Abstract
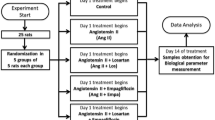
The aim of this study was to assess whether endogenous Ang II and oxidative stress produced by acute hypertonic sodium overload may regulate the expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP-1) and aquaporin-2 (AQP-2) in the kidney. Groups of anesthetized male Sprague–Dawley rats were infused with isotonic saline solution (control) or with hypertonic saline solution (Na group, 1 M NaCl), either alone or with losartan (10 mg kg−1) or tempol (0.5 mg min−1 kg−1) during 2 h. Renal function parameters were measured. Groups of unanesthetized animals were injected intraperitoneally with hypertonic saline solution, with or without free access to water intake, Na+W, and Na−W, respectively. The expression of AQP-1, AQP-2, Ang II, eNOS, and NF-kB were evaluated in the kidney by Western blot and immunohistochemistry. AQP-2 distribution was assessed by immunofluorescence. Na group showed increased natriuresis and diuresis, and Ang II and NF-kB expression, but decreased eNOS expression. Losartan or tempol enhanced further the diuresis, and AQP-2 and eNOS expression, as well as decreased Ang II and NF-kB expression. Confocal immunofluorescence imaging revealed labeling of AQP-2 in the apical plasma membrane with less labeling in the intracellular vesicles than the apical membrane in kidney medullary collecting duct principal cells both in C and Na groups. Importantly, our data also show that losartan and tempol induces a predominantly accumulation of AQP-2 in intracellular vesicles. In unanesthetized rats, Na+W group presented increased diuresis, natriuresis, and AQP-2 expression (112 ± 25 vs 64 ± 16; *p < 0.05). Water deprivation increased plasma sodium and diuresis but decreased AQP-2 (46 ± 22 vs 112 ± 25; §p < 0.05) and eNOS expression in the kidney. This study is a novel demonstration that renal endogenous Ang II–oxidative stress, induced in vivo in hypernatremic rats by an acute sodium overload, regulates AQP-2 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertoni Borghese MF, Bettini LM, Nitta CH, de Frutos S, Majowicz M, Gonzalez Bosc LV (2011) Aquaporin-2 promoter is synergistically regulated by nitric oxide and nuclear factor of activated T cells. Nephron Extra 1(1):124–138
Conner MT, Conner AC, Brown JE, Bill RM (2010) Membrane trafficking of aquaporin 1 is mediated by protein kinase C via microtubules and regulated by tonicity. Biochemistry 49(5):821–823
Hasler U (2011) An example of functional interaction between NFAT5/TonEBP and nuclear factor-κB by hypertonic stress: aquaporin-2 transcription. Cell Cycle 10(3):364–365
Hasler U, Leroy V, Jeon US, Bouley R, Dimitrov M, Kim JA et al (2008) NF-κB modulates aquaporin-2 transcription in renal collecting duct principal cells. J Biol Chem 283(42):28095–28105
Hasler U, Leroy V, Martin PY, Féraille E (2009) Aquaporin-2 abundance in the renal collecting duct: new insights from cultured cell models. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(1):F10–F18
Hasler U, Nielsen S, Féraille E, Martin PY (2006) Posttranscriptional control of aquaporin-2 abundance by vasopressin in renal collecting duct principal cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290(1):F177–F187
Hasler U, Vinciguerra M, Vandewalle A, Martin PY, Féraille E (2005) Dual effects of hypertonicity on aquaporin-2 expression in cultured renal collecting duct principal cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(6):1571–1582
King LS, Nielsen S, Agre P (1996) Aquaporin-1 water channel protein in lung: ontogeny, steroid-induced expression, and distribution in rat. J Clin Invest 97:2183–2191
Lahajnar G, Pecar S (2007) Sepe A Na-nitroprusside and HgCl2 modify the water permeability and volume of human erythrocytes. Bioelectrochemistry 70(2):462–468
Lanaspa MA, Andres-Hernando A, Li N, Rivard CJ, Cicerchi C, Roncal-Jimenez C et al (2010) The expression of aquaporin-1 in the medulla of the kidney is dependent on the transcription factor associated with hypertonicity, TonEBP. J Biol Chem 285(41):31694–31703
Li C, Wang W, Summer SN, Cadnapaphornchai MA, Falk S, Umenishi F, Schrier RW (2006) Hyperosmolality in vivo upregulates aquaporin 2 water channel and Na-K-2Cl co-transporter in Brattleboro rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(6):1657–1664
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Massey KJ, Hong NJ, Garvin JL (2012) Angiotensin II stimulates superoxide production in the thick ascending limb by activating NOX4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 303(7):C781–C789
Nielsen S, Kwon TH, Frokier J, Agre P (2007) Regulation and dysregulation of aquaporins in water balance disorders. J Intern Med 261:53–64
Pallone TL, Edwards A, Ma T, Silldorff EP, Verkman AS (2000) Requirement of aquaporin-1 for NaCl-driven water transport across descending vasa recta. J Clin Invest 105:215–222
Pendergrass KD, Gwathmey TM, Michalek RD, Grayson JM, Chappell MC (2009) The angiotensin II-AT1 receptor stimulates reactive oxygen species within the cell nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(2):149–154
Rosón MI, Cavallero S, Della Penna S, Cao G, Gorzalczany S, Pandolfo M et al (2006) Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats. Kidney Int 70(8):1439–1446
Rosón MI, Della Penna SL, Cao G, Gorzalczany S, Pandolfo M, Toblli JE et al (2010) Different protective actions of losartan and tempol on the renal inflammatory response to acute sodium overload. J Cell Physiol 224(1):41–48
Sabolic I, Valenti G, Verbavatz JM, Van Hoek AN, Verkman AS, Ausiello DA et al (1992) Localization of the CHIP28 water channel in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 263:C1225–C1233
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM, Moreno JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A (2010) NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(8):1254–1262
Schnermann J, Chou CL, Ma T, Traynor T, Knepper MA, Verkman AS (1998) Defective proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in transgenic aquaporin-1 null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9660–9664
Sinke AP, Deen PM (2011) The physiological implication of novel proteins in systemic osmoregulation. FASEB J 25(10):3279–3289
Takata K, Matsuzaki T, Tajika Y, Ablimit A, Hasegawa T (2008) Localization and trafficking of aquaporin 2 in the kidney. Histochem Cell Biol 130(2):197–209
Umenishi F, Narikiyo T, Schrier RW (2005) Effect on stability, degradation, expression, and targeting of aquaporin-2 water channel by hyperosmolality in renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338(3):1593–1599
Vellaichamy E, Sommana NK, Pandey KN (2005) Reduced cGMP signaling activates NF-kappaB in hypertrophied hearts of mice lacking natriuretic peptide receptor-A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327(1):106–111
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET, PIP 1337) and Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina (UBACYT B113, 20020100100688, and 20020110200048)
Conflict of interests
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Della Penna, S.L., Cao, G., Kouyoumdzian, N.M. et al. Role of angiotensin II and oxidative stress on renal aquaporins expression in hypernatremic rats. J Physiol Biochem 70, 465–478 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0324-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0324-5