Abstract
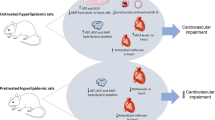
The present study was undertaken to assess the chronology of major pathological events associated with high cholesterol (HC) diet and their modulation by anti-platelet drugs. Male Golden Syrian hamsters were fed HC diet up to 90 days. Plasma lipid, glucose and coagulation parameters (commercial kits), platelet activation (whole blood aggregation and static adhesion), endothelial dysfunction (aortic ring vasoreactivity), splenocyte TNF-α, IFN-γ and iNOS mRNA transcripts (RT–PCR), and ferric chloride (time to occlusion) induced thrombosis were monitored at 15, 30, 60, and 90 days after HC feeding and compared with normolipidemic hamsters. A significant increase in plasma lipid levels was observed at 15 days of HC feeding, but other parameters remain unaltered. Enhanced ADP, collagen, and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, splenocyte TNF-α expression along with endothelial dysfunction were observed from 30 to 90 days of HC feeding. Platelet adhesion on collagen-/fibrinogen-coated surface and IFN-γ expression were augmented only after 60 days, while enhanced iNOS expression, reduction in thrombin time, and potentiation of ferric chloride-induced thrombosis was observed only at 90 days of HC feeding. Thus, pathological changes induced by HC diet depend on the duration and extent of hyperlipidemia. Moreover, hamsters treated with anti-platelet drugs aspirin (5 mg/kg) or clopidogrel (10 mg/kg) along with HC feeding exhibited reduction in platelet activation as well as subsequent changes observed in the abovementioned parameters following HC feeding. Since reduction in TNF-α was associated with reversion in endothelial dysfunction and prothrombotic state, the role of platelets is implicated in the pathological changes associated with HC feeding.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexaki A, Wilson TA, Atallah MT, Handelman G, Nicolosi RJ (2004) Hamsters fed diets high in saturated fat have increased cholesterol accumulation and cytokine production in the aortic arch compared with cholesterol-fed hamsters with moderately elevated plasma non-HDL cholesterol concentrations. J Nutr 134:410–415
Angel K, Provan SA, Gulseth HL, Mowinckel P, Kvien TK, Atar D (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists improve aortic stiffness in patients with inflammatory arthropathies: a controlled study. Hypertension 55:333–338
Aoki R, Ikarugi H, Naemura A, Ijiri Y, Yamashita T, Yamamoto J (2006) Endothelial dysfunction precedes atherosclerotic lesions and platelet activation in high fat diet-induced prothrombotic state. Thromb Res 117:529–535
Arakawa M, Mita T, Azuma K, Ebato C, Goto H, Nomiyama T, Fujitani Y, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Watada H (2010) Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4. Diabetes 59:1030–1037
Bartus M, Lomnicka M, Lorkowska B, Franczyk M, Kostogrys RB, Pisulewski PM, Chlopicki S (2005) Hypertriglyceridemia but not hypercholesterolemia induces endothelial dysfunction in the rat. Pharmacol Rep 57 Suppl:127–137
Basu R, Bhaumik S, Basu JM, Naskar K, De T, Roy S (2005) Kinetoplastid membrane protein-11 DNA vaccination induces complete protection against both pentavalent antimonial-sensitive and -resistant strains of Leishmania donovani that correlates with inducible nitric oxide synthase activity and IL-4 generation: evidence for mixed Th1- and Th2-like responses in visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol 174:7160–7171
Bekker LG, Freeman S, Murray PJ, Ryffel B, Kaplan G (2001) TNF-alpha controls intracellular mycobacterial growth by both inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent and inducible nitric oxide synthase-independent pathways. J Immunol 166:6728–6734
Cappelli-Bigazzi M, Rubattu S, Battaglia C, Russo R, Enea I, Ambrosio G, Chiariello M, Volpe M (1997) Effects of high-cholesterol and atherogenic diets on vascular relaxation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 273:H647–H654
Davignon J, Ganz P (2004) Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 109:III27–III32
Felmeden D, Nadar SK, Lip GY (2005) Aspirin and endothelial function in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 19:663–665
Ferroni P, Basili S, Davi G (2003) Platelet activation, inflammatory mediators and hypercholesterolemia. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 1:157–169
Glass CK, Witztum JL (2001) Atherosclerosis. The road ahead. Cell 104:503–516
Gurbel PA, Bliden KP, Tantry US (2006) Effect of clopidogrel with and without eptifibatide on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and C-reactive protein release after elective stenting: results from the CLEAR PLATELETS 1b study. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:2186–2191
Heitzer T, Rudolph V, Schwedhelm E, Karstens M, Sydow K, Ortak M, Tschentscher P, Meinertz T, Boger R, Baldus S (2006) Clopidogrel improves systemic endothelial nitric oxide bioavailability in patients with coronary artery disease: evidence for antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1648–1652
Hundal RS, Petersen KF, Mayerson AB, Randhawa PS, Inzucchi S, Shoelson SE, Shulman GI (2002) Mechanism by which high-dose aspirin improves glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 109:1321–1326
Ikenoya M, Yoshinaka Y, Kobayashi H, Kawamine K, Shibuya K, Sato F, Sawanobori K, Watanabe T, Miyazaki A (2007) A selective ACAT-1 inhibitor, K-604, suppresses fatty streak lesions in fat-fed hamsters without affecting plasma cholesterol levels. Atherosclerosis 191:290–297
Ivandic BT, Schlick P, Staritz P, Kurz K, Katus HA, Giannitsis E (2006) Determination of clopidogrel resistance by whole blood platelet aggregometry and inhibitors of the P2Y12 receptor. Clin Chem 52:383–388
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Mitsiades N, Kirchhof B, Koizumi K, Dohmen S, Adamis AP (2002) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prevent early diabetic retinopathy via TNF-alpha suppression. FASEB J 16:438–440
Kouraklis G, Patapis P, Misiakos E, Glinavou A, Sioka C, Karayiannakos PE (2004) Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on experimental atherogenesis induced in rabbits. Int Angiol 23:139–143
Lazar HL, Joseph L, San Mateo C, Frame J, Cabral HJ, McDonnell M, Chipkin S (2010) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in conduits used in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing coronary revascularization. J Card Surg 25:120–126
Mangiapane EH, McAteer MA, Benson GM, White DA, Salter AM (1999) Modulation of the regression of atherosclerosis in the hamster by dietary lipids: comparison of coconut oil and olive oil. Br J Nutr 82:401–409
Mito N, Yoshino H, Hosoda T, Sato K (2004) Analysis of the effect of leptin on immune function in vivo using diet-induced obese mice. J Endocrinol 180:167–173
Monroe DM, Hoffman M, Roberts HR (2002) Platelets and thrombin generation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1381–1389
Nakamura T, Jamieson GA, Okuma M, Kambayashi J, Tandon NN (1998) Platelet adhesion to native type I collagen fibrils. Role of GPVI in divalent cation-dependent and -independent adhesion and thromboxane A2 generation. J Biol Chem 273:4338–4344
Onley DJ, Knight CG, Tuckwell DS, Barnes MJ, Farndale RW (2000) Micromolar Ca2+ concentrations are essential for Mg2+-dependent binding of collagen by the integrin alpha 2beta 1 in human platelets. J Biol Chem 275:24560–24564
Picchi A, Gao X, Belmadani S, Potter BJ, Focardi M, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in the prediabetic metabolic syndrome. Circ Res 99:69–77
Prociuk MA, Edel AL, Richard MN, Gavel NT, Ander BP, Dupasquier CM, Pierce GN (2008) Cholesterol-induced stimulation of platelet aggregation is prevented by a hempseed-enriched diet. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 86:153–159
Raymond C, Menon V (2009) Dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease: a case-based approach. Cleve Clin J Med 76:663–670
Remijn JA, Wu YP, Jeninga EH, IJ MJ, van Willigen G, de Groot PG, Sixma JJ, Nurden AT, Nurden P (2002) Role of ADP receptor P2Y(12) in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation in flowing blood. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:686–691
Santhanam AV, Viswanathan S, Dikshit M (2007) Activation of protein kinase B/Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates agmatine-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation. Eur J Pharmacol 572:189–196
Schafer A, Bauersachs J (2008) Endothelial dysfunction, impaired endogenous platelet inhibition and platelet activation in diabetes and atherosclerosis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 6:52–60
Shenkman B, Matetzky S, Fefer P, Hod H, Einav Y, Lubetsky A, Varon D, Savion N (2008) Variable responsiveness to clopidogrel and aspirin among patients with acute coronary syndrome as assessed by platelet function tests. Thromb Res 122:336–345
Siegel-Axel D, Daub K, Seizer P, Lindemann S, Gawaz M (2008) Platelet lipoprotein interplay: trigger of foam cell formation and driver of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 78:8–17
Singh V, Tiwari RL, Dikshit M, Barthwal MK (2009) Models to study atherosclerosis: a mechanistic insight. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 7:75–109
Surin WR, Prakash P, Barthwal MK, Dikshit M (2010) Optimization of ferric chloride induced thrombosis model in rats: effect of anti-platelet and anti-coagulant drugs. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 61:287–291
Tancevski I, Wehinger A, Schgoer W, Eller P, Cuzzocrea S, Foeger B, Patsch JR, Ritsch A (2006) Aspirin regulates expression and function of scavenger receptor-BI in macrophages: studies in primary human macrophages and in mice. FASEB J 20:1328–1335
Tandon NN, Kralisz U, Jamieson GA (1989) Identification of glycoprotein IV (CD36) as a primary receptor for platelet–collagen adhesion. J Biol Chem 264:7576–7583
Tauseef M, Shahid M, Sharma KK, Fahim M (2008) Antioxidative action of aspirin on endothelial function in hypercholesterolaemic rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 103:314–321
Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2006) Cytokines in atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev 86:515–581
Tiwari RL, Singh V, Barthwal MK (2008) Macrophages: an elusive yet emerging therapeutic target of atherosclerosis. Med Res Rev 28:483–544
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, Smith HO, Yandell M, Evans CA, Holt RA et al (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science 291:1304–1351
Waksman R, Ajani AE, White RL, Pinnow E, Dieble R, Bui AB, Taaffe M, Gruberg L, Mintz GS, Satler LF et al (2001) Prolonged antiplatelet therapy to prevent late thrombosis after intracoronary gamma-radiation in patients with in-stent restenosis: Washington radiation for in-stent restenosis trial plus 6 months of clopidogrel (WRIST PLUS). Circulation 103:2332–2335
Waksman R, Pakala R, Roy P, Baffour R, Hellinga D, Seabron R, Chan R, Scheinowitz M, Kolodgie F, Virmani R (2008) Effect of clopidogrel on neointimal formation and inflammation in balloon-denuded and radiated hypercholesterolemic rabbit iliac arteries. J Interv Cardiol 21:122–128
Zhou X, Paulsson G, Stemme S, Hansson GK (1998) Hypercholesterolemia is associated with a T helper (Th) 1/Th2 switch of the autoimmune response in atherosclerotic apo E-knockout mice. J Clin Invest 101:1717–1725
Acknowledgments
Financial support to Manoj Kumar Barthwal and Madhu Dikshit from Central Drug Research Institute and NWP0034 is acknowledged. Financial support from the Department of Science and Technology, India to Manoj Kumar Barthwal is also acknowledged. Fellowship money from Indian Council of Medical Research, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India to the other team members is acknowledged. The authors are also thankful to Mr. MPS Negi from the Biometry and Statistics Division, Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow for helping in the statistical analysis of the data. Both Manoj Kumar Barthwal and Madhu Dikshit were equally responsible for the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Vishal Singh, Manish Jain and Prem Prakash have contributed equally to this work
CDRI communication number: 7810
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Jain, M., Prakash, P. et al. A time course study on prothrombotic parameters and their modulation by anti-platelet drugs in hyperlipidemic hamsters. J Physiol Biochem 67, 205–216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-010-0065-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-010-0065-z