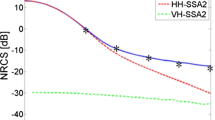
Abstract
Sea ice concentration is an important parameter for polar sea ice monitoring. Based on 89 GHz AMSR-E (Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for Earth Observing System) data, a gridded high-resolution passive microwave sea ice concentration product can be obtained using the ASI (the Arctic Radiation And Turbulence Interaction Study (ARTIST) Sea Ice) retrieval algorithm. Instead of using fixed-point values, we developed ASI algorithm based on daily changed tie points, called as the dynamic tie point ASI algorithm in this study. Here the tie points are expressed as the brightness temperature polarization difference of open water and 100% sea ice. In 2010, the yearly-averaged tie points of open water and sea ice in Arctic are estimated to be 50.8 K and 7.8 K, respectively. It is confirmed that the sea ice concentrations retrieved by the dynamic tie point ASI algorithm can increase (decrease) the sea ice concentrations in low-value (high-value) areas. This improved the sea ice concentrations by present retrieval algorithm from microwave data to some extent. Comparing with the products using fixed tie points, the sea ice concentrations retrieved from AMSR-E data by using the dynamic tie point ASI algorithm are closer to those obtained from MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data. In 40 selected cloud-free sample regions, 95% of our results have smaller mean differences and 75% of our results have lower root mean square (RMS) differences compare with those by the fixed tie points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi Haibo, Huang Haijun, Su Qiao, et al. 2014. An Arctic sea ice thickness variability revealed from satellite altimetric measurements. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33(11): 134–140
Cavalieri D J, Gloersen P, Campbell W J. 1984. Determination of sea ice parameters with the Nimbus 7 SMMR. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(D4): 5355–5369
Cavalieri D J, St Germain K M. 1995. Arctic sea ice research with satellite passive microwave radiometers. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society Newsletter, 97(1): 6–12
Cavalieri D J, Markus T, Hall D K, et al. 2006. Assessment of EOSAQUAAMSR-EArctic sea ice concentrations using landsat-7 and airborne microwave imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 44(11): 3057–3069
Cavalieri D J, Markus T, Hall D K, et al. 2010. Assessment of AMSR-E Antarctic winter sea-ice concentrations using Aqua MODIS. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 48(9): 3331–3339
Comiso J C. 1995. SSM/I sea ice concentrations using the bootstrap algorithm. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. NASA RefPubl, R., 1380. 49
Comiso J C, Kwok R. 1996. Surface and radiative characteristics of the summer Arctic sea ice cover from multisensor satellite observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101(C12): 28397–28416
Comiso J C, Cavalieri D J, Markus T. 2003. Sea ice concentration, ice temperature, and snow depth using AMSR-E data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(2): 243–252
de Vernal A, Gersonde R, Goosse H, et al. 2013. Sea ice in the paleoclimate system: the challenge of reconstructing sea ice from proxies—an introduction. Quaternary Science Reviews, 79: 1–8
Eastwood S, Larsen K R, Lavergne T, et al. 2011. Global Sea Ice Concentration Reprocessing Product User Manual, Version 1.3, EUMETSAT
Emery W J, Fowler C, Maslanik J. 1994. Arctic sea ice concentrations from special sensor microwave imager and advanced very high resolution radiometer satellite data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99(C9): 18329–18342
Gloersen P, Cavalieri D J. 1986. Reduction of weather effects in the calculation of sea ice concentration from microwave radiances. Journal of Geophysical Research, 91(C3): 3913–3919
Han H, Lee H. 2007. Compartive study of sea ice concentration by using DMSP SSM/I, Aqua AMSR-E and Kompsat-1 EOC. In: IEEE InternationalGeoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. 2007. IGARS. 2007. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 4249–4252
Kaleschke L, Lüpkes C, Vihma T, et al. 2001. SSM/I sea ice remote sensing for mesoscale ocean-atmosphere interaction analysis: Ice and icebergs. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(5): 526–537
Kern S. 2001. A new algorithm to retrieve the sea ice concentration using weather-corrected 85GHz SSM/I measurements. Logos-Verlag, Institute of Environmental Physics, Bremen, Germany
Kern S, Heygster G. 2001. Sea-ice concentration retrieval in the Antarctic based on the SSM/I 85. 5 GHz polarization. Annals of Glaciology, 33(1): 109–114
KernS L, Kaleschke L, Clausi D A. 2003. A comparison of two 85-GHz SSM/I ice concentration algorithms with AVHRR and ERS-2 SAR imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(10): 2294–2306
Kern S. 2004. A new method for medium-resolution sea ice analysis using weather-influencecprrection rected Special Sensor Microwave/Imager 85 GHz data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(21): 4555–4582
Liang Shunlin, Strahler A, Walthall C. 1998. Retrieval of land surface Albedo from satellite observations: A simulation study. In: IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Seattle, WA: IEEE, 1286–1288
Liu Jiping, Curry J A, Martinson D G. 2004. Interpretation of recent Antarctic sea ice variability. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(2)
Markus T, Cavalieri D J. 2000. An enhancement of the NASA Team sea ice algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 38(3): 1387–1398
Meier W N. 2005. Comparison of passive microwave ice concentration algorithm retrievals with AVHRR imagery in Arctic peripheral seas. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 43(6): 1324–1337
Rind D, Healy R, Parkinson C, et al. 1995. The role of seaice in 2×CO2 climate model sensitivity. Part I: The total influence of sea ice thickness and extent. Journal of Climate, 8(3): 449–463
Serreze M C, Maslanik J A, Scambos T A, et al. 2003. A record minimum arctic sea ice extent and area i. 2002. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(3): 1110
Spreen G. 2004. Meereisfernerkundung Mit Dem Satellitengestützten Mikrowellenradiometer AMSR (-E)—Bestimmung der Eiskonzentration und Eiskante unter Verwendung-der-89-GHz-Kanäle, Diplomarbeit [dissertation] (in German). Hamburg, Germany: Universityof Hamburg
Spreen G, Kaleschke L, Heygster G. 2008. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113(C2)
Steffen K, Schweiger A. 1991. NASA team algorithm for sea ice concentration retrieval from Defense Meteorological Satellite Program special sensor microwave imager: Comparison with Landsat satellite imagery. Journal of Geophysical Research, 96(C12): 21971–21987
Svendsen E, Matzler C, Grenfell T C. 1987. A model for retrieving total sea ice concentration from a spaceborne dual-polarized passive microwave instrument operating near 90 GHz. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 8(10): 1479–1487
Su Jie, Hao Guanghua, Ye Xinxin, et al. 2013. The experiment and validation of sea ice concentration AMSR-E retrieval algorithm in polar region. Journal of Remote Sensing (in Chinese), 173(3): 495–513
Vavrus S, Harrison S P. 2003. The impact of sea-ice dynamics on the Arctic climate system. Climate Dynamics, 20(7-8): 741–757
Wiebe H, Heygster G, Markus T. 2009. Comparison of the ASI ice concentration algorithm with Landsat-7 ETM+ and SAR imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(9): 3008–3015
Ye Xinxin, Su Jie, Wang Yang, et al. 2011. Assessment of AMSR-E sea ice concentration in ice margin zone using MODIS data. In: 2011 International Conference onRemote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 3869–3873
Zhang S G. 2012. Sea ice concentration algorithm and study on the physical process about sea ice and melt-pond change in central Arctic [dissertation]. Qingdao, China: Ocean University of China
Zhang Shugang, Zhao Jinping, Frey K, et al. 2013. Dual-polarized ratio algorithm for retrieving Arctic sea ice concentration from passive microwave brightness temperature. Journal of Oceanography, 69(2): 215–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Global Change Research Program of China under contract No. 2015CB953901; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41330960 and 41276193.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, G., Su, J. A study on the dynamic tie points ASI algorithm in the Arctic Ocean. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 34, 126–135 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0659-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0659-y