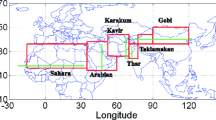
Abstract
The spatial distributions of annual mean concentrations and the annual total depositions of the Asian dust (AD) aerosol and the anthropogenic aerosol (AA) in 2010 are investigated with pollutant emissions over the whole model domain of Asia and without the pollutant emission from South Korea using the Aerosol Modeling System (AMS) that is modified from the Asian Dust Aerosol Model2 (ADAM2) and the Community Multi-Scale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling System. The annual mean surface aerosol concentrations in Asia are found to affect a wide region as a complex mixture of AA and AD aerosols. However, the contribution of the pollutant emission from South Korea is found to be limited to the neighboring regions. The annual total aerosol deposition in Asia is 485.2 Tg. However, the contribution due to the pollutant emission from South Korea is about 1.9 Tg, suggesting of no significant contribution to the environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, A. R., and P. L. Croot, 2010: Atmospheric and marine controls on aerosol iron solubility in seawater. Mar. Chem., 120, 4–13.
Balásházy, I., W. Hofmann, and T. Heistracher, 2003: Local particle deposition pattern may play a key role in the development of lung cancer. J. Appl. Physiol., 94, 1719–1725.
Bates, D. V., B. R. Fish, T. F. Hatch, T. T. Mercer, and P. E. Morrow, 1966: Deposition and retention models for internal dosimetry of the human respiratory tract. Task group on lung dynamics. Health Phys., 12, 173–207.
Binkowski, F. S., and U. Shankar, 1995: The regional particulate matter model, 1. Model description and preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res., 100(D12), 26191–26209.
—, and S. J. Roselle, 2003: Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model aerosol component 1.Model description. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D6), 4183.
Chang, L.-S., and S.-U. Park, 2004: Direct radiative forcing due to anthropogenic aerosols in East Asia during April 2001. Atmos. Environ., 38, 4467–4482.
Chan, C. C., K. J. Chuang, W. J. Chen, W. T. Chang, C. T. Lee, and C. M. Peng, 2008: Increasing cardiopulmonary emergency visits by longrange transported Asian dust storms in Taiwan. Environ Res., 106, 393–400.
Chun, Y., and J. Y. Lim, 2004: The recent characteristics of Asian dust and haze event in Seoul, Korea. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 87, 143–152.
Crutzen, P., 2004: New directions: the growing urban heat and pollution island effect- impact on chemistry and climate. Atmos. Environ., 38, 3539–3540.
Cowie, G., W. Lawson, and N. Kim, 2010: Australian dust causing respiratory disease admissions in some North Island, New Zealand Hospitals. N Z Med. J., 123, 87–88.
Davis, M. E., F. Laden, J. E. Hart, E. Gashick, and T. J. Smith, 2010: Economic activity and trends in ambient air pollution. Environ. Health Persp., 118, 614–619.
Dockery, D. W., J. Schwartz, and J. D. Spengler, 1992: Air pollution and daily mortality: Associations with particulates and acid aerosols. Environ. Res., 59, 362–373.
—, C. A. Pope, X. Xu, J. D. Spengler, J. H. Ware, M. E. Fay, B. G. Ferris, and F. E. Speizer, 1993: An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. New Engl. J. Med., 329, 1753–1759.
Dudhia, J., D. Grill, Y. R. Guo, D. Hausen, K. Manning, and W. Wang, 1998: PSU/NCAR mesoscale modelling system tutorial class notes (MM5 modelling system version 2).
Finlayson-Pitts, B. J., and J. N. Pitts, Jr., 2000: Chemistry of the upper and lower atmosphere: Theory, Experiments, and Application. San Diego, California, USA: Academic Press.
Gao, Q. X., L. J. Li, Y. G. Zhang, and M. Hu, 2000: Studies on the springtime dust storm of China. China Environ. Sci., 20 495–500.
Gomes, L., G. Bergametti, F. Dulac, and U. Ezat, 1990: Assessing the actual size distribution of atmospheric aerosols collected with a cascade impactor. J. Aerosol Sci., 21, 47–59.
Grell, G. A., J. Dudhia, and D. R. Stauffer, 1994: A description of 5th generation Penn State/NCAR mesoscale model (MM5). NCAR TECH. Note NCAR/TN-398.
Husar, R. B., and Coauthors, 2001: Asian dust events of April 1998. J. Geophys. Res., 106(D16), 18317–18330.
IPCC 1995, 1996: The science of Climate change. Cambridge University Press.
In, H.-J., and S.-U. Park, 2003: The soil particle size dependent emission parameterization for an Asian dust (Yellow Sand observed in Korea on April 2002. Atmos. Environ., 37, 4625–2636.
Jacobson, M. Z., 2001: Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature, 409(6821), 695–697.
Jiménez Moreno, Fauquette, S., and J.-P. Suc, 2010: Miocene to Pliocene vegetation reconstruction and climate estimates in the Iberian Peninsula from pollen data. Rev. Palaeobot. Palyno., 162, 403–415.
Jung, J., H. Lee, Y. J. Kim, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Gu, and S. Fan, 2009: Aerosol chemistry and the effect of aerosol water content on visibility impairment and radiative forcing in Guangzhou during the 2006 Pearl River Delta campaign. J. Environ. Manage., 90, 3231–3244.
Kaufman, Y. J., J. V. Martins, L. A. Remer, M. R. Schoeberl, and M. A. Yamasoe, 2002: Satellite retrieval of aerosol absorption over the oceans using sunglint. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 1928.
Kim, K. W., Y. J. Kim, and S. Y. Bang, 2008: Summer time haze characteristics of the urban atmosphere of Gwangju and the rural atmosphere of Anmyon. Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess., 141, 189–199.
Lai, L. Y., and R. Sequeira, 2001.Visibility degradation across Hong Kong: its components and their relative contributions. Atmos. Environ., 35, 5861–5872.
Lee, K. H., Y. J. Kim, and M. J. Kim, 2006: Characteristics of aerosol observed during two severe haze events over Korea in June and October 2004. Atmos. Environ., 40, 5146–5155.
Lu, H., and Y. Shao, 1999: A new model for dust emission by saltation bombardment. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 16827–16842.
Middleton, N., P. Yiallouros, S. Kleanthous, O. Kolokotroni, J. Schwartz, and D. W. Dockery, 2008: A 10-year time-series analysis of respiratory and cardiovascular morbidity in Nicosia, Cyprus: the effect of shortterm changes in air pollution and dust storms. Environ. Health., 7, 1–16.
Miller, R. L., and I. Tegen, 1998: Climate response to soil dust aerosols. J. Climate., 11, 3247–3267.
Park, S.-U, 2015: Spatial distributions of aerosol loadings and depositions in East Asia during the year 2010. Atmos. Environ., 107, 244–254
—, and H.-J. In, 2003: Parameterization of dust emission for the simulation of the yellow sand (Asian dust) observed in March 2002 in Korea. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D19), 4618.
—, and E.-H. Lee, 2004: Parameterization of Asian dust (Hwangsa) particle-size distributions for use in dust emission model. Atmos. Environ., 38, 2155–2162.
—, L.-S. Chang, and E.-H. Lee, 2005: Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in East Asia during a Hwangsa (Asian dust) event observed in 18-23 March 202 in Korea. Atmos. Environ., 39, 2593–2606.
—, J. H. Cho, and M.-S. Park, 2012: A simulation of Aerosols in Asia with the use of ADAM2 and CMAQ. Adv. Fluid Mech. Heat & Mass Trans., 258–263.
—, —, and —, 2013a: Identification of visibility reducing weather phenomena due to aerosols. Environ. Manage. Sustain. Dev., 2, 126–142.
—, —, and —, 2013b: A simulation of haze and mist events observed in east Asia during 19-22 May 2010 using the Aerosol Modeling System (AMS). Rec. Adv. Environ. Sci., 204–210 (WSEAS).
—, I.-H. Lee, A. Choe, and S. J. Joo, 2014: Spatial and temporal distributions of aerosol concentrations and depositions in Asia during the year 2010. Submitted. Sci. Total Environ.
—, A. Choe, E.-H. Lee, M.-S. Park, X. Song, 2010: The Asian dust aerosol model 2 (ADAM2) with the use of normalized difference vegetation data (NDVI) obtained from the spot4/vegetation data. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 101, 191–208.
Penner, J. E. P., X. Dong, and Y. Chen, 2004: Observational evidence of change in radiative forcing due to the indirect aerosol effect. Nature, 427(6971), 231–234.
Perez, L., A. Tobias, X. Querol, N. Künzli, J. Pey, and A. Alastuey, 2008: Coarse particles from Saharan dust and daily mortality. Epidemiology, 19, 800–807.
Sajani, Z. S., R. Miglio, P. Bonasoni, P. Cristofanelli, A. Marinoni, and C. Sartini, 2010: Saharan dust and daily mortality in Emilia-Romagna (Italy). Occup. Environ. Med., 68, 446–451.
Seinfeld, J. H., 1986: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Air Pollution. New York: John Wiley.
Shao, Y., E. Jung, and L. M. Leslie, 2002: Numerical prediction of northeast Asian dust storms using an integrated wind erosion modeling system. J. Geophy. Res., 107(D24), 4814 (doi:10.1029/2001JD001493).
University of North Carolina, Operational Guidance for the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System. Community Modeling and Analysis System Institute for the Environment 2010.
Warneck, P., 1988: Chemistry of the Natural Atmosphere. Academic Press, Inc., New York, 422–425.
Watson, J. G., 2002: Visibility: Science and regulation. J. Air Waste Manage., 52, 628–713.
Yadav, A. K., K. Kumar, A. Kasim, M. P. Sing, S. K. Parida, and M. Sharan, 2003: Visibility and incidence of respiratory diseases during the 1998 haze episode in Brunei Darussala. Air Qual. Birkhäuser Basel, 265–277.
Yu, X., B. Zhu, Y. Yin, J. Yang, Y. Li, and Bu, X., 2011: A comparative analysis of aerosol properties in dust and haze-fog days in a Chinese urban region. Atmos. Res., 99, 241–247.
Zhang, Q., and Coauthors, 2009: Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 5131–5153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SU., Lee, IH., Choe, A. et al. Contributions of the pollutant emission in South Korea to the aerosol concentrations and depositions in Asia. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 51, 183–195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-015-0069-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-015-0069-2