Abstract
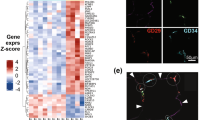
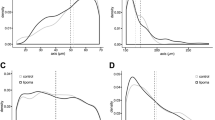
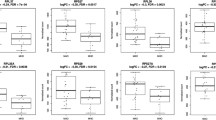
HIV-associated lipoatrophy (LA) has considerable implications for risk of metabolic diseases, quality of life, and adherence to treatments. Although it has decreased in high-income countries, it is still very common in resource-limited countries. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of LA can open the possibility to explore new ways to treat or prevent this condition. To identify new markers for an accurate and quick diagnosis will be also of interest. Thus, we aimed to examine functional classes of genes implicated in LA and to identify potential new markers for an accurate/quick diagnosis of LA and future complications. Eighteen participants were recruited: seven healthy volunteers, five non-LA-HIV patients, and six LA-HIV subjects. Clinical lipoatrophy was considered when changes in fat volume in the cheeks next to the nose, lateral aspect of the face, legs, arms, and buttocks were observed by the physicians. mRNA was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to perform a transcriptomic and Gene Ontology analysis. To confirm RNA sequencing results, qPCRs were developed. A total of 55 genes were differentially expressed between LA and non-LA patients. Thirty-seven genes were overexpressed, whereas 18 genes were repressed. Functional analysis showed that overexpressed genes were involved in lymphocyte/neutrophil activation, inflammation, and atherogenesis. Several lymphoma markers and members of the lipocalin and aquaporin families were also found more expressed in LA patients. In contrast, most of the genes found less expressed in LA subjects were involved in angiogenesis and protection against myocardial infarction. Our results demonstrated a distinct transcriptomic signature in PBMCs of LA patients in comparison with non-LA-HIV subjects and, therefore, provided novel insights to the pathogenesis of HIV-associated lipoatrophy. Our study also highlights the potential usage of some of these genes as early markers of future complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 October 2017
Volume 73 issue 3 was published with an incorrect cover date. Correct is August 2017. The Publisher apologizes for this mistake and all related inconveniences caused by this.
References
Agre P, Kozono D (2003) Aquaporin water channels: molecular mechanisms for human diseases. FEBS Lett 555(1):72–78
Alonso-Villaverde C, Coll B, Parra S, Montero M, Calvo N, Tous M, Joven J, Masana L (2004) Atherosclerosis in patients infected with HIV is influenced by a mutant monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 allele. Circulation 110(15):2204–2209
Anastasiou G, Gialeraki A, Merkouri E, Politou M, Travlou A (2012) Thrombomodulin as a regulator of the anticoagulant pathway: implication in the development of thrombosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 23(1):1–10
Baggiolini M (1998) Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature 392(6676):565–568
Bonta PI, van Tiel CM, Vos M, Pols TW, van Thienen JV, Ferreira V, Arkenbout EK, Seppen J, Spek CA, van der Poll T, Pannekoek H, de Vries CJ (2006) Nuclear receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 expressed in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages reduce lipid loading and inflammatory responses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(10):2288–2294
Capeau J, Magre J, Lascols O, Caron M, Bereziat V, Vigouroux C, Bastard JP (2005) Diseases of adipose tissue: genetic and acquired lipodystrophies. Biochem Soc Trans 33(Pt 5):1073–1077
Carr A, Samaras K, Burton S, Law M, Freund J, Chisholm DJ, Cooper DA (1998) A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS 12(7):F51–F58
Castilhos JK, Sprinz E, Lazzaretti RK, Kuhmmer R, Mattevi VS (2015) Polymorphisms in adiponectin receptor genes are associated with lipodystrophy-related phenotypes in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. HIV Med 16(8):494–501
Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Ramirez B, Silva C, Rotellar F, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G (2009) Increased adipose tissue expression of lipocalin-2 in obesity is related to inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 activities in humans. J Mol Med (Berl) 87(8):803–813
Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Ramirez B, Silva C, Rotellar F, Hernandez-Lizoain JL, Baixauli J, Valenti V, Pardo F, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G (2011) Up-regulation of the novel proinflammatory adipokines lipocalin-2, chitinase-3 like-1 and osteopontin as well as angiogenic-related factors in visceral adipose tissue of patients with colon cancer. J Nutr Biochem 22(7):634–641
Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Ramirez B, Valenti V, Moncada R, Silva C, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G (2015) Peripheral mononuclear blood cells contribute to the obesity-associated inflammatory state independently of glycemic status: involvement of the novel proinflammatory adipokines chemerin, chitinase-3-like protein 1, lipocalin-2 and osteopontin. Genes Nutr 10(3):460
Coats AJ, Cruickshank JM (2014) Hypertensive subjects with type-2 diabetes, the sympathetic nervous system, and treatment implications. Int J Cardiol 174(3):702–709
Coll B, Parra S, Alonso-Villaverde C, de Groot E, Aragones G, Montero M, Tous M, Camps J, Joven J, Masana L (2006) HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy have higher rates of carotid atherosclerosis: the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Cytokine 34(1–2):51–55
Crean D, Cummins EP, Bahar B, Mohan H, McMorrow JP, Murphy EP (2015) Adenosine modulates NR4A orphan nuclear receptors to attenuate hyperinflammatory responses in monocytic cells. J Immunol 195(4):1436–1448
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Martinez JA (2008) Differential expression of oxidative stress and inflammation related genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to a low-calorie diet: a nutrigenomics study. OMICS 12(4):251–261
DeFuria J, Belkina AC, Jagannathan-Bogdan M, Snyder-Cappione J, Carr JD, Nersesova YR, Markham D, Strissel KJ, Watkins AA, Zhu M, Allen J, Bouchard J, Toraldo G, Jasuja R, Obin MS, McDonnell ME, Apovian C, Denis GV, Nikolajczyk BS (2013) B cells promote inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes through regulation of T-cell function and an inflammatory cytokine profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(13):5133–5138
Duffaut C, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, Bouloumie A (2009) Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(4):482–485
Egana-Gorrono L, Martinez E, Cormand B, Escriba T, Gatell J, Arnedo M (2013) Impact of genetic factors on dyslipidemia in HIV-infected patients starting antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 27(4):529–538
Egana-Gorrono L, Martinez E, Perez I, Escriba T, Domingo P, Gatell JM, Arnedo M (2014) Contribution of genetic background and antiretroviral therapy to body fat changes in antiretroviral-naive HIV-infected adults. J Antimicrob Chemother 69(11):3076–3084
Finkelstein JL, Gala P, Rochford R, Glesby MJ, Mehta S (2015) HIV/AIDS and lipodystrophy: implications for clinical management in resource-limited settings. J Int AIDS Soc 18(1):19033
Gealekman O, Guseva N, Hartigan C, Apotheker S, Gorgoglione M, Gurav K, Tran KV, Straubhaar J, Nicoloro S, Czech MP, Thompson M, Perugini RA, Corvera S (2011) Depot-specific differences and insufficient subcutaneous adipose tissue angiogenesis in human obesity. Circulation 123(2):186–194
Ghanim H, Aljada A, Hofmeyer D, Syed T, Mohanty P, Dandona P (2004) Circulating mononuclear cells in the obese are in a proinflammatory state. Circulation 110(12):1564–1571
Haugaard SB, Andersen O, Dela F, Holst JJ, Storgaard H, Fenger M, Iversen J, Madsbad S (2005) Defective glucose and lipid metabolism in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with lipodystrophy involve liver, muscle tissue and pancreatic beta-cells. Eur J Endocrinol 152(1):103–112
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57
Karsunky H, Merad M, Cozzio A, Weissman IL, Manz MG (2003) Flt3 ligand regulates dendritic cell development from Flt3+ lymphoid and myeloid-committed progenitors to Flt3+ dendritic cells in vivo. J Exp Med 198(2):305–313
Kim MJ, Park SK, Lee JH, Jung CY, Sung DJ, Park JH, Yoon YS, Park J, Park KG, Song DK, Cho H, Kim ST, Koo SH (2015) Salt-inducible kinase 1 terminates cAMP signaling by an evolutionarily conserved negative-feedback loop in beta-cells. Diabetes 64(9):3189–3202
King LS, Kozono D, Agre P (2004) From structure to disease: the evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(9):687–698
King RG, Herrin BR, Justement LB (2006) Trem-like transcript 2 is expressed on cells of the myeloid/granuloid and B lymphoid lineage and is up-regulated in response to inflammation. J Immunol 176(10):6012–6021
Laforenza U, Scaffino MF, Gastaldi G (2013) Aquaporin-10 represents an alternative pathway for glycerol efflux from human adipocytes. PLoS One 8(1):e54474
Larrayoz IM, Rúa Ó, Velilla S, Martínez A (2014) Transcriptomic profiling explains racial disparities in pterygium patients treated with doxycycline. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55(11):7553–7561
Lopez-Dupla M, Maymo-Masip E, Martinez E, Domingo P, Leal M, Peraire J, Vilades C, Veloso S, Arnedo M, Ferrando-Martinez S, Beltran-Debon R, Alba V, Gatell JM, Vendrell J, Vidal F, Chacon MR (2015) HIV-1/HAART-related lipodystrophy syndrome (HALS) is associated with decreased circulating sTWEAK levels. PLoS One 10(12):e0144789
Mahajan S, Saini A, Chandra V, Nanduri R, Kalra R, Bhagyaraj E, Khatri N, Gupta P (2015) Nuclear receptor Nr4a2 promotes alternative polarization of macrophages and confers protection in sepsis. J Biol Chem 290(30):18304–18314
Mallewa JE, Wilkins E, Vilar J, Mallewa M, Doran D, Back D, Pirmohamed M (2008) HIV-associated lipodystrophy: a review of underlying mechanisms and therapeutic options. J Antimicrob Chemother 62(4):648–660
Manneras-Holm L, Krook A (2012) Targeting adipose tissue angiogenesis to enhance insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia 55(10):2562–2564
Marzocchetti A, Schwarz J, Di Giambenedetto S, Colafigli M, Bracciale L, Fabbiani M, Fantoni M, Trecarichi E, Cauda R, De Luca A (2011) The effect of polymorphisms in candidate genes on the long-term risk of lipodystrophy and dyslipidemia in HIV-infected white patients starting antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 27(12):1299–1309
Mendez-Gimenez L, Rodriguez A, Balaguer I, Fruhbeck G (2014) Role of aquaglyceroporins and caveolins in energy and metabolic homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 397(1–2):78–92
Minervino D, Gumiero D, Nicolazzi MA, Carnicelli A, Fuorlo M, Guidone C, Di Gennaro L, Fattorossi A, Mingrone G, Landolfi R (2015) Leukocyte activation in obese patients: effect of bariatric surgery. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(40):e1382
Nolan D, Hammond E, James I, McKinnon E, Mallal S (2003) Contribution of nucleoside-analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy to lipoatrophy from the population to the cellular level. Antivir Ther 8(6):617–626
Ozaki K, Inoue K, Sato H, Iida A, Ohnishi Y, Sekine A, Odashiro K, Nobuyoshi M, Hori M, Nakamura Y, Tanaka T (2004) Functional variation in LGALS2 confers risk of myocardial infarction and regulates lymphotoxin-alpha secretion in vitro. Nature 429(6987):72–75
Perez-Matute P, Neville MJ, Tan GD, Frayn KN, Karpe F (2009) Transcriptional control of human adipose tissue blood flow. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17(4):681–688
Perez-Matute P, Perez-Martinez L, Blanco JR, Ibarra V, Metola L, Sanz M, Hernando L, Martinez S, Ramirez A, Ramalle-Gomara E, Oteo JA (2013) Multiple frequency bioimpedance is an adequate tool to assess total and regional fat mass in HIV-positive patients but not to diagnose HIV-associated lipoatrophy: a pilot study. J Int AIDS Soc 16:18609
Reeds DN, Yarasheski KE, Fontana L, Cade WT, Laciny E, DeMoss A, Patterson BW, Powderly WG, Klein S (2006) Alterations in liver, muscle, and adipose tissue insulin sensitivity in men with HIV infection and dyslipidemia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290(1):E47–E53
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G (2006) Role of aquaporin-7 in the pathophysiological control of fat accumulation in mice. FEBS Lett 580(20):4771–4776
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G (2011) Aquaglyceroporins serve as metabolic gateways in adiposity and insulin resistance control. Cell Cycle 10(10):1548–1556
Rodriguez A, Gena P, Mendez-Gimenez L, Rosito A, Valenti V, Rotellar F, Sola I, Moncada R, Silva C, Svelto M, Salvador J, Calamita G, Fruhbeck G (2014) Reduced hepatic aquaporin-9 and glycerol permeability are related to insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Obes 38(9):1213–1220
Rotger M, Dalmau J, Rauch A, McLaren P, Bosinger SE, Martinez R, Sandler NG, Roque A, Liebner J, Battegay M, Bernasconi E, Descombes P, Erkizia I, Fellay J, Hirschel B, Miró JM, Palou E, Hoffmann M, Massanella M, Blanco J, Woods M, Günthard HF, de Bakker P, Douek DC, Silvestri G, Martinez-Picado J, Telenti A (2011) Comparative transcriptomics of extreme phenotypes of human HIV-1 infection and SIV infection in sooty mangabey and rhesus macaque. J Clin Invest 121(6):2391–2400
Sears DD, Miles PD, Chapman J, Ofrecio JM, Almazan F, Thapar D, Miller YI (2009) 12/15-lipoxygenase is required for the early onset of high fat diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. PLoS One 4(9):e7250
Stefanovic-Racic M, Yang X, Turner MS, Mantell BS, Stolz DB, Sumpter TL, Sipula IJ, Dedousis N, Scott DK, Morel PA, Thomson AW, O'Doherty RM (2012) Dendritic cells promote macrophage infiltration and comprise a substantial proportion of obesity-associated increases in CD11c+ cells in adipose tissue and liver. Diabetes 61(9):2330–2339
Stoynev N, Dimova I, Rukova B, Hadjidekova S, Nikolova D, Toncheva D, Tankova T (2014) Gene expression in peripheral blood of patients with hypertension and patients with type 2 diabetes. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 15(9):702–709
Suwalak T, Srisawasdi P, Puangpetch A, Santon S, Koomdee N, Chamnanphon M, Charoenyingwattana A, Chantratita W, Sukasem C (2015) Polymorphisms of the ApoE (apolipoprotein E) gene and their influence on dyslipidemia in HIV-1-infected individuals. Jpn J Infect Dis 68(1):5–12
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7(3):562–578
Uttayamakul S, Oudot-Mellakh T, Nakayama EE, Tengtrakulcharoen P, Guergnon J, Delfraissy JF, Khusmith S, Sangsajja C, Likanonsakul S, Theodorou I, Shioda T (2015) Genome-wide association study of HIV-related lipoatrophy in Thai patients: association of a DLGAP1 polymorphism with fat loss. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 31(8):792–796
van der Laan AM, Schirmer SH, de Vries MR, Koning JJ, Volger OL, Fledderus JO, Bastiaansen AJ, Hollander MR, Baggen JM, Koch KT, Baan J Jr, Henriques JP, van der Schaaf RJ, Vis MM, Mebius RE, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Quax PH, Piek JJ, Horrevoets AJ, van Royen N (2012) Galectin-2 expression is dependent on the rs7291467 polymorphism and acts as an inhibitor of arteriogenesis. Eur Heart J 33(9):1076–1084
Vijil C, Hermansson C, Jeppsson A, Bergstrom G, Hulten LM (2014) Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase enzyme products increase platelet aggregation and thrombin generation. PLoS One 9(2):e88546
Villarroya F, Domingo P, Giralt M (2007) Lipodystrophy in HIV 1-infected patients: lessons for obesity research. Int J Obes 31(12):1763–1776
Watanabe Y, Nakamura T, Ishikawa S, Fujisaka S, Usui I, Tsuneyama K, Ichihara Y, Wada T, Hirata Y, Suganami T, Izaki H, Akira S, Miyake K, Kanayama HO, Shimabukuro M, Sata M, Sasaoka T, Ogawa Y, Tobe K, Takatsu K, Nagai Y (2012) The radioprotective 105/MD-1 complex contributes to diet-induced obesity and adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes 61(5):1199–1209
Winer DA, Winer S, Shen L, Wadia PP, Yantha J, Paltser G, Tsui H, Wu P, Davidson MG, Alonso MN, Leong HX, Glassford A, Caimol M, Kenkel JA, Tedder TF, McLaughlin T, Miklos DB, Dosch HM, Engleman EG (2011) B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat Med 17(5):610–617
Woodhouse SD, Narayan R, Latham S, Lee S, Antrobus R, Gangadharan B, Luo S, Schroth GP, Klenerman P, Zitzmann N (2010) Transcriptome sequencing, microarray, and proteomic analyses reveal cellular and metabolic impact of hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Hepatology 52(2):443–453
Wu L, Liu YJ (2007) Development of dendritic-cell lineages. Immunity 26(6):741–750
Yamaoka M, Maeda N, Nakamura S, Kashine S, Nakagawa Y, Hiuge-Shimizu A, Okita K, Imagawa A, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K, Funahashi T, Shimomura I (2012) A pilot investigation of visceral fat adiposity and gene expression profile in peripheral blood cells. PLoS One 7(10):e47377
Yamaoka M, Maeda N, Nakamura S, Mori T, Inoue K, Matsuda K, Sekimoto R, Kashine S, Nakagawa Y, Tsushima Y, Fujishima Y, Komura N, Hirata A, Nishizawa H, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K, Funahashi T, Shimomura I (2013) Gene expression levels of S100 protein family in blood cells are associated with insulin resistance and inflammation (peripheral blood S100 mRNAs and metabolic syndrome). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 433(4):450–455
Yildirim C, Vogel DY, Hollander MR, Baggen JM, Fontijn RD, Nieuwenhuis S, Haverkamp A, de Vries MR, Quax PH, Garcia-Vallejo JJ, van der Laan AM, Dijkstra CD, van der Pouw Kraan TC, van Royen N, Horrevoets AJ (2015) Galectin-2 induces a proinflammatory, anti-arteriogenic phenotype in monocytes and macrophages. PLoS One 10(4):e0124347
Zhang ZN, Xu JJ, Fu YJ, Liu J, Jiang YJ, Cui HL, Zhao B, Sun H, He YW, Li QJ, Shang H (2013) Transcriptomic analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rapid progressors in early HIV infection identifies a signature closely correlated with disease progression. Clin Chem 59(8):1175–1186
Zhao J, Yi L, Lu J, Yang ZR, Chen Y, Zheng C, Huang D, Li YF, Chen L, Cheng J, Kung HF, He ML (2012) Transcriptomic assay of CD8+ T cells in treatment-naïve HIV, HCV-mono-infected and HIV/HCV-co-infected Chinese. PLoS One 7(9):e45200
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the excellent technical assistance of Dr. Pérez-Martínez and the helpful pieces of advise from Dr. Larráyoz (CIBIR, Logroño, Spain). We thank the physicians from the Infectious Diseases Department (Hospital San Pedro, Logroño) for their help in the recruitment of subjects included in this study. We also thank all the subjects that collaborated in this study. This work was supported by Fundación Rioja Salud (FRS). FRS had no role in study design, data collection, and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Patricia Pérez-Matute and María Iñiguez contributed equally.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0593-x.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(XLS 31 kb)
Online Resource 2
(XLS 49 kb)
Online Resource 3
(XLS 50 kb)
Online Resource 4
(XLS 37 kb)
Online Resource 5
(XLS 236 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Matute, P., Iñiguez, M., Recio-Fernández, E. et al. Deciphering the molecular mechanisms involved in HIV-associated lipoatrophy by transcriptomics: a pilot study. J Physiol Biochem 73, 431–443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0547-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0547-8