Abstract
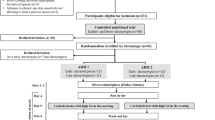
Food intake is regulated by not only neurohormonal, but also social, educational, and even cultural factors. Within the former, there is a complex interaction between orexigenic (ghrelin) and anorexigenic (glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)) factors in order to adjust the food intake to caloric expenditure; however, the number of subjects that are unable to properly balance appetite and body weight is increasing continuously. A loss of circadian or diurnal coordination of any of these factors may be implied in this situation. Special attention has retrieved GLP-1 due to its usefulness as a therapeutic agent against obesity and related alterations. Thus, the objective of the present study was to compare GLP-1 diurnal synthesis between normal weight and overweight/obese subjects, and to evaluate whether weight loss can restore the synthesis rhythms of GLP-1. Three groups of 25 subjects were divided attending to their body mass index (BMI) in normal weight, overweight, or obese subjects. Diurnal (5 points) GLP-1 levels were analyzed. Secondly, an intervention (behavioral-dietary treatment) study was conducted to analyze the effect of weight loss on plasma GLP-1 concentrations. Our results showed that baseline GLP-1 level was significantly lower in normal weight subjects (p = 0.003); furthermore, our cosinor analysis revealed a higher amplitude (p = 0.040) and daily GLP-1 variation (47 %) in these subjects. In fact, our ANOVA data showed a lack of rhythmicity in overweight/obese patients. Weight loss was not able to restore a diurnal rhythm of plasma GLP-1 levels. In summary, the present work shows a disruption of diurnal GLP-1 levels in overweight/obese subjects, which worsen as body fat progresses. The attenuation of the GLP-1 synthesis rhythms may be important to understand the impairment of food intake regulation in overweight/obese subjects.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OCDE:
-
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- CCK:
-
Cholecystokinin
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- NPY:
-
Neuropeptide Y
- AgRP:
-
Agouti-related protein
- SEEDO:
-
Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity
- MetS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
References
Adam TC, Jocken J, Westerterp-Plantenga MS (2005) Decreased glucagon-like peptide 1 release after weight loss in overweight/obese subjects. Obes Res 13:710–716
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2006) Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 23:469–480
Ando H, Yanagihara H, Hayashi Y, Obi Y, Tsuruoka S, Takamura T, Kaneko S, Fujimura A (2005) Rhythmic messenger ribonucleic acid expression of clock genes and adipocytokines in mouse visceral adipose tissue. Endocrinology 146:5631–5636
Baillie-Hamilton PF (2002) Chemical toxins: a hypothesis to explain the global obesity epidemic. J Altern Complement Med 8:185–192
Bose M, Teixeira J, Olivan B, Bawa B, Arias S, Machineni S, Pi-Sunyer X, Scherer PE, Laferrere B (2010) Weight loss and incretin responsiveness improve glucose control independently after gastric bypass surgery. J Diabetes 2:47–55
Byberg S, Hansen AL, Christensen DL, Vistisen D, Aadahl M, Linneberg A, Witte DR (2012) Sleep duration and sleep quality are associated differently with alterations of glucose homeostasis. Diabet Med 29:e354–e360
Carr RD, Larsen MO, Jelic K, Lindgren O, Vikman J, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Ahrén B (2010) Secretion and dipeptidyl peptidase-4-mediated metabolism of incretin hormones after a mixed meal or glucose ingestion in obese compared to lean, nondiabetic men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:872–878
Carter S, Caron A, Richard D, Picard F (2013) Role of leptin resistance in the development of obesity in older patients. Clin Interv Aging 8:829–844
Duffey KJ, Popkin BM (2011) Energy density, portion size, and eating occasions: contributions to increased energy intake in the United States, 1977–2006. PLoS Med 8:e1001050
Elliot RM, Morgan LM, Tredger JA, Deacon S, Wright J, Marks V (1993) Glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36) amide and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide secretion in response to nutrient ingestion in man—acute postprandial and 24-h secretion patterns. J Endocrinol 138:159–166
Foster GD, Makris AP, Bailer BA (2005) Behavioral treatment of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 82(1 Suppl):230S–235S
García-Prieto MD, Tébar FJ, Nicolás F, Larqué E, Zamora S, Garaulet M (2007) Cortisol secretary pattern and glucocorticoid feedback sensitivity in women from a Mediterranean area: relationship with anthropometric characteristics, dietary intake and plasma fatty acid profile. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 66:185–191
Gargallo Fernández MM, Breton Lesmes I, Basulto Marset J, Quiles Izquierdo J, Formiguera Sala X, Salas-Salvadó J; FESNAD-SEEDO consensus group (2012) Evidence-based nutritional recommendations for the prevention and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults (FESNAD-SEEDO consensus document). The role of diet in obesity treatment (III/III). Nutr Hosp 27:833–864
Hernandez-Morante JJ, Gomez-Santos C, Margareto J, Formiguera X, Martínez CM, González R, Martínez-Augustín O, Madrid JA, Ordovas JM, Garaulet M (2012) Influence of menopause on adipose tissue clock gene genotype and its relationship with metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese women. Age (Dordr) 34:1369–1380
Hernandez-Morante JJ, Gomez-Santos C, Milagro F, Campión J, Martínez JA, Zamora S, Garaulet M (2009) Expression of cortisol metabolism-related genes shows circadian rhythmic patterns in human adipose tissue. Int J Obes 33:473–480
Lionetti L, Mollica MP, Lombardi A, Cavaliere G, Gifuni G, Barletta A (2009) From chronic overnutrition to insulin resistance: the role of fat-storing capacity and inflammation. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 19:146–152
Cuervo-Zapatel M, Muñoz-Hornillos M, Astiasarán-Anchía I, Martínez-Hernández JA (2004) Alimentación Hospitalaria. Díaz de Santos, Madrid
Mayr S, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Faul F (2007) A short tutorial of GPower. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol 3:51–59
Meyer-Gerspach AC, Wölnerhanssen B, Beglinger B, Nessenius F, Napitupulu M, Schulte FH, Steinert RE, Beglinger C (2014) Gastric and intestinal satiation in obese and normal weight healthy people. Physiol Behav 129:265–271
Mingrone G, Nolfe G, Gissey GC, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, Guidone C, Nanni G, Holst JJ (2009) Circadian rhythms of GIP and GLP1 in glucose-tolerant and in type 2 diabetic patients after biliopancreatic diversion. Diabetologia 52:873–881
Mul JD, Begg DP, Barrera JG, Li B, Matter EK, D’Alessio DA, Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Sandoval DA (2013) High-fat diet changes the temporal profile of GLP-1 receptor-mediated hypophagia in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305:R68–R77
Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2010) Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:643–651
OCDE (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) (2010) In: Obesity and the economics of fat: fit not fat. París, France. http://www.oecd.org/els/health-systems/46068529.pdf. Accessed 23 Sept 2014
Patton DF, Mistlberger RE (2013) Circadian adaptations to meal timing: neuroendocrine mechanisms. Front Neurosci 7:185
Peterli R, Steinert RE, Woelnerhanssen B, Peters T, Christoffel-Courtin C, Gass M, Kern B, von Fluee M, Beglinger C (2012) Metabolic and hormonal changes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: a randomized, prospective trial. Obes Surg 22:740–748
Quilliot D, Böhme P, Zannad F, Ziegler O (2008) Sympathetic-leptin relationship in obesity: effect of weight loss. Metabolism 57:555–562
Rocca AS, Brubaker PL (1999) Role of the vagus nerve in mediating proximal nutrient-induced glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Endocrinology 140:1687–1694
Salas-Salvadó J, Rubio MA, Barbany M, Moreno B (2007) Grupo Colaborativo de la SEEDO 2007 consensus for the evaluation of overweight and obesity and the establishment of therapeutic intervention criteria. Med Clin (Barc) 128:184–196
Sohn JW, Elmquist JK, Williams KW (2013) Neuronal circuits that regulate feeding behavior and metabolism. Trends Neurosci 36:504–512
Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, Purcell K, Shulkes A, Kriketos A, Proietto J (2011) Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N Engl J Med 365:1597–1604
Tchernof A, Després JP (2013) Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: an update. Physiol Rev 93:359–404
Valassi E, Scacchi M, Cavagnini F (2008) Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 18:158–168
Varela-Moreiras G, Ruiz E, Valero T, Avila JM, del Pozo S (2013) The Spanish diet: an update. Nutr Hosp 28:13–20
Willett WC (1998) Is dietary fat a major determinant of body fat? Am J Clin Nutr 67:556S–562S
Yamaoka-Tojo M, Tojo T, Takahira N, Matsunaga A, Aoyama N, Masuda T, Izumi T (2010) Elevated circulating levels of an incretin hormone, glucagon-like peptide-1, are associated with metabolic components in high-risk patients with cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 9:17
Zhao L (2013) The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:639–647
Zuther P, Gorbey S, Lemmer B (2009) Chronos-Fit 1.06. http://www.ma.uni-heidelberg.de/inst/phar/lehre/chrono.html. Accessed 23 Sept 2014
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the psychologists Magdalena Gomez and Rosario Gomez for their assistance in the psychological and behavioral treatment of overweight and obese patients of the present study. We also want to thank Rubén Cañavate for his assistance in the language editing of the manuscript. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The present work was funded by PMAFI/14/12 project, from the Support for Research Help Program of the Catholic University of Murcia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, J.S.G., Rodríguez, D.J. & Morante, J.J.H. Diurnal rhythms of plasma GLP-1 levels in normal and overweight/obese subjects: lack of effect of weight loss. J Physiol Biochem 71, 17–28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0375-7