Abstract
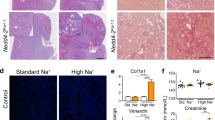
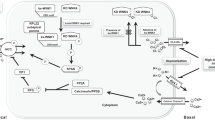
Increased renal reabsorption of sodium is a significant risk factor in hypertension. An established clinical marker for essential hypertension is elevated sodium lithium countertransport (SLC) activity. NHA2 is a newly identified Na+(Li+)/H+ antiporter with potential genetic links to hypertension, which has been shown to mediate SLC activity and H+-coupled Na+(Li+) efflux in kidney-derived MDCK cells. To evaluate a putative role in sodium homeostasis, we determined the effect of dietary salt on NHA2. In murine kidney sections, NHA2 localized apically to distal convoluted (both DCT1 and 2) and connecting tubules, partially overlapping in distribution with V-ATPase, AQP2, and NCC1 transporters. Mice fed a diet high in sodium chloride showed elevated transcripts and expression of NHA2 protein. We propose a model in which NHA2 plays a dual role in salt reabsorption or secretion, depending on the coupling ion (sodium or protons). The identified novel regulation of Na+/H+ antiporter in the kidney suggests new roles in salt homeostasis and disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCT:
-
Distal convoluted tubule
- NCC:
-
Sodium chloride cotransporter
- CNT:
-
Connecting tubule (CNT)
- AQP2:
-
Aquaporin 2
- CPA:
-
Cation proton antiporter
- CCD:
-
Cortical collecting duct
References
Brett CL, Donowitz M, Rao R (2005) Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. American journal of physiology Cell physiology 288:C223–C239. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2004
Calinescu O, Fendler K (2015) A universal mechanism for transport and regulation of CPA sodium proton exchangers. Biol Chem 396:1091–1096. doi:10.1515/hsz-2014-0278
Canessa M (1995) Red cell sodium-lithium countertransport and cardiovascular risk factors in essential hypertension. Trends in cardiovascular medicine 5:102–108. doi:10.1016/1050-1738(95)00004-S
Canessa M, Adragna N, Solomon HS, Connolly TM, Tosteson DC (1980) Increased sodium-lithium countertransport in red cells of patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 302:772–776. doi:10.1056/NEJM198004033021403
Chintapalli VR, Kato A, Henderson L, Hirata T, Woods DJ, Overend G, Davies SA, Romero MF, Dow JA (2015) Transport proteins NHA1 and NHA2 are essential for survival, but have distinct transport modalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:11720–11725. doi:10.1073/pnas.1508031112
Cruz DN, Simon DB, Nelson-Williams C, Farhi A, Finberg K, Burleson L, Gill JR, Lifton RP (2001) Mutations in the Na-Cl cotransporter reduce blood pressure in humans. Hypertension 37:1458–1464
de Wardener HE, He FJ, MacGregor GA (2004) Plasma sodium and hypertension. Kidney Int 66:2454–2466. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.66018.x
Duhm J, Becker BF (1979) Studies on lithium transport across the red cell membrane. V. On the nature of the Na + −dependent Li + countertransport system of mammalian erythrocytes. J Membr Biol 51:263–286
Ecelbarger CA, Tiwari S (2006) Sodium transporters in the distal nephron and disease implications. Curr Hypertens Rep 8:158–165
Ergonul Z, Frindt G, Palmer LG (2006) Regulation of maturation and processing of ENaC subunits in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F683–F693. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00422.2005
Fuster DG, Zhang J, Shi M, Bobulescu IA, Andersson S, Moe OW (2008) Characterization of the sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHA2. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1547–1556. doi:10.1681/ASN.2007111245
Gluck SL, Underhill DM, Iyori M, Holliday LS, Kostrominova TY, Lee BS (1996) Physiology and biochemistry of the kidney vacuolar H + −ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol 58:427–445. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.58.030196.002235
Kammerer CM, Cox LA, Mahaney MC, Rogers J, Shade RE (2001) Sodium-lithium countertransport activity is linked to chromosome 5 in baboons. Hypertension 37:398–402
Kondapalli KC, Kallay LM, Muszelik M, Rao R (2012) Unconventional chemiosmotic coupling of NHA2, a mammalian Na+/H+ antiporter, to a plasma membrane H+ gradient. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.403550
Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS (2001) Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104:545–556
Malnic G, Klose RM, Giebisch G (1964) Micropuncture study of renal potassium excretion in the rat. Am J Phys 206:674–686
Malnic G, Klose RM, Giebisch G (1966) Microperfusion study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transfer in rat kidney. Am J Phys 211:548–559
McCormick JA, Yang CL, Ellison DH (2008) WNK kinases and renal sodium transport in health and disease: an integrated view. Hypertension 51:588–596. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.103788
Meneton P, Jeunemaitre X, de Wardener HE, MacGregor GA (2005) Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Rev 85:679–715. doi:10.1152/physrev.00056.2003
Meneton P, Loffing J, Warnock DG (2004) Sodium and potassium handling by the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron: the pivotal role of the distal and connecting tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F593–F601. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00454.2003
Nijenhuis T, Hoenderop JG, van der Kemp AW, Bindels RJ (2003) Localization and regulation of the epithelial Ca2+ channel TRPV6 in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2731–2740
Nurnberger A, Rabiger M, Mack A, Diaz J, Sokoloff P, Muhlbauer B, Luippold G (2004) Subapical localization of the dopamine D3 receptor in proximal tubules of the rat kidney. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society 52:1647–1655. doi:10.1369/jhc.4A6359.2004
Reineck HJ, Osgood RW, Ferris TF, Stein JH (1975) Potassium transport in the distal tubule and collecting duct of the rat. Am J Phys 229:1403–1409
Tamkun MM, Fambrough DM (1986) The (Na+ + K+)-ATPase of chick sensory neurons. Studies on biosynthesis and intracellular transport. J Biol Chem 261:1009–1019
Verlander JW (2007) The thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter: a new target for acute regulation of salt and water transport by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F660–F661. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00260.2007
Wagner CA, Finberg KE, Stehberger PA, Lifton RP, Giebisch GH, Aronson PS, Geibel JP (2002) Regulation of the expression of the Cl−/anion exchanger pendrin in mouse kidney by acid-base status. Kidney Int 62:2109–2117. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00671.x
Wieczorek H, Putzenlechner M, Zeiske W, Klein U (1991) A vacuolar-type proton pump energizes K+/H+ antiport in an animal plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 266:15340–15347
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP (2001) Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 293:1107–1112. doi:10.1126/science.1062844
Xiang M, Feng M, Muend S, Rao R (2007) A human Na+/H+ antiporter sharing evolutionary origins with bacterial NhaA may be a candidate gene for essential hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18677–18681. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707120104
Zerbini G, Mangili R, Gabellini D, Pozza G (1997) Modes of operation of an electroneutral Na+/Li + countertransport in human skin fibroblasts. Am J Phys 272:C1373–C1379
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health R01 DK108304 (to R.R.), DK081610 (J.L.P.), Canadian Institute of Health Research (R.T.A.), and University of Michigan-Dearborn startup funds (KCK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondapalli, K.C., Todd Alexander, R., Pluznick, J.L. et al. NHA2 is expressed in distal nephron and regulated by dietary sodium. J Physiol Biochem 73, 199–205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0539-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0539-8