveira FAR, Brecht JK (2002) Modeling respiration rate of fresh fruits and vegetables for modified atmosphere packages: a review. J Food Engg 52:99–119
Fonseca SC, Oliveira FAR, Lino IBM, Brecht JK, Chau KV (2000) Modeling O2 and CO2 exchange for development of perforation–mediated modified atmosphere packaging. J Fd Engg 43:9–15
Geysen S, Verlinden BE, Conesa A, Nicolai BM (2005) Modelling respiration of strawberry (cv. Elsanta) as a function of temperature, carbon dioxide, low and superatmospheric oxygen concentration. Frutic 05, 12–16 September 2005, Montpellier, France
Gorny JR (1997) A summary of CA and MA requirements and recommendations for fresh cut (minimally processed) fruits and vegetables, pp 30–66, In: Gorney J (ed) CA’97 Proceedings vol. 5, Fresh cut fruits and vegetables and MAP. Univ. California. Postharvest Hort. Ser. 19
Hallauer AR (2000) Specialty corns, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hertog MLATM, Peppelenbos HW, Evelo RG, Tijskens LMM (1998) A dynamic and generic model of gas exchange of respiring produce: the effects of oxygen, carbon dioxide and temperature. Postharvest Biol and Technol 14:335–349
Ishikawa Y, Sato H, Ishitani T, Hirata T (1992) Evaluation of broccoli respiration rate in modified atmosphere packaging. J Pack Sci Technol 1:143–153
Jacxsens L, Devlieghere F, Rudder TD, Debevere J (2000) Designing equilibrium modified atmosphere packages for fresh-cut vegetables subjected to changes in temperature. LWT 33:178–187
Kaur P, Rai DR, Paul S (2011) Nonlinear estimation of respiratory dynamics of fresh-cut spinach (Spinacia Oleracea) based on enzyme kinetics. J of Fd Process Engg. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4530.2009.00508.x
Lee DS, Haggar PE, Lee J, Yam KL (1991) Model for fresh produce respiration in modified atmospheres based on the principles of enzyme kinetics. J Fd Sci 56(6):1580–1585
Moretti CL, Arajulo AL, Mattos LM (2003) Evaluation of different oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen combinations employed to extend the shelf life of fresh-cut collard greens. Hort Brass 21:676–680
Nobile MAD, Biaiano A, Benedetto A, Massignan L (2006) Respiration rate of minimally processed lettuce as affected by packaging. J Food Engg 74(1):60–69
Pandey M, Sudhir K, Ahuja R and Tewari D (2010) Field fresh foods: could baby corn create the platform for a big agribusiness? Yale Case :10–036
Peppelenbos HW, Van’t Leven J (1996) Evaluation of four types of inhibition for modeling influence of carbon dioxide on oxygen consumption of fruits and vegetables. Postharvest Biol Technol 7:27–40
Rai DR, Chadha S, Kaur MP, Jaiswal P, Patil RT (2011) Biochemical, microbiological and physiological changes in Jamun (Syzyium cumini L.) kept for long term storage under modified atmosphere packaging. J Fd. Sci Technol 48(3):357–365
Salvador ML, Jaime P, Oria R (2002) Modeling of O2 and CO2 exchange dynamics in modified atmosphere packaging of burlet cherries. J Fd Sci 67:231–235
Talasila PC, Chau KV, Brecht JK and Emond JP (1991) A mathematical model for modified atmosphere packaging of fruits and vegetables. American Society Agricultural Engineers No. 91–6022:16
Talasila PC, Chau KV, Brecht JK (1995) Modified atmosphere packaging under varying surrounding temperatures. Trans ASAE 38(3):869–76
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support in form of Research Associateship provided by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for carrying out this research study. The authors are also grateful to Field Fresh Foods Pvt. Ltd., India for providing the required crop material as and when required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Kumar, A. & Kaur, P. Respiratory dynamics of fresh baby corn (Zea mays L.) under modified atmospheres based on enzyme kinetics. J Food Sci Technol 51, 1911–1919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0735-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0735-7