Abstract
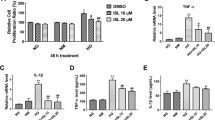
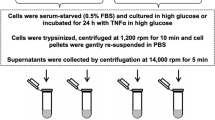
We determined in cultured kidney epithelial cells (LLC-PK1) the effects of high glucose, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) on mRNA and protein expression of the renal glucose transporters SGLT1 and SGLT2. Cultured monolayers were incubated with similar concentrations of IL-6 and TNF-α to those produced by LLC-PK1 in the presence of 20 mM glucose. Confluent monolayers with either 5 (controls, C) or 20 mM glucose (high glucose, HG) were incubated in the presence of 5 mM glucose, 20 mM glucose, 10 pg/ml IL-6, or TNF-α alone or in combination. Separate groups with IL-6 and TNF-α were incubated with antibodies to their respective receptors. HG induced an increased SGLT1 mRNA at 48 h (p < 0.05 vs. C) and protein expression in 120 h (p < 0.05 vs. C). HG also induced an increased SGLT2 mRNA at 72 and 96 h (P < 0.05 vs. C) and SGLT2 protein expression at 120 h (p < 0.05 vs. C). In C, 10 pg/ml IL-6 or TNF-α did not modify SGLT1 mRNA (n.s vs. in the absence of cytokines). In contrast, cytokines induced an increased expression of SGLT1 protein at 120 h (p < 0.05 vs. in the absence of cytokines), and SGLT2 mRNA and protein were increased at 96 and 120 h, respectively (p < 0.05 vs. in absence of cytokines). No changes were observed when cells were incubated with cytokines and HG (n.s vs. C). In conclusion, this study showed that SGLT2 increased in the presence of IL-6 and TNF-α, indicating an autocrine modulation of the expression of this transporter by cytokines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed KA, Muniandy S, Ismail IS (2010) Type 2 diabetes and vascular complications: a pathophysiologic view. Biomed Res 21(2):147–155
Angelo LS, Talpaz M, Kurzrock R (2002) Autocrine interleukin-6 production in renal cell carcinoma: evidence for the involvement of p53. Cancer Res 62:932–940
Baer PC, Wegner B, Geiger H (2004) Effects of mycophenolic acid on IL-6 expression of human renal proximal and distal tubular cells in vitro. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:47–52
David S, Biancone L, Caserta C et al (1997) Alternative pathway complement activation induces proinflammatory activity in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:51–56
Dominguez JH, Camp K, Maianu L et al (1994) Molecular adaptations of GLUT1 and GLUT2 in renal proximal tubules of diabetic rats. Am J Physiol 266:F283–F290
Dronavalli S, Duka I, Bakris GL (2008) The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4(8):444–452
Greenberg AS, Obin MS (2006) Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 83:461S–465S
Gu JW, Tian N, Shparago M et al (2006) Renal NF-kappaB activation and TNF-alpha upregulation correlate with salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291(6):R1817–R1824
Han S, Hagan DL, Joseph R et al (2008) Dapagliflozin, a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, improves glucose homeostasis in normal and diabetic rats. Diabetes 57:1723–1729
Haspel HC, Mynarcik DC, Ortiz PA et al (1991) Glucose deprivation induces the selective accumulation of hexose transporter protein GLUT-1 in the plasma membrane of normal rat kidney cells. Mol Endocrinol 5:61–72
Hediger MA, Rhoads DB (1994) Molecular physiology of sodium-glucose cotransporters. Physiol Rev 74:993–1026
Hummel Ch S, Lu Ch, Loo DDF et al (2011) Glucose transport by human renal Na+/D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300:C14–C21
Ishibashi F (2004) High glucose reduces albumin uptake in cultured proximal tubular cells (LLC-PK1). Diabetes Res Clin Pract 65:217–225
Jung-MY IJ, Sridevi D (2011) Epigenetic regulation of high glucose-induced proinflammatory cytokine production in monocytes by curcumin. J Nutr Biochem 22:450–458
Kamran M, Peterson RG, Dominguez JH (1997) Overexpression of GLUT2 gene in renal proximal tubules of diabetic Zucker rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:943–948
Lee YJ, Park SH, Han HJ (2005) ATP stimulates Na+-glucose cotransporter activity via cAMP and p38 MAPK in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289(5):C1268–C1276
Lescale-Matys L, Dyer J, Scott D et al (1993) Regulation of the ovine intestinal Na+/glucose co-transporter (SGLT1) is dissociated from mRNA abundance. Biochem J 291:435–440
MacKenzie B, Loo DDF, Panayotova-Heiermann M et al (1996) Biophysical characteristics of the pig kidney Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT2 reveal a common mechanism for SGLT1 and SGLT2. J Biol Chem 271:32678–32683
Marks J, Carvou NJC, Debnam ES et al (2003) Diabetes increases facilitative glucose uptake and GLUT2 expression in the rat proximal tubule brush border membrane. J Physiol 553:137–145
Mathieu P, Poirier P, Pibarot P et al (2009) Visceral obesity, the link among inflammation, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 53:577–584
Matthew SH, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-Κβ. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Meldrum KK, Meldrum DR, Hile KL et al (2001) p38 MAPK mediates renal tubular cell TNF-α production and TNF-α-dependent apoptosis during simulated ischemia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C563–C570
Moran A, Davis LJ, Turner RJ (1988) High affinity phlorizin binding to the LLC-PK1 cells exhibits a sodium:phlorizin stoichiometry of 2: 1. J Biol Chem 263:187–192
Mullin JM, Kofeldt LM, Russo LM (1992) Basolateral 3-0-methylglucose transport by cultured kidney (LLC-PK1) epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 262:F480–F487
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Fernandez-Navarro CM (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:433–442
Ohta T, Isselbacher KJ, Rhoads DB (1990) Regulation of glucose transporters in LLC-PK1 cells: effects of D-glucose and monosaccharides. Mol Cell Biol 10:6491–6499
Pajor AM, Hirayama BA, Wright EM (1992) Molecular evidence for two renal Na+/glucose cotransporters. Biochim Biophys Acta 1106(1):216–220
Peng H, Lever JE (1995) Regulation of Na+-coupled glucose transport in LLC-PK1 cells. J Biol Chem 270:23996–24003
Phillips AO (2003) The role of renal proximal tubular cells in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep 3:491–496
Phillips AO, Steadman R, Topley N et al (1995) Elevated D-glucose concentrations modulate TGF- β1 synthesis by human cultured renal proximal tubular cells the permissive role of platelet-derived growth factor. Am J Pathol 147:362–374
Phillips AO, Topley N, Steadman R et al (1996) Induction of TGFβ1 synthesis in D-glucose primed human proximal tubular cells by IL-1β and TNFα. Kidney Int 50:1546–1554
Rahmoune H, Thompson PW, Ward JM (2005) Glucose transporters in human renal proximal tubular cells isolated from the urine of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 54(12):3427–3434
Santer R, Calado J (2010) Familial renal glucosuria and SGLT2: from a mendelian trait to a therapeutic target. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:133–141
Santer R, Kinner M, Lassen Ch L et al (2003) Molecular analysis of the SGLT2 gene in patients with renal glucosuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2873–2882
Schmidt Ch, Höcherl K, Bucher M (2007) Regulation of renal glucose transporters during severe inflammation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F804–F811
Soodsma JF, Legler B, Nordlie RC (1967) The inhibition by phlorizin of kidney microsomal inorganic pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase and glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem 242(8):1955–1960
Turner RJ, Moran A (1982) Heterogeneity of sodium-dependent D-glucose transport sites along the proximal tubule: evidence from vesicle studies. Am J Physiol 242:F406–F414
Turner RJ, Moran A (1982) Further studies of proximal tubular brush border membrane D-glucose transport heterogeneity. J Membr Biol 70(1):37–45
Vayro S, Wood IS, Dyer J et al (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the ovine intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT1 gene. Eur J Biochem 268:5460–5470
Wang SN, Hirschberg R (1999) Tubular epithelial cell activation and interstitial fibrosis. The role of glomerular ultrafiltration of growth factors in the nephrotic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:2072–2074
White JR, PharmD PA (2010) Apple trees to sodium glucose co-transporter inhibitors: a review of SGLT2 inhibition. Clinical Diabetes 28:5–10
Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2003) Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT): expanded families of sugar transport protein. Br J Nutr 89:3–9
Wright EM (2001) Renal Na+/glucose cotransporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F10–F18
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q et al (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112:1821–1830
Yaqoob M, McClelland P, Patrick AW et al (1994) Evidence of oxidant injury and tubular damage in early diabetic nephropathy. QJM 87:601–607
Yung S, Lee CY, Zhang Q et al (2006) Elevated glucose induction of thrombospondin-1 up-regulates fibronectin synthesis in proximal renal tubular epithelial cells through TGF- β1 dependent and TGF- β1 independent pathways. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1504–1513
Zhao FQ, Keating AF (2007) Functional properties and genomics of glucose transporters. Curr Genomics 8:113–128
Zierler K (1999) Whole body glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol 276:E409–E426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maldonado-Cervantes, M.I., Galicia, O.G., Moreno-Jaime, B. et al. Autocrine modulation of glucose transporter SGLT2 by IL-6 and TNF-α in LLC-PK1 cells. J Physiol Biochem 68, 411–420 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0153-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0153-3