Abstract
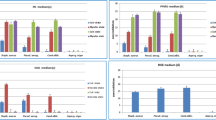
The study investigated the effects of salinity on growth, antimicrobial activities and secondary metabolites of 47 marine filamentous fungi isolated from the East China Sea near the western shore of the Taiwan Straits. The results indicate that NaCl promoted the growth up to 91.5% of test strains. However, only 14.9% of them showed a significant increase of antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans. When incubated in different concentrations of NaCl, the colony growth, antimicrobial activities and composition of secondary metabolites of the strain Ty01b-8 of Penicillium sp. varied. Treatment with KCl also showed a similar effect. An alkaloid isolated from the fermentation broth of Ty01b-8 was identified as chrysogine, inhibition activity of which against Hela cells was 15.05% at 20 µg/ml, and yield was 4.4 and 4.9 times higher in 3 percent and 6 percent NaCl treatments, respectively, compared with the non-salt culture condition. These findings prove that salinity is an important factor influencing growth and secondary metabolites of some marine fungi, which can be used to screen for new metabolites from marine fungi, and to enhance their metabolites production in industrial fermentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett H L, Hunter B B. 1977. Illustrated Genera of Imperfect Fungi (in Chinese). 3rd edn. Beijing: Science Press
Bugni T S, Ireland C M. 2004. Marine derived fungi: a chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat Prod Rep, 21: 143–163
Cantrell S A, Casillas-Martinez L, Molina M. 2006. Characterization of fungi from hypersaline environments of solar salterns using morphological and molecular techniques. Mycol Res, 110: 962–970
Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Anderson K C. 2006. A novel proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 as an anticancer therapy. Br J Cancer, 95: 961–965
Dela Cruz T E, Wagner S, Schulz B. 2006. Physiological responses of marine Dendryphiella species from different geographical locations. Mycol Progress, 5: 108–119
Hentschel U, Schmid M, Wagner M, et al. 2001. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of bacteria with antogonistic activities from the Mediterranean sponges Aplysina aerophoba and Aplysina cavernicola. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 35: 305–312
Kohlmeyer J, Kohlmeyer E. 1979. Marine Mycology, the Higher Fungi. New York: Academic Press
Lin Xin, Huang Yaojian, Fang Meijuan, et al. 2005. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial metabolites from marine lignicolous fungi, Diaporthe sp. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 251: 53–58
Masuma R, Yamaguchi Y, Noumi M, et al. 2001. Effect of sea water concentration on hyphal growth and antimicrobial metabolite production in marine fungi. Mycoscience, 42: 455–459
Mosmann F. 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods, 65: 55–63
Newman D J, Cragg G M. 2004. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J Nat Prod, 67: 1216–1238
Tan L T. 2007. Bioactive natural products from marine cyanobacteria for drug discovery. Phytochemistry, 68: 954–979
Yang Laihuang, Mao Li, Lee O O, et al. 2007. Effect of culture conditions on antifouling compound production of a sponge-associated fungus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 74: 1221–1231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Key Program of International Cooperation, Ministry of Science and Technology of China under contract No. 2007DFA30970; Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under contract No. 2010121092.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Lu, C., Qian, X. et al. Effect of salinity on the growth, biological activity and secondary metabolites of some marine fungi. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 30, 118–123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0126-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0126-3